
EASL Congress 2023
21-24 June Vienna

|
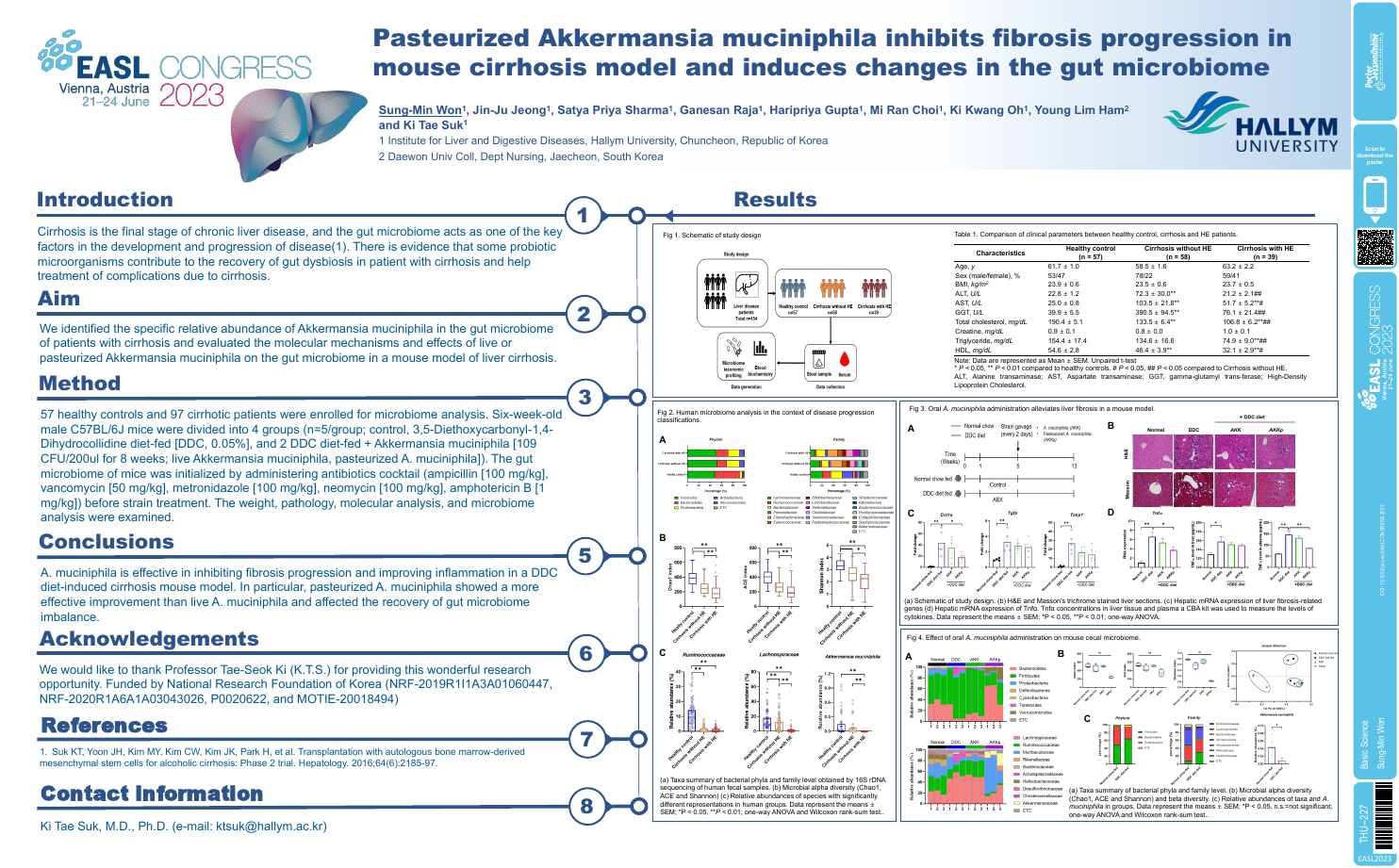



| Pasteurized Akkermansia muciniphila inhi.. | Sung-Min Won .. | .. | Basic Science.. | - - | |
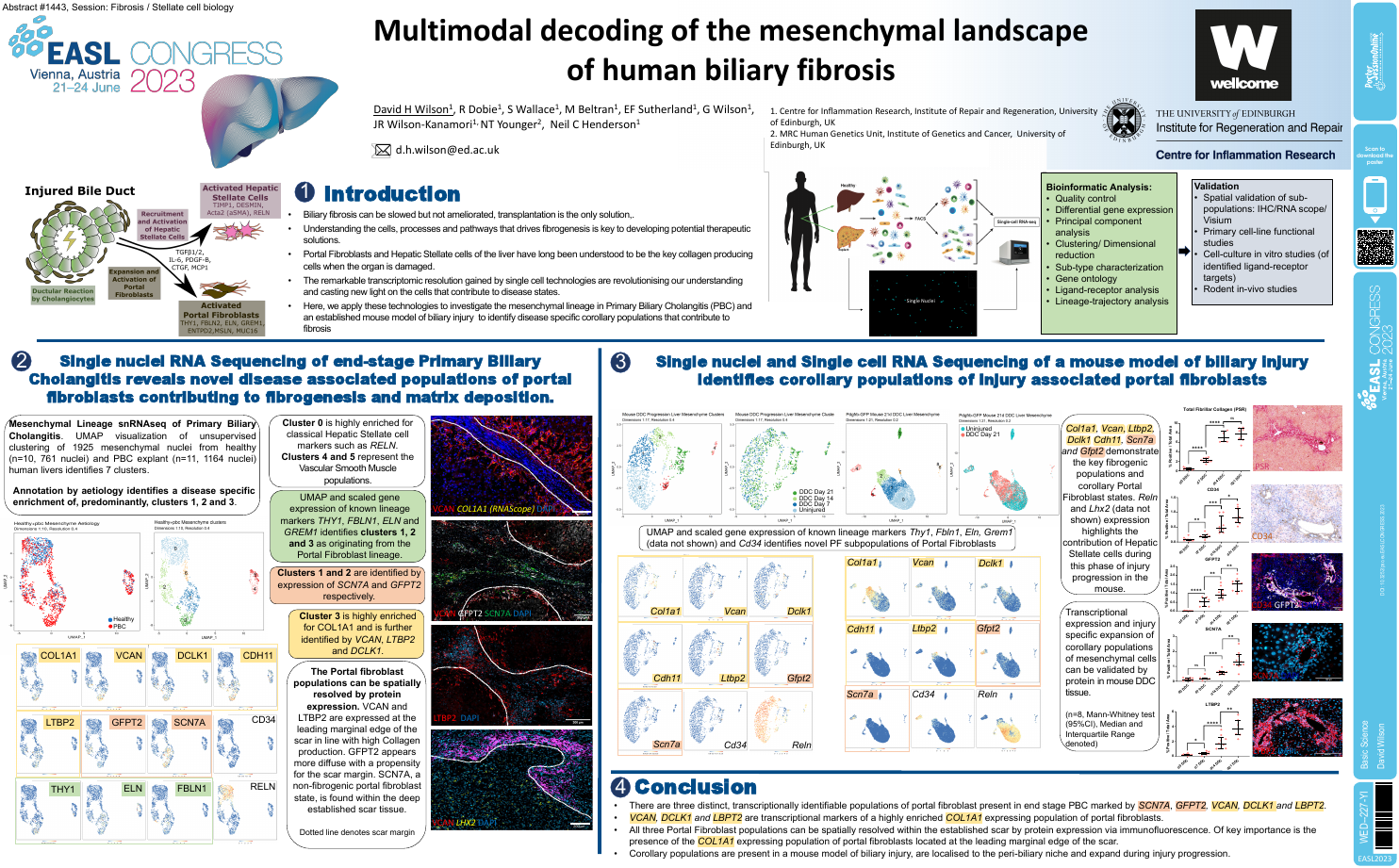
| Multimodal decoding of the mesenchymal l.. | David Wilson .. | Prof. Neil Henderson.. | Basic Science.. | - - | |
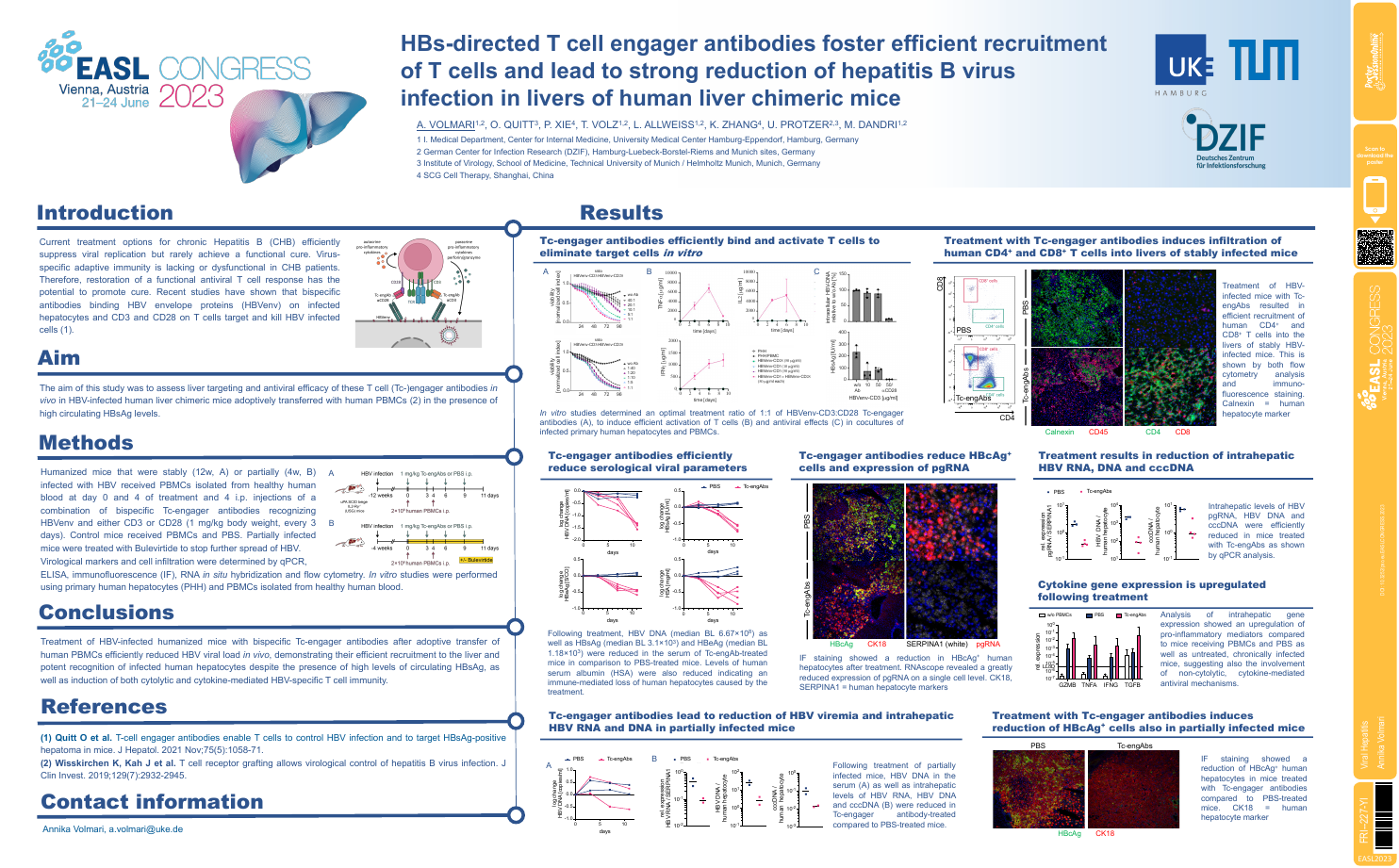
| HBs-directed T cell engager antibodies f.. | Annika Volmari .. | .. | Viral Hepatitis.. | - - | |
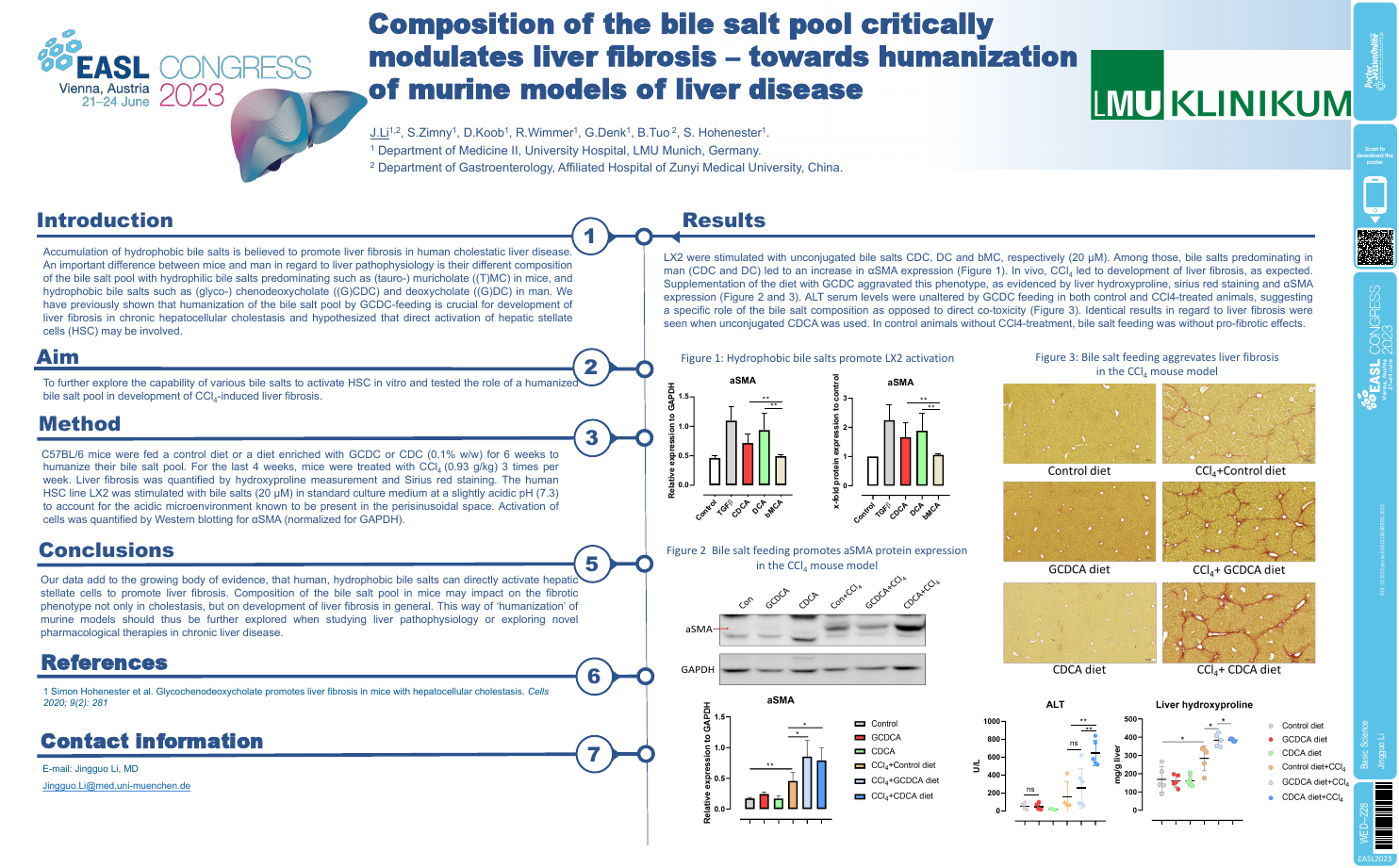
| Composition of the bile salt pool critic.. | Jingguo Li .. | .. | Basic Science.. | - - | |
| Investigating the correlation of a poly-.. | Nadeen Habboub .. | .. | Basic Science.. | - - | |
| Infiltrating suppressive myeloid cells d.. | Yvonne Vercoulen .. | Daniëlle Krijgsman1,2*, Lianne.. | Liver tumours.. | - - | |
| HBV and HDV interaction and variability .. | Maria Francesca Cortese .. | Pacín Ruiz B, Camps Ramón G, G.. | Viral Hepatitis.. | - - | |
| Fatty Acid Synthase expression promotes .. | Mirella Pastore .. | .. | Liver tumours.. | - - | |
| Rapid functional secretome analysis of H.. | Nina Le Bert .. | .. | Viral Hepatitis.. | - - | |
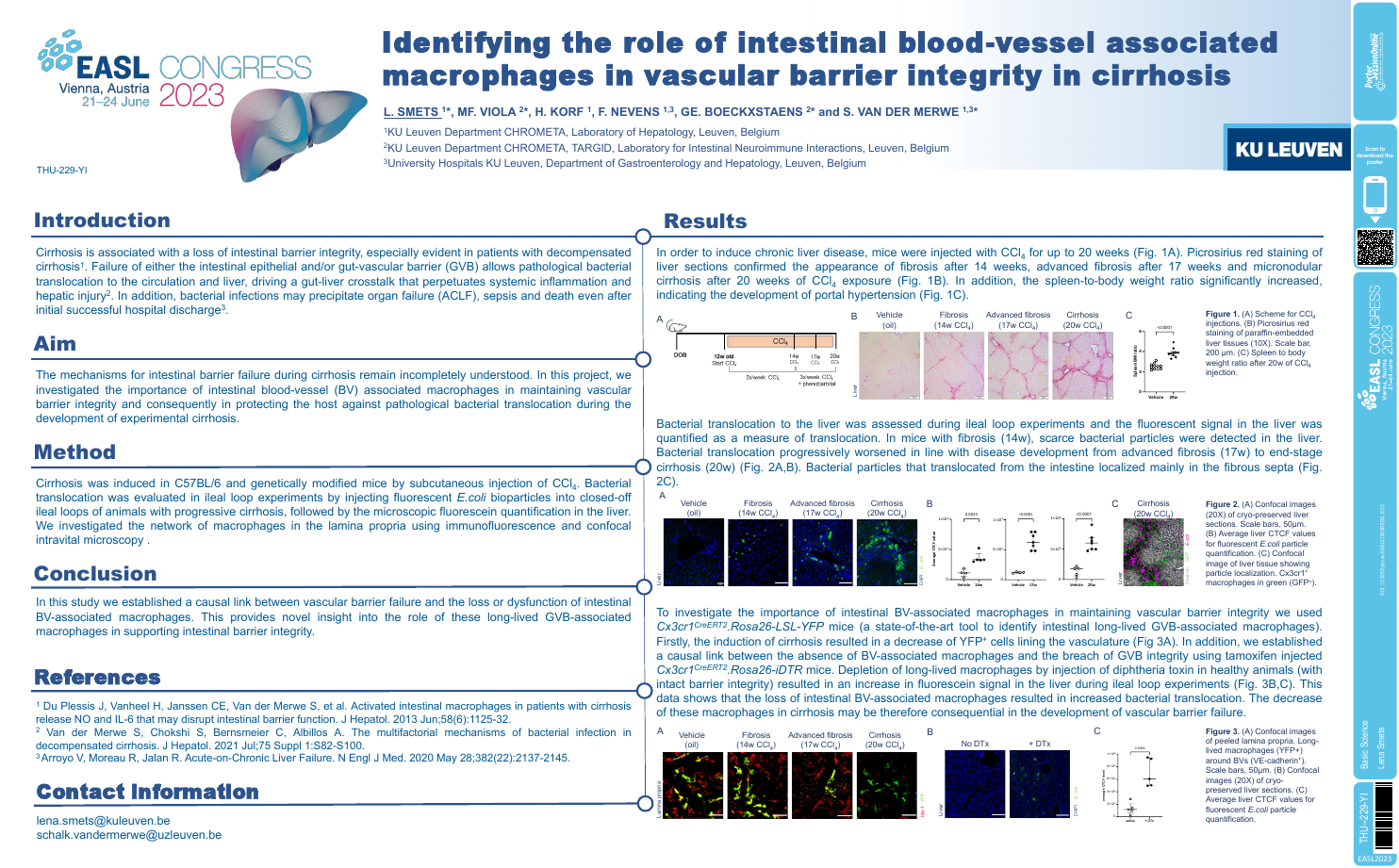
| Identifying the role of intestinal blood.. | Lena Smets .. | .. | Basic Science.. | - - | |
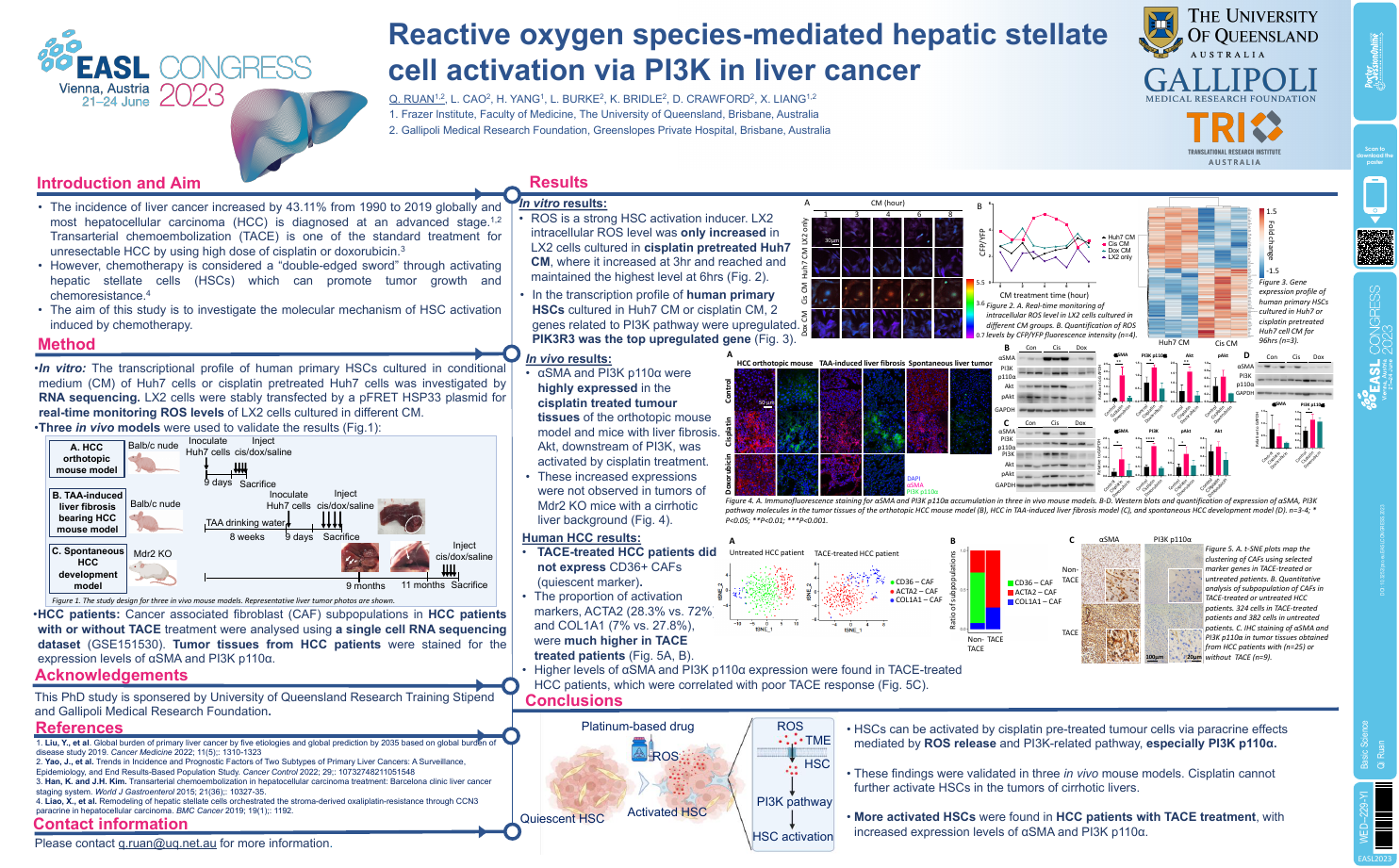
| Reactive oxygen species-mediated hepatic.. | Qi Ruan .. | Lu Cao, Haotian Yang, Leslie J.. | Basic Science.. | - - | |
| Altered gut microbiome and stool bile ac.. | Benard Aliwa .. | Angela Horvath, Julia Traub, N.. | Basic Science.. | - - | |
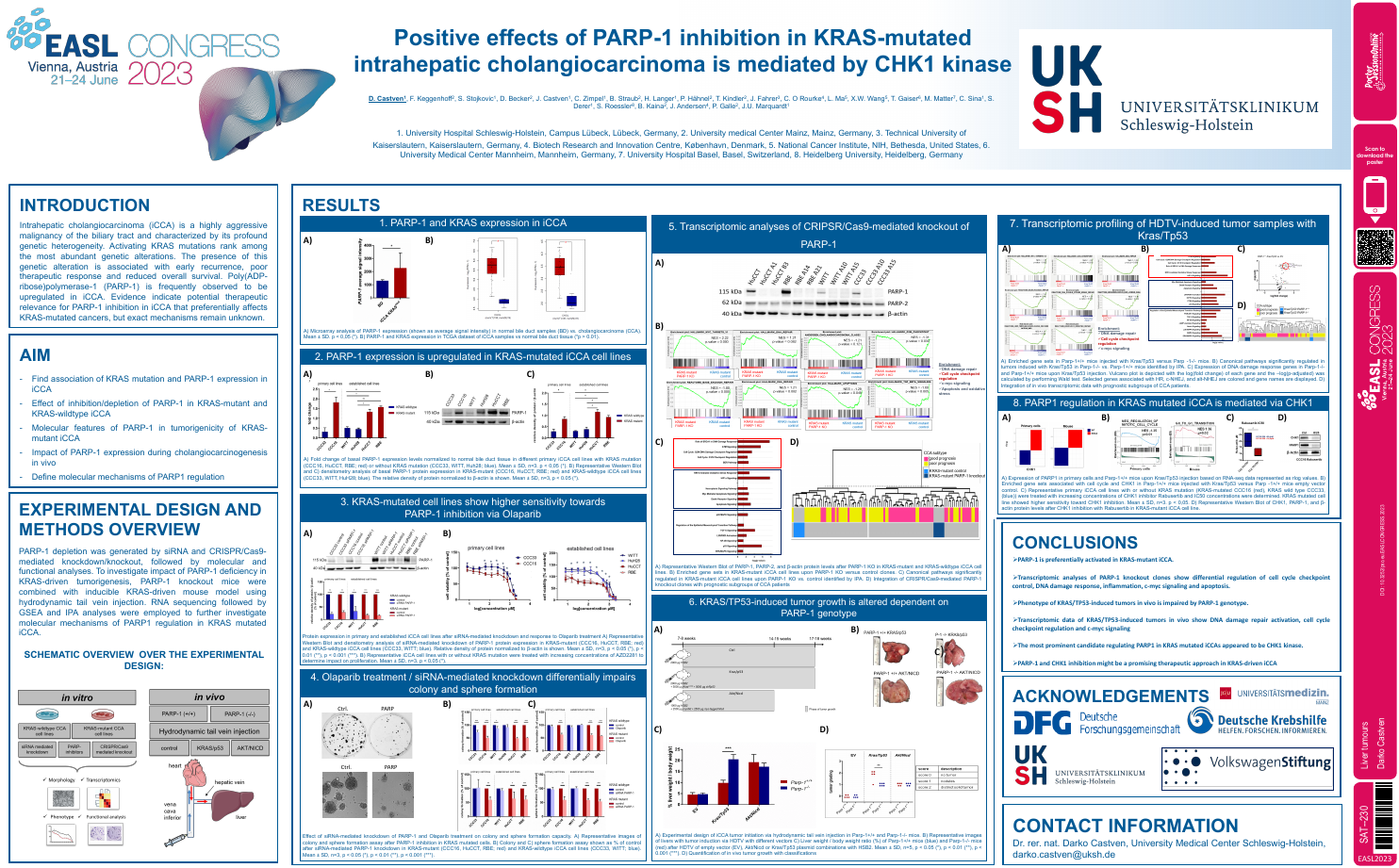
| Positive effects of PARP-1 inhibition in.. | Darko Castven .. | .. | Liver tumours.. | - - | |
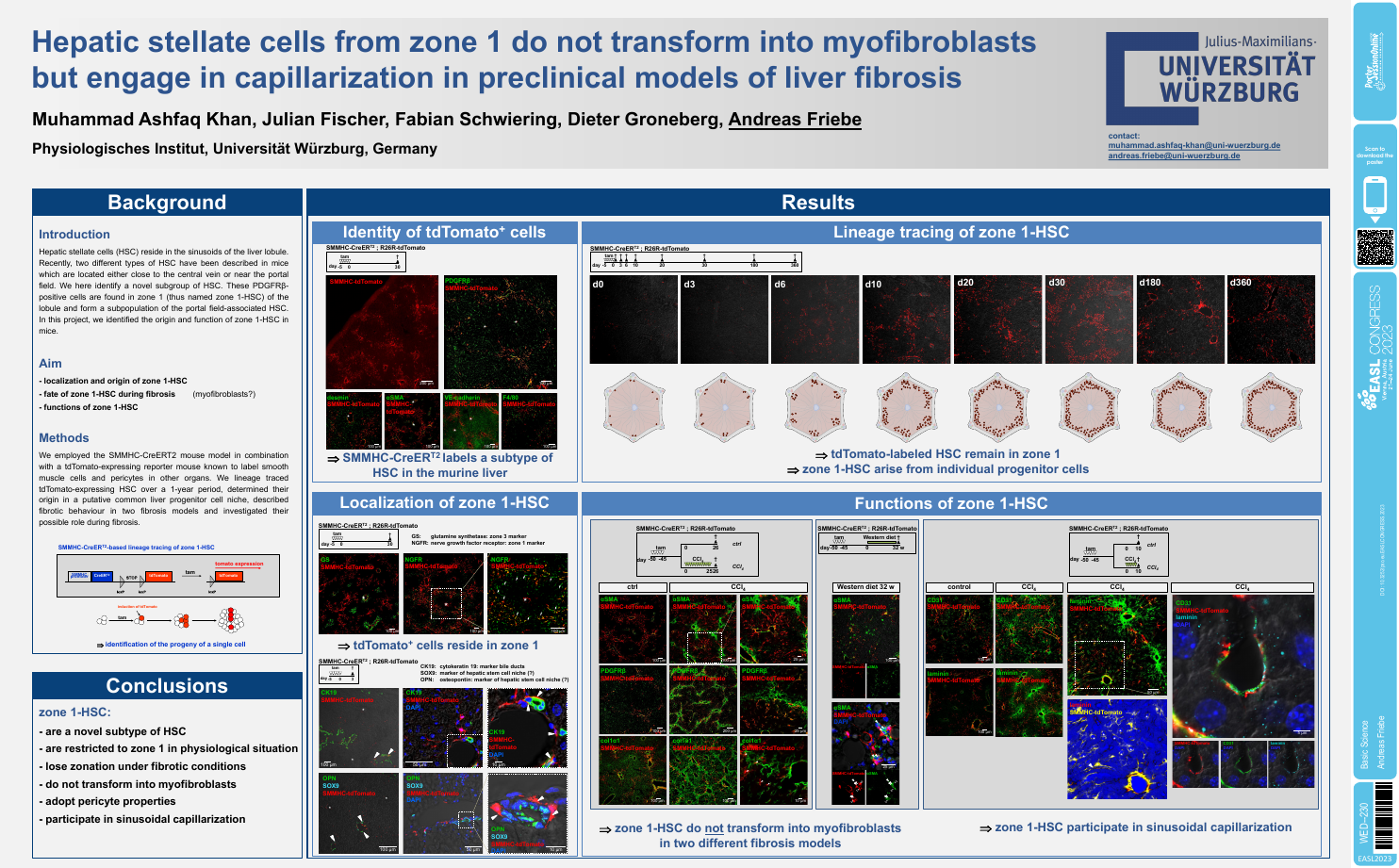
| Hepatic stellate cells from zone 1 do no.. | Andreas Friebe .. | .. | Basic Science.. | - - | |
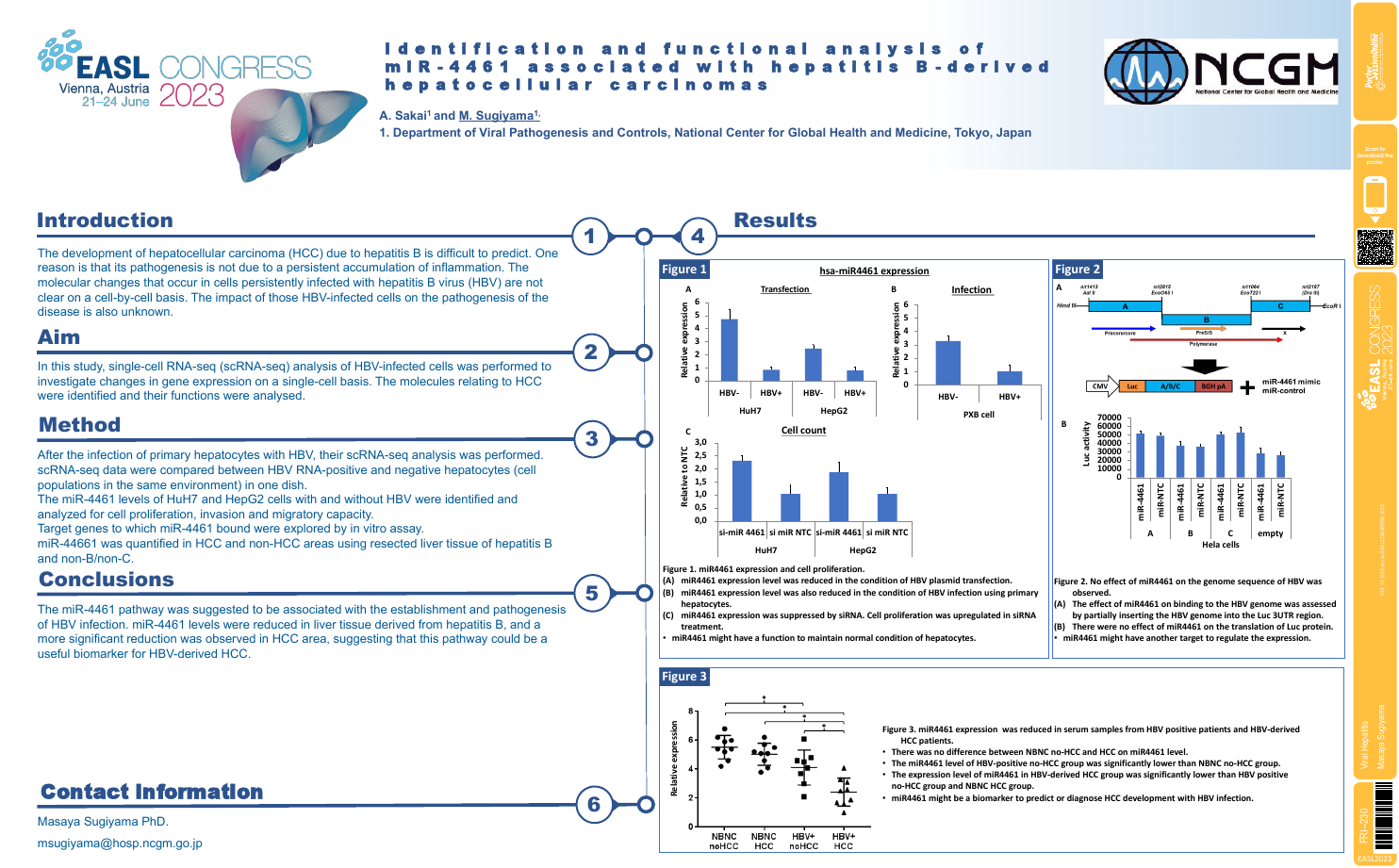
| Identification and functional analysis o.. | Masaya Sugiyama .. | .. | Viral Hepatitis.. | - - | |
| Role of the hepatocyte Epidermal Growth .. | Isabel Fabregat .. | .. | Basic Science.. | - - | |
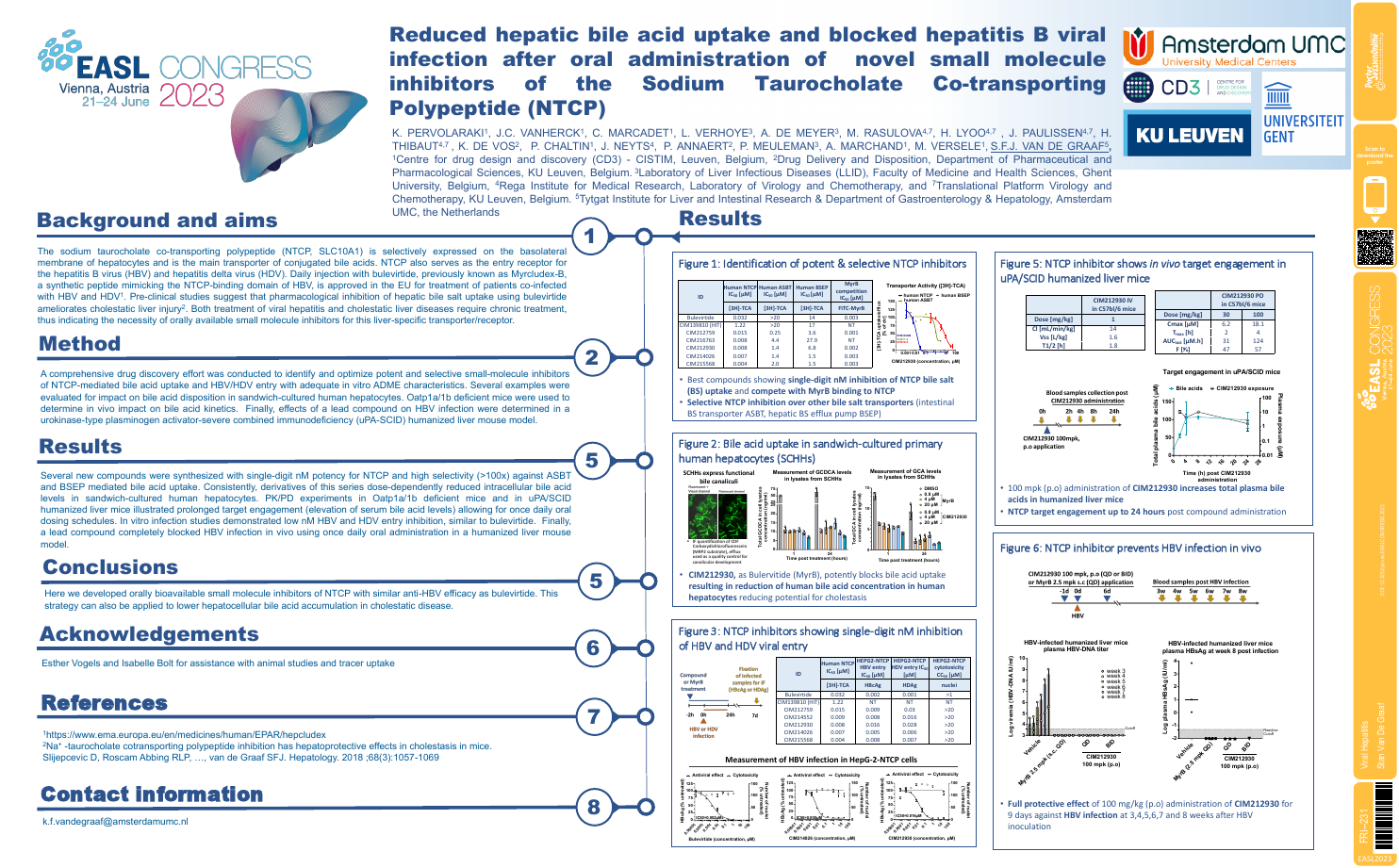
| Reduced hepatic bile acid uptake and blo.. | Stan Van De Graaf .. | .. | Viral Hepatitis.. | - - | |
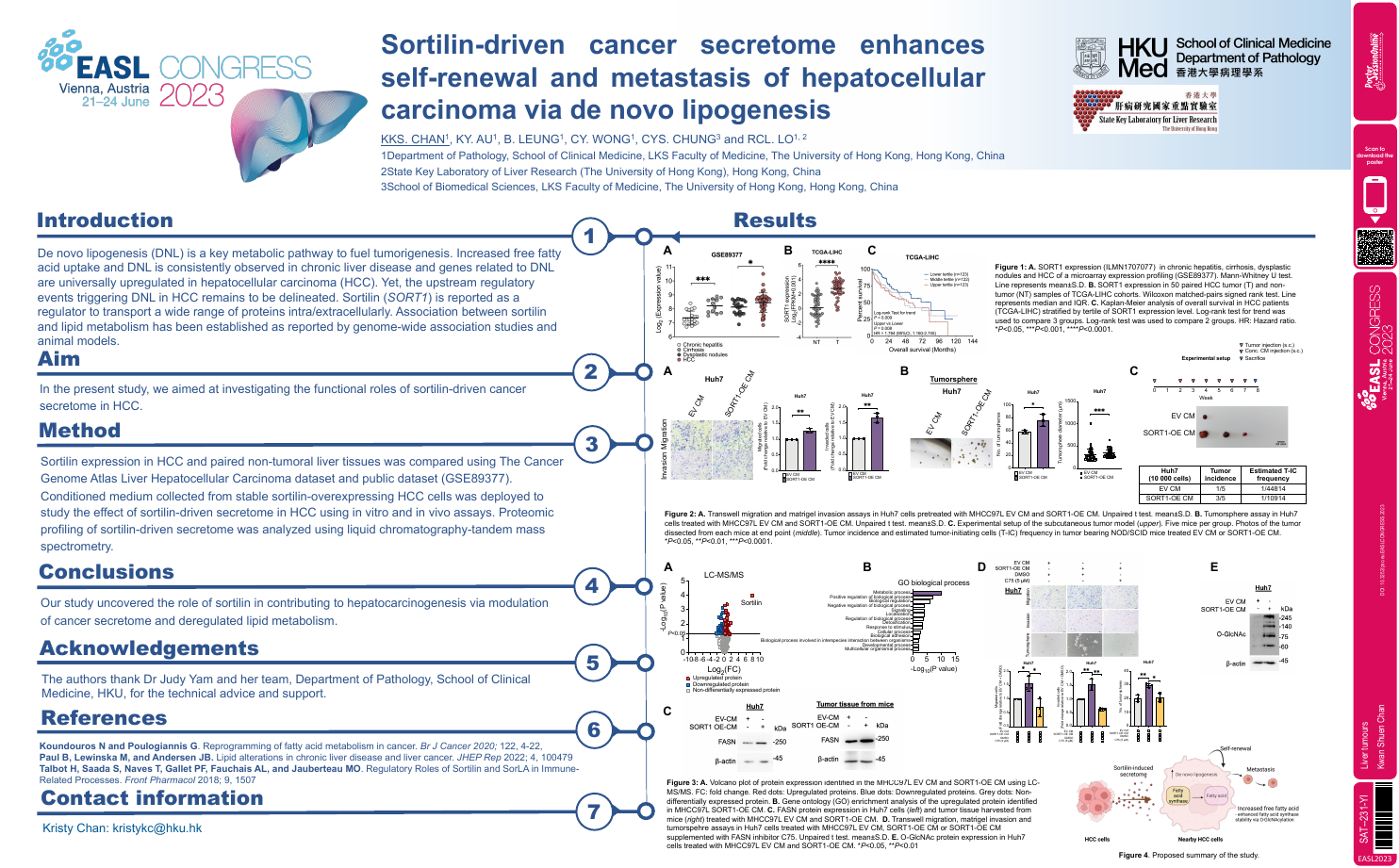
| Sortilin-driven cancer secretome enhance.. | Kwan Shuen Chan .. | .. | Liver tumours.. | - - | |
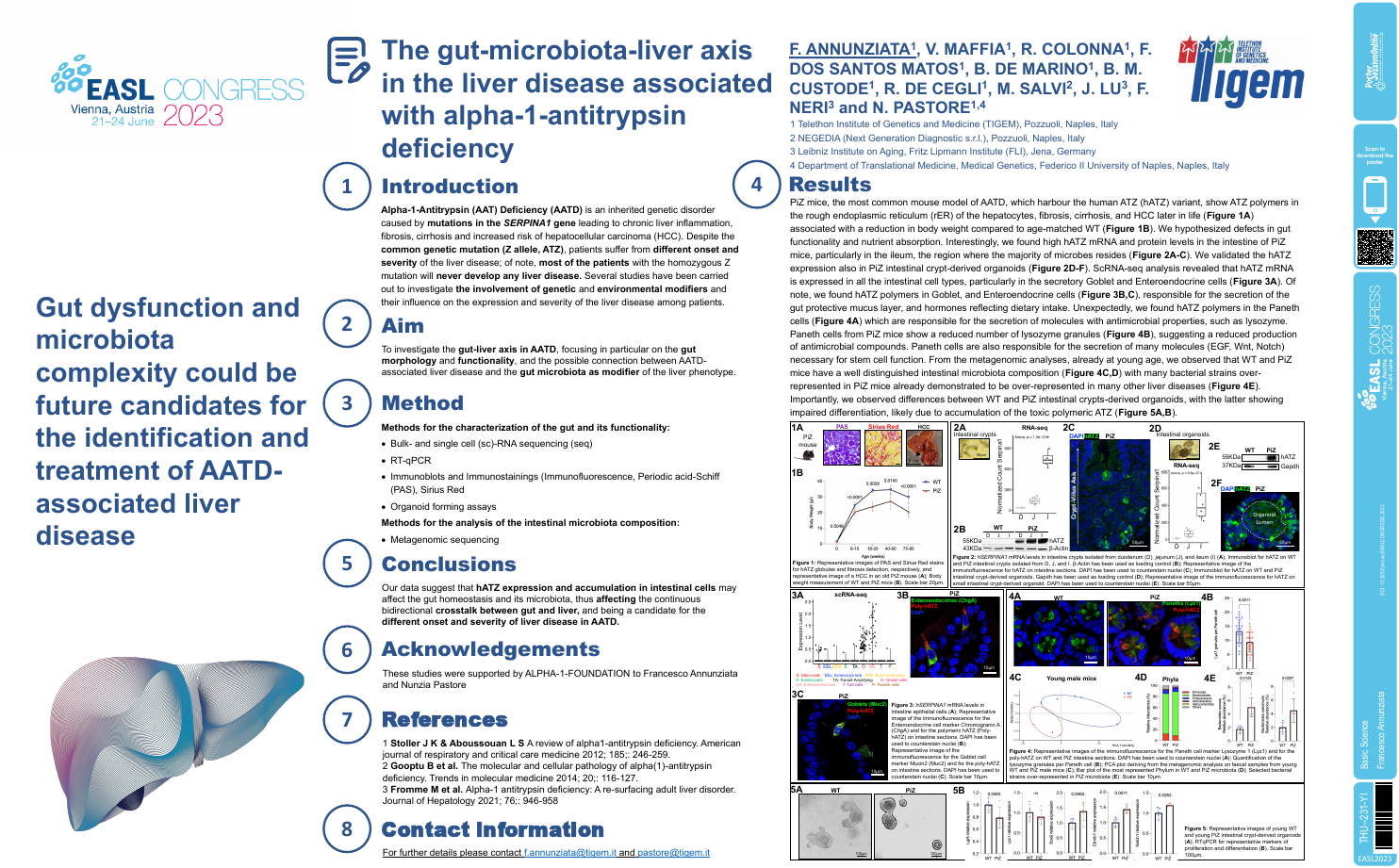
| The gut (and its microbiota)-liver axis .. | Francesco Annunziata .. | Veronica Maffia, Rita Colonna,.. | Basic Science.. | - - | |
| The divergent C-termini of L-HDAg regula.. | Hongbo Guo .. | .. | Viral Hepatitis.. | - - | |
Abstract
Thunderstorm-related asthma in patients sensitised to olea europaea pollen: twenty emergency department visits for asthmatic symptoms in one single day Losappio, Laura1; Heffler, Enrico2; Falco, Antonio1; Contento, Francesco1; Cannito, Cosimo1; Rolla, Giovanni2 1"Dimiccoli" Hospital, Emergency Department, Barletta, Italy; 2University of Torino - AO Mauriziano "Umberto I", Allergy and Clinical Immunology, Torino, Italy
Background: Associations between thunderstorm and asthma morbidity have been reported in several countries. Common to all epidemics of thunderstorm-related asthma is a significant increase in atmospheric allergen load during and immediately after a thunderstorm. Sensitization to Alternaria species or to grass and parietaria pollens has been suggested to play a key role in thunderstorm-related asthma. The only reported event of thunderstorm-related asthma in Mediterranean area was attributed to sensitization to parietaria pollen.
Method: here we describe a series of 20 patients who presented to Emergency Department in Barletta (94,000 inhabitants), Puglia (Italy) for sudden and severe asthmatic symptoms between May 27th and 28th 2010 (from15:36 to 5:02), immediately after a violent thunderstorm which occurred following a very hot morning (mean temperature: 29°C). All the patients have been subsequently visited by an allergist and underwent allergological work-up which included skin prick tests and a careful clinical history. Local pollen counts were available.
Result: Between May 10th and June 10th 2010, 86 Emergency Department asthma visits were recorded, 20 of them during the study day. Patients' mean age was 44.25 +/- 18.5 years (range: 9-81), 8/20 females, 2 smokers, 16 with a previous history of known respiratory allergy. Only two patients regularly took anti-asthma drugs. All 20 patients were sensitized to Olea europaea pollen, 7 of whom were monosensitized. Ten patients were sensitized to grass, 7 to parietaria, 5 to compositae, 5 to cypress, 5 to house dust mites, 3 to dog and 1 to cat danders. No patient was sensitized to Alternaria. Mean pollen count was 17 granules/m3 for Olea europaea, 6 granules/m3 for grass pollen.
Conclusion: This is, in our knowledge, the second epidemic of thunderstorm related asthma described in Mediterranean area and the first one in which sensitization to Olea europaea played a key-role. In conclusion, our report indicates that thunderstorm asthma may involve different allergens (not only fungal spores and grass or parietaria pollen) in different geographic areas, depending on the seasonality of thunderstorms and allergenic pollen.