
EASL Congress 2023
21-24 June Vienna

|
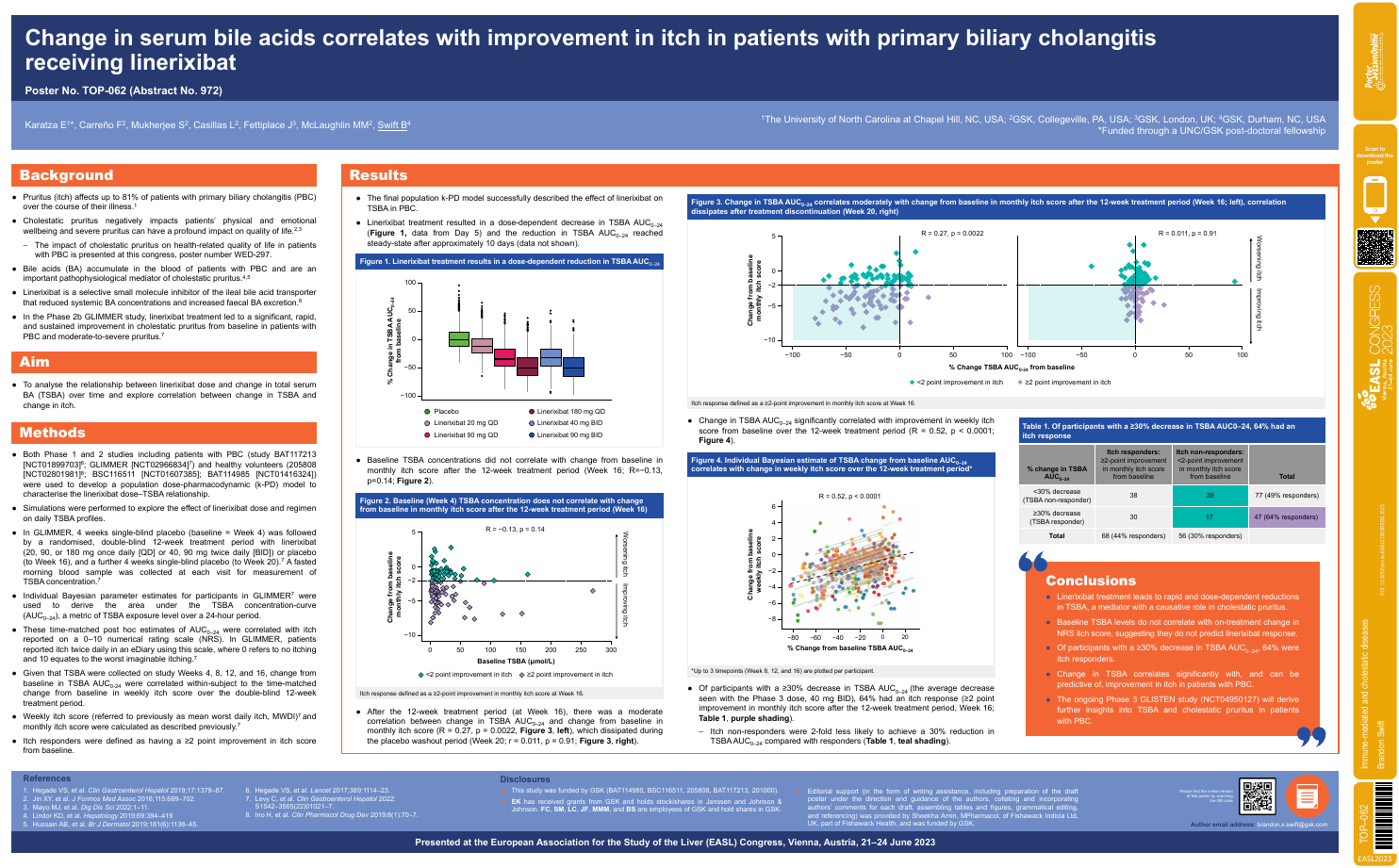





| Change in serum bile acids correlates wi.. | Brandon Swift .. | .. | Immune-mediated and cholestatic diseases.. | - - | |
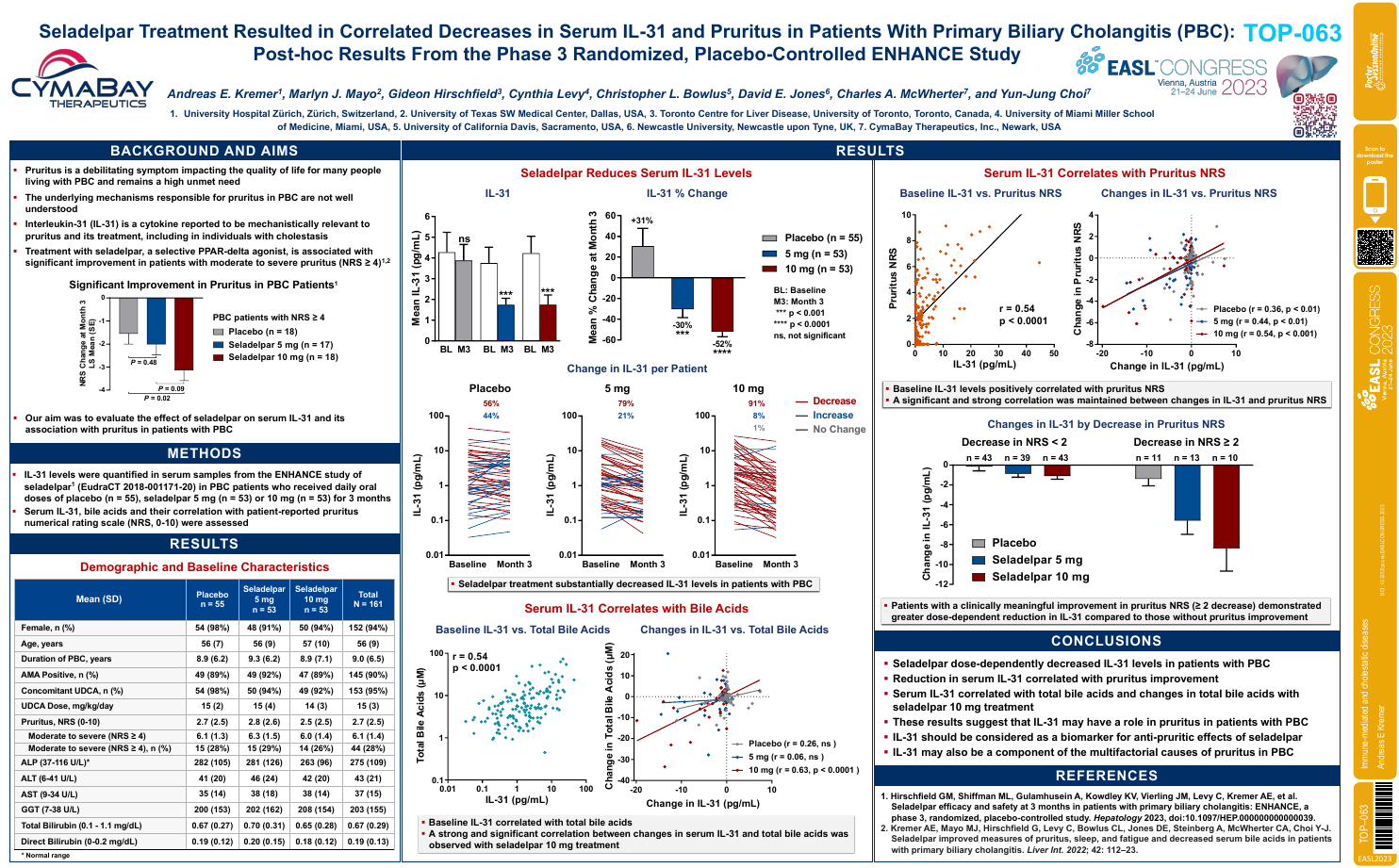
| Seladelpar treatment resulted in correla.. | Andreas E Kremer .. | .. | Immune-mediated and cholestatic diseases.. | - - | |
| Development of an in vitro bile-duct-on-.. | Anna Katharina Frank .. | Henry W. Hoyle, Kayoko Hirayam.. | Immune-mediated and cholestatic diseases.. | - - | |
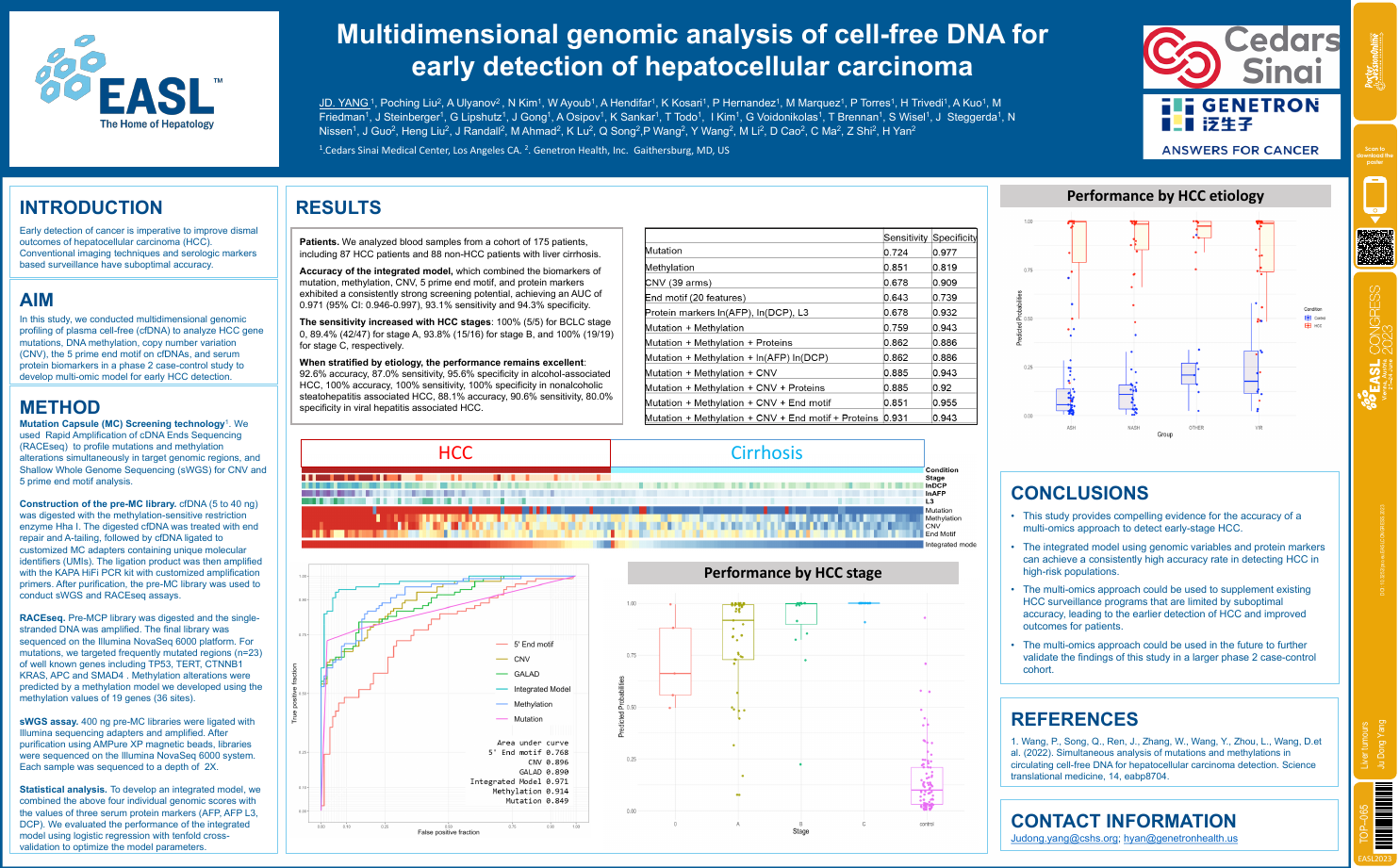
| Multidimensional genomic analysis of cel.. | Ju Dong Yang .. | .. | Liver tumours.. | - - | |
| PD1-negative CD45RA effector-memory CD8 .. | Sarah Cappuyns .. | .. | Liver tumours.. | - - | |
| A simple characterization of dynamic cha.. | Fabio Piscaglia .. | .. | Liver tumours.. | - - | |
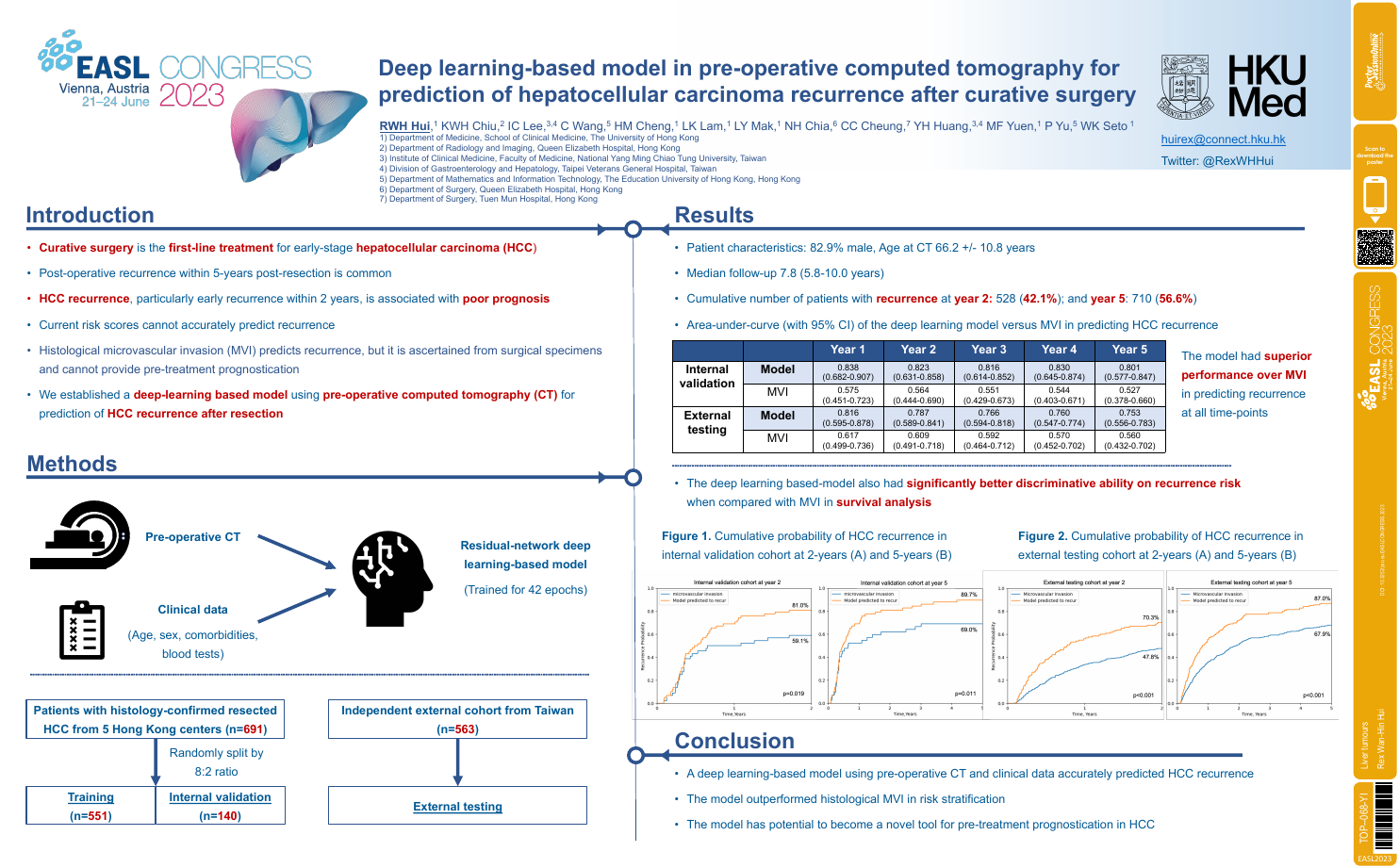
| Deep learning-based model in pre-operati.. | Rex Wan-Hin Hui .. | .. | Liver tumours.. | - - | |
| Interleukin 10-mediated signaling dampen.. | Tao Zhang .. | .. | Liver tumours.. | - - | |
| Constitutive signaling from an engineere.. | Wei Zhu .. | .. | Liver tumours.. | - - | |
| Antitumoral activity of the G9a inhibito.. | Maite G Fernandez-Barrena .. | .. | Liver tumours.. | - - | |
| AKR1B10 as a novel molecular driver of a.. | Maria Hernandez-Tejero .. | .. | Metabolism, alcohol and toxicity.. | - - | |
| Significant dose-dependent reduction in .. | Rohit Loomba .. | .. | Metabolism, alcohol and toxicity.. | - - | |
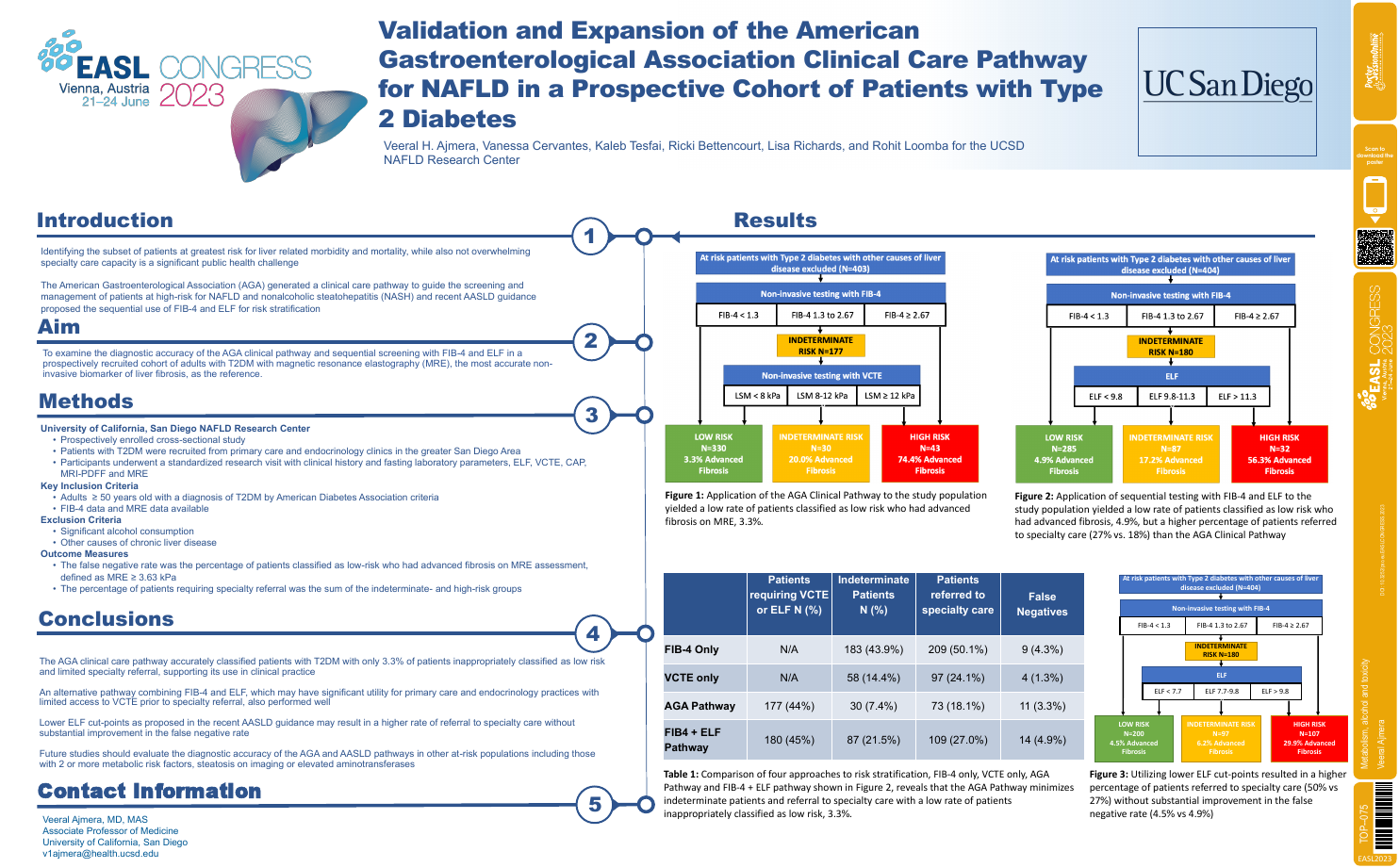
| Validation and expansion of the American.. | Veeral Ajmera .. | .. | Metabolism, alcohol and toxicity.. | - - | |
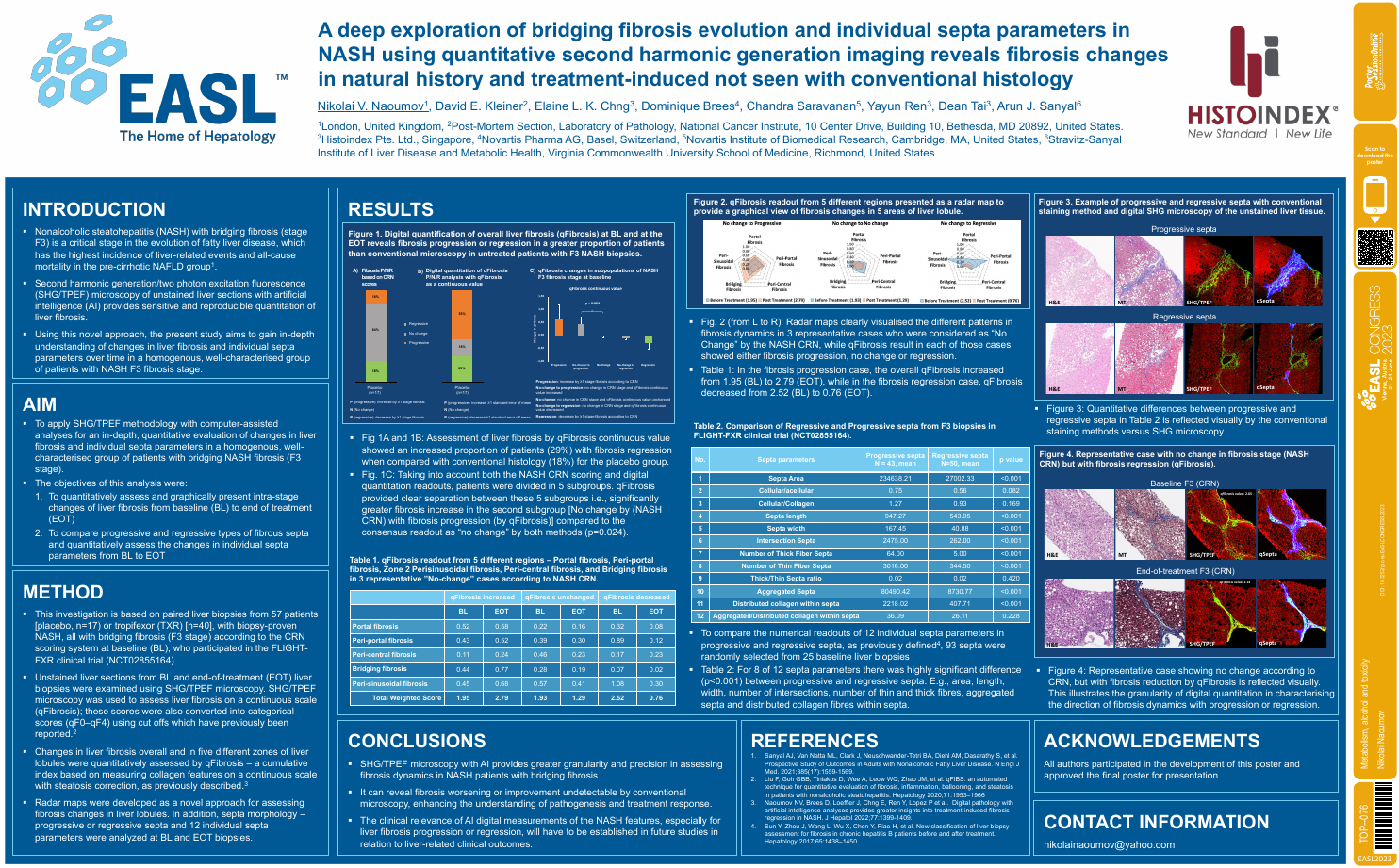
| A deep exploration of bridging fibrosis .. | Nikolai Naoumov .. | David E. Kleiner, Elaine L. K... | Metabolism, alcohol and toxicity.. | - - | |
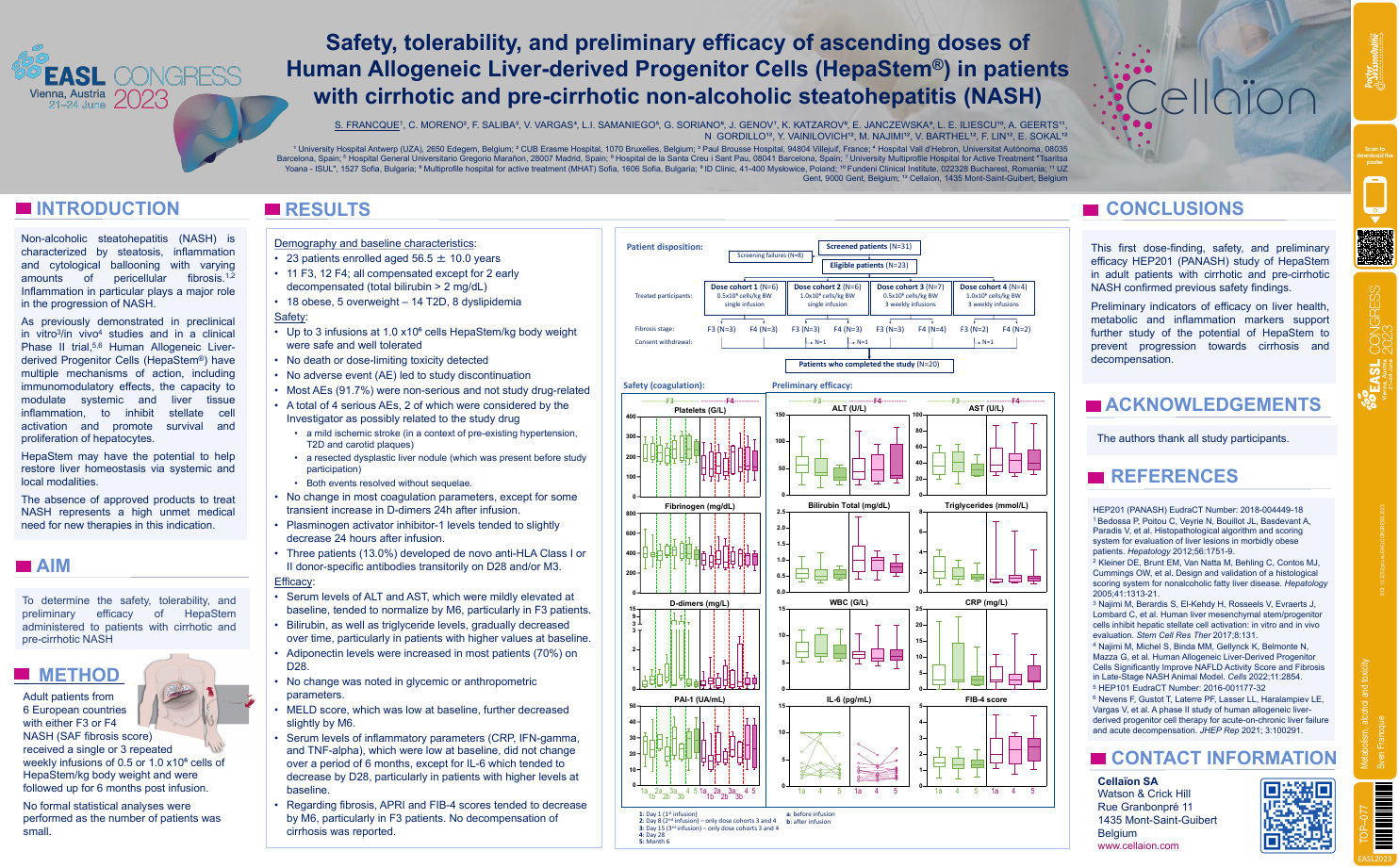
| Safety, tolerability, and preliminary ef.. | Sven Francque .. | .. | Metabolism, alcohol and toxicity.. | - - | |
| Risk of bacterial infections in non-alco.. | Axel Wester .. | .. | Metabolism, alcohol and toxicity.. | - - | |
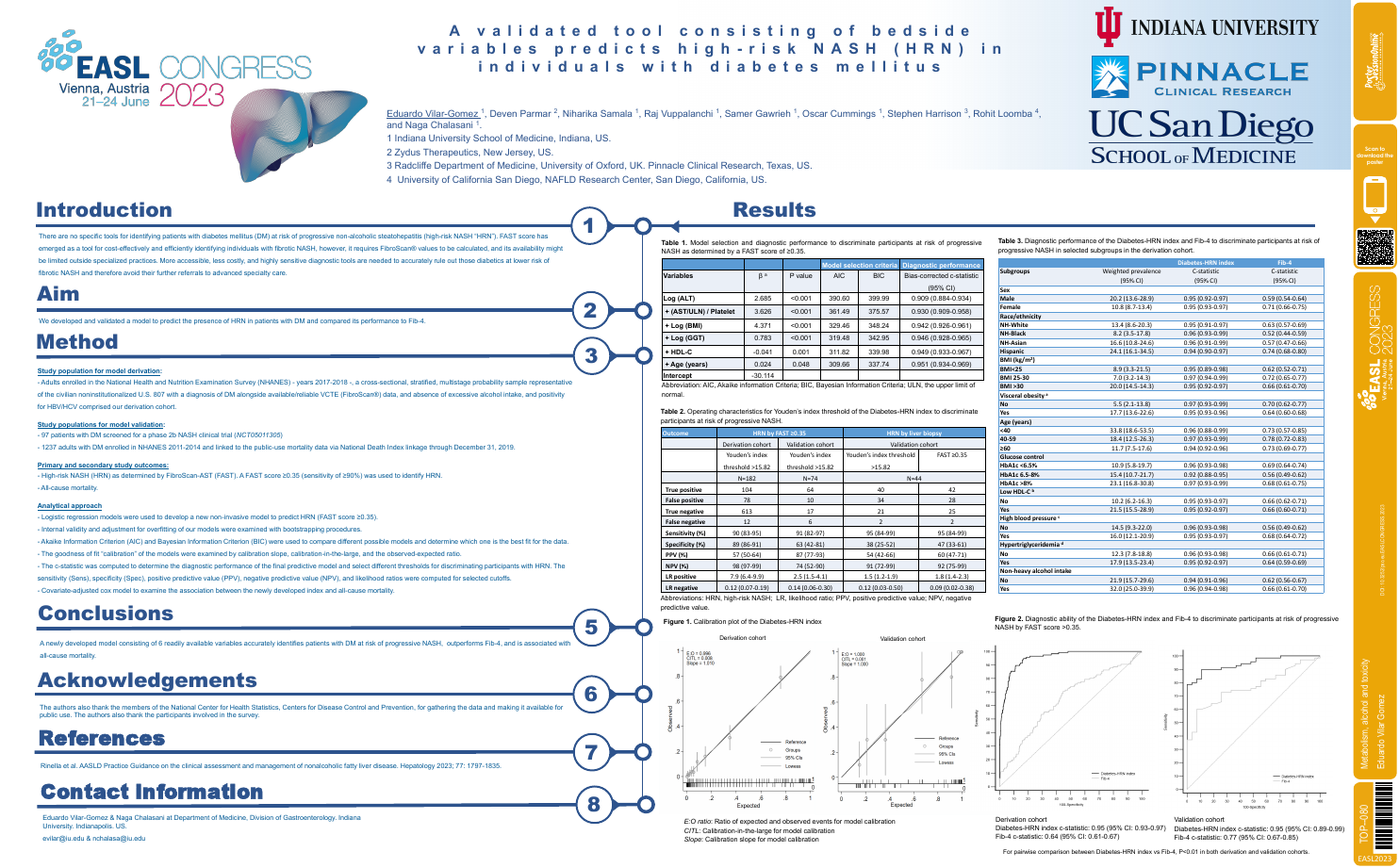
| A validated tool consisting of bedside v.. | Eduardo Vilar Gomez .. | .. | Metabolism, alcohol and toxicity.. | - - | |
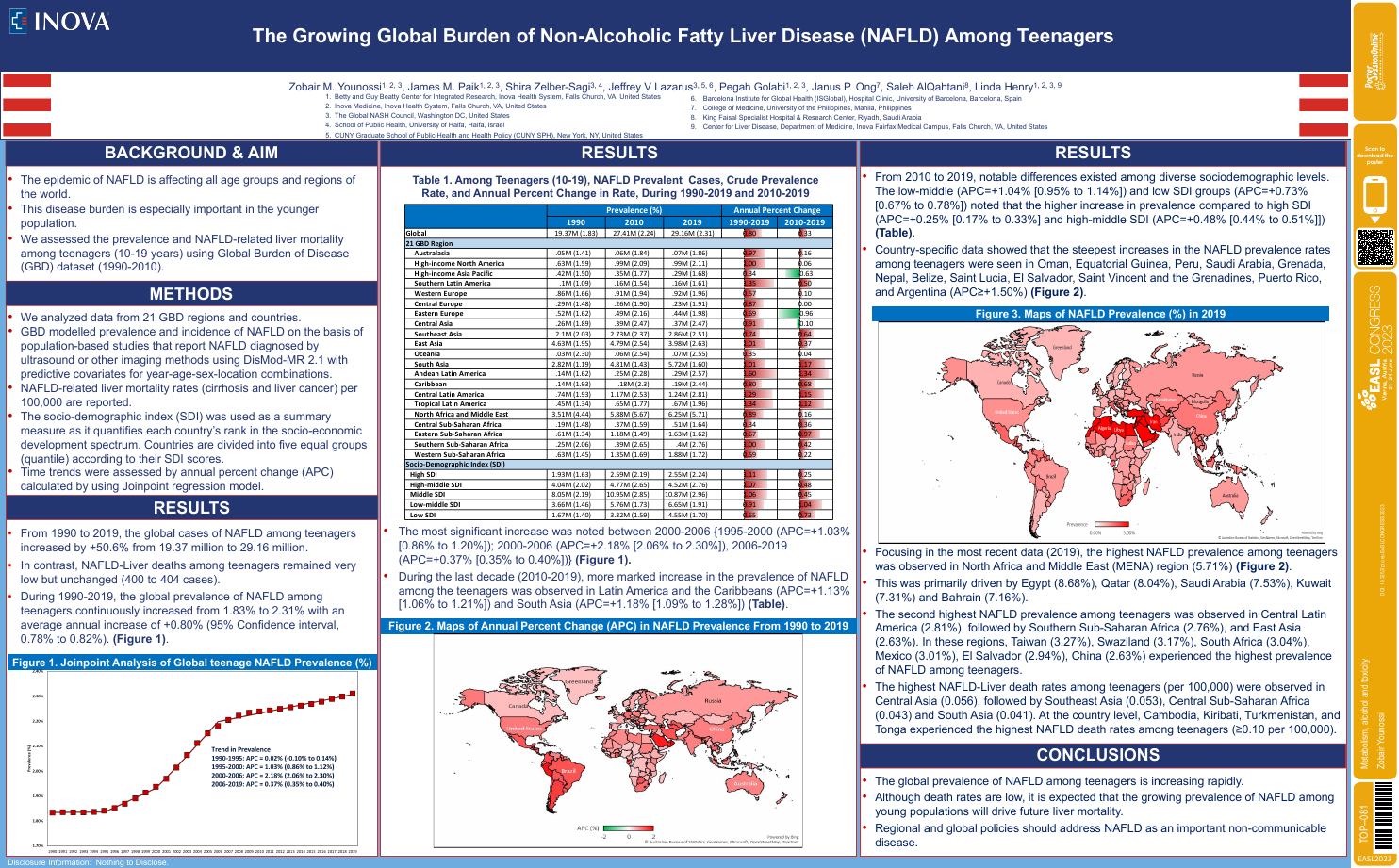
| The growing global burden of non-alcohol.. | Zobair Younossi .. | .. | Metabolism, alcohol and toxicity.. | - - | |
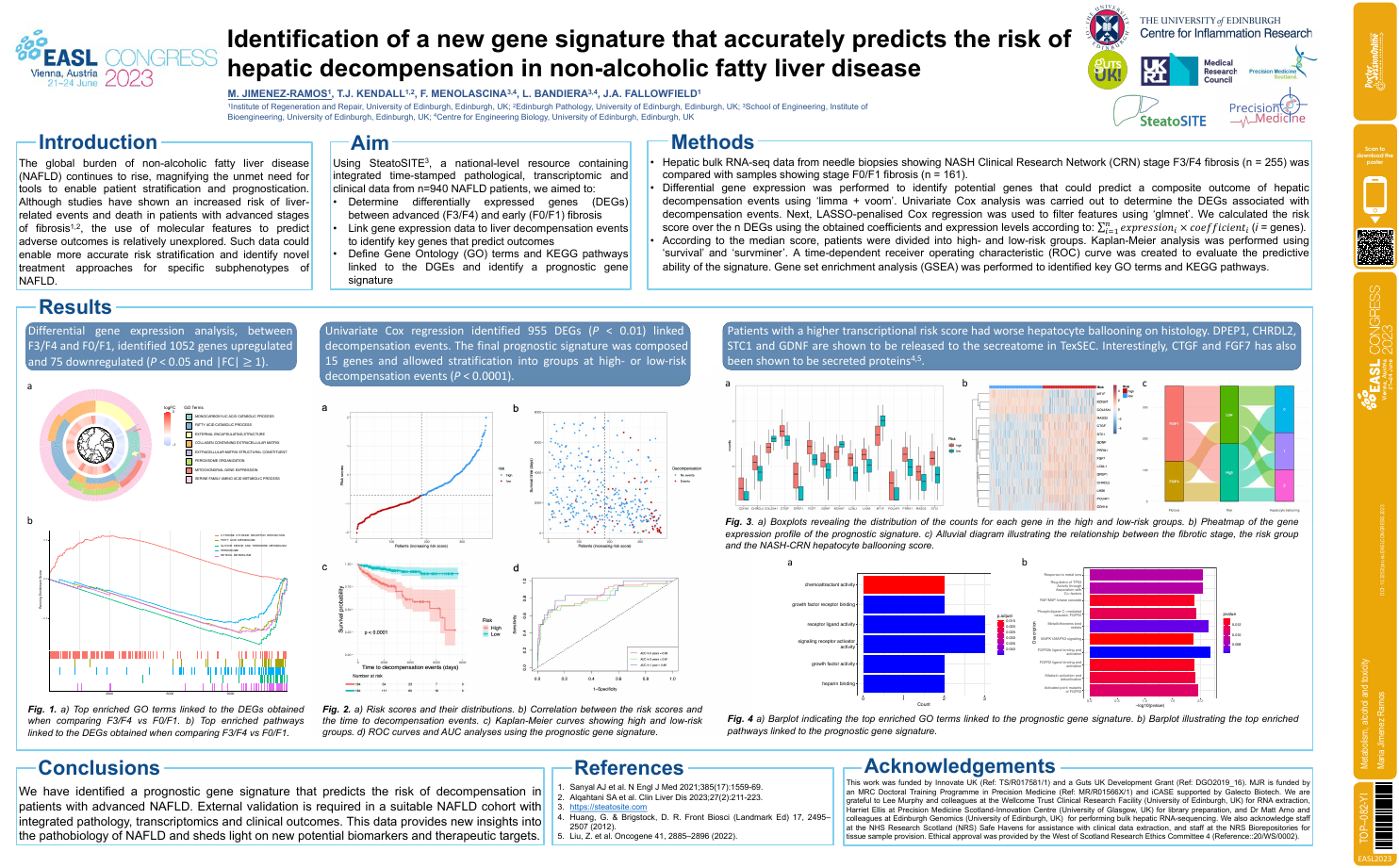
| Identification of a new gene signature t.. | Maria Jimenez Ramos .. | T. J. Kendall, F. Menolascina,.. | Metabolism, alcohol and toxicity.. | - - | |
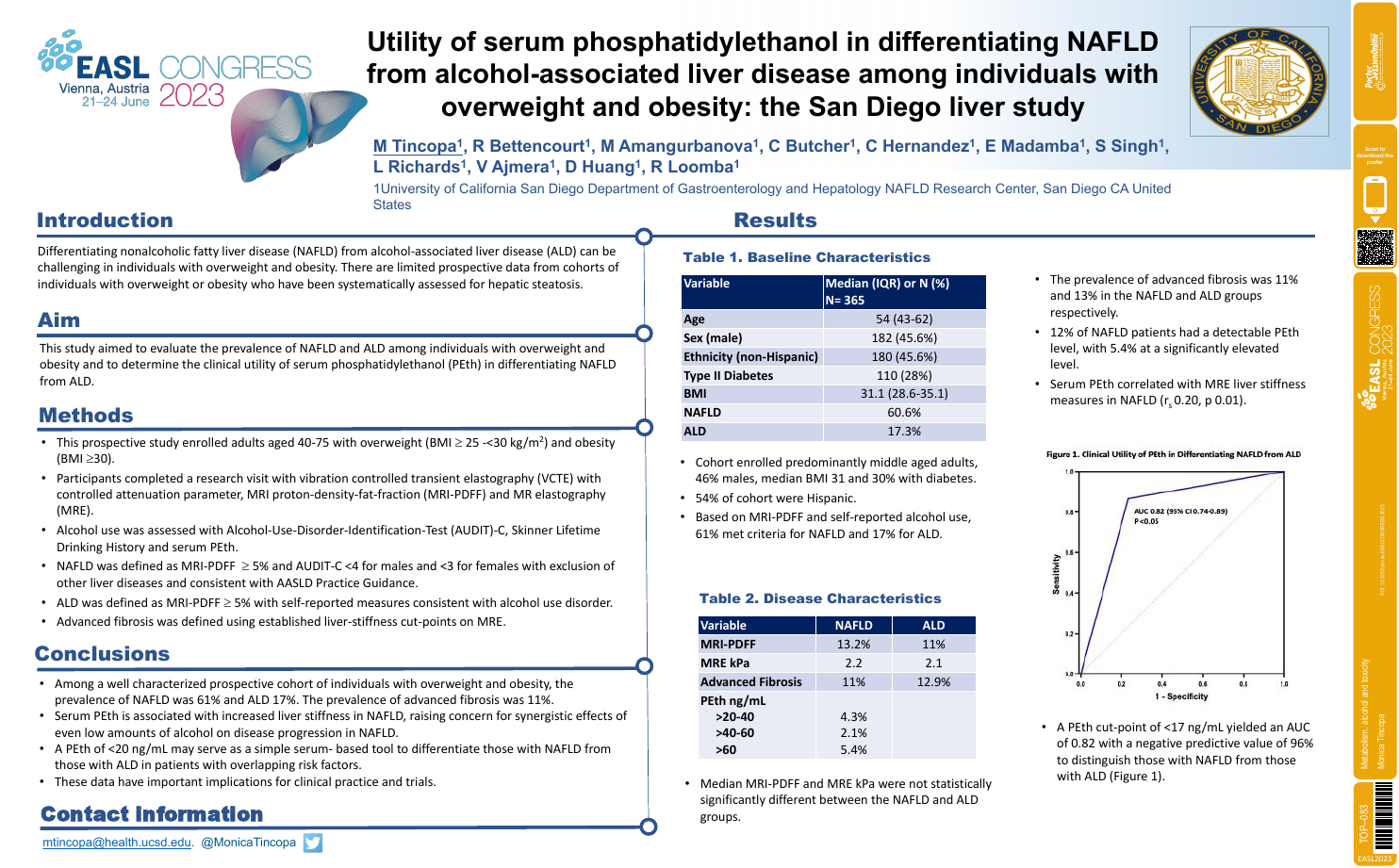
| Utility of serum phosphatidylethanol in .. | Monica Tincopa .. | .. | Metabolism, alcohol and toxicity.. | - - | |
Abstract
Thunderstorm-related asthma in patients sensitised to olea europaea pollen: twenty emergency department visits for asthmatic symptoms in one single day Losappio, Laura1; Heffler, Enrico2; Falco, Antonio1; Contento, Francesco1; Cannito, Cosimo1; Rolla, Giovanni2 1"Dimiccoli" Hospital, Emergency Department, Barletta, Italy; 2University of Torino - AO Mauriziano "Umberto I", Allergy and Clinical Immunology, Torino, Italy
Background: Associations between thunderstorm and asthma morbidity have been reported in several countries. Common to all epidemics of thunderstorm-related asthma is a significant increase in atmospheric allergen load during and immediately after a thunderstorm. Sensitization to Alternaria species or to grass and parietaria pollens has been suggested to play a key role in thunderstorm-related asthma. The only reported event of thunderstorm-related asthma in Mediterranean area was attributed to sensitization to parietaria pollen.
Method: here we describe a series of 20 patients who presented to Emergency Department in Barletta (94,000 inhabitants), Puglia (Italy) for sudden and severe asthmatic symptoms between May 27th and 28th 2010 (from15:36 to 5:02), immediately after a violent thunderstorm which occurred following a very hot morning (mean temperature: 29°C). All the patients have been subsequently visited by an allergist and underwent allergological work-up which included skin prick tests and a careful clinical history. Local pollen counts were available.
Result: Between May 10th and June 10th 2010, 86 Emergency Department asthma visits were recorded, 20 of them during the study day. Patients' mean age was 44.25 +/- 18.5 years (range: 9-81), 8/20 females, 2 smokers, 16 with a previous history of known respiratory allergy. Only two patients regularly took anti-asthma drugs. All 20 patients were sensitized to Olea europaea pollen, 7 of whom were monosensitized. Ten patients were sensitized to grass, 7 to parietaria, 5 to compositae, 5 to cypress, 5 to house dust mites, 3 to dog and 1 to cat danders. No patient was sensitized to Alternaria. Mean pollen count was 17 granules/m3 for Olea europaea, 6 granules/m3 for grass pollen.
Conclusion: This is, in our knowledge, the second epidemic of thunderstorm related asthma described in Mediterranean area and the first one in which sensitization to Olea europaea played a key-role. In conclusion, our report indicates that thunderstorm asthma may involve different allergens (not only fungal spores and grass or parietaria pollen) in different geographic areas, depending on the seasonality of thunderstorms and allergenic pollen.