
EASL Congress 2023
21-24 June Vienna

|
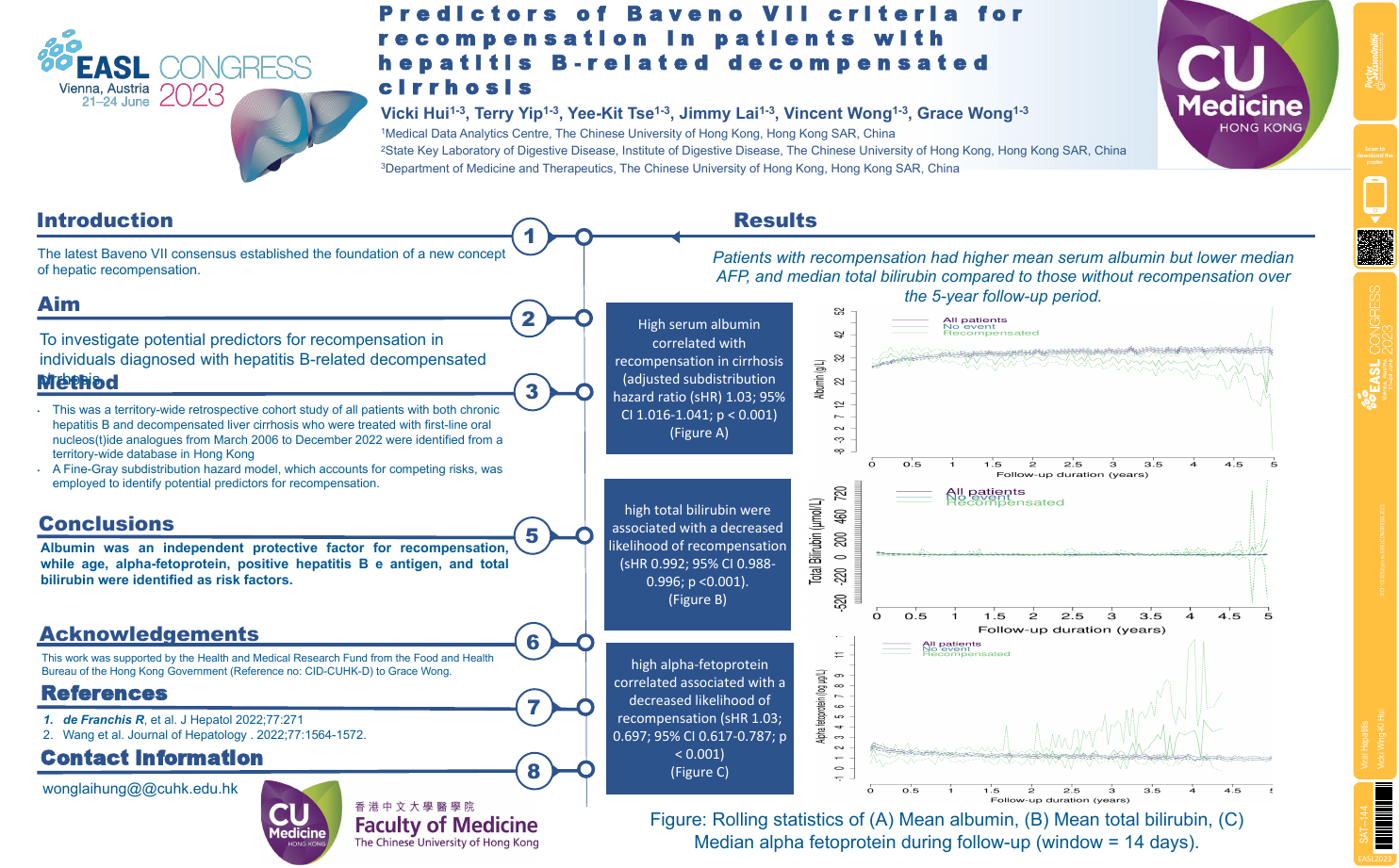



| Predictors of Baveno VII criteria for re.. | Vicki Wing-Ki Hui .. | .. | Viral Hepatitis.. | - - | |
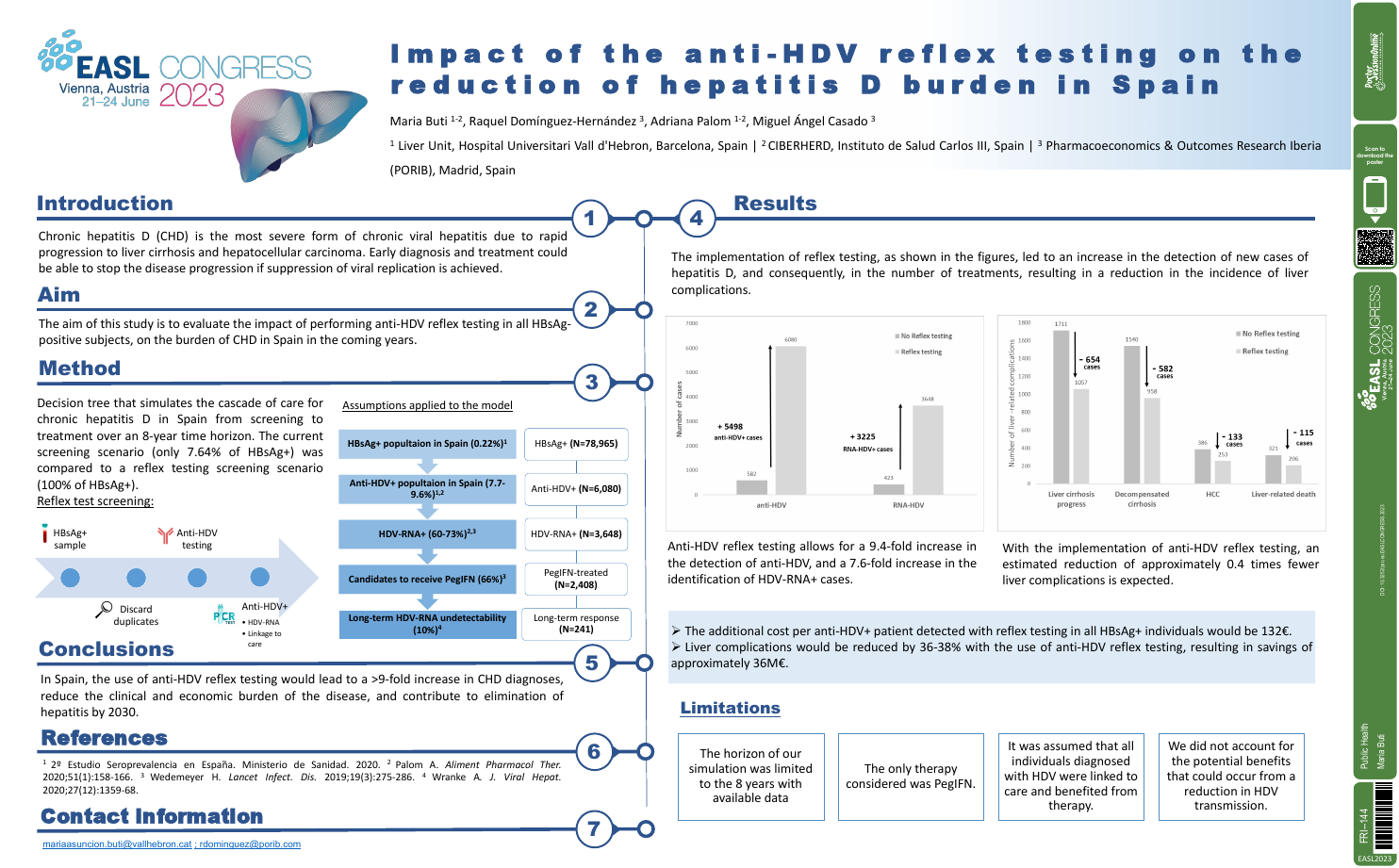
| Impact of the anti-HDV reflex testing on.. | Maria Buti .. | .. | Public Health.. | - - | |
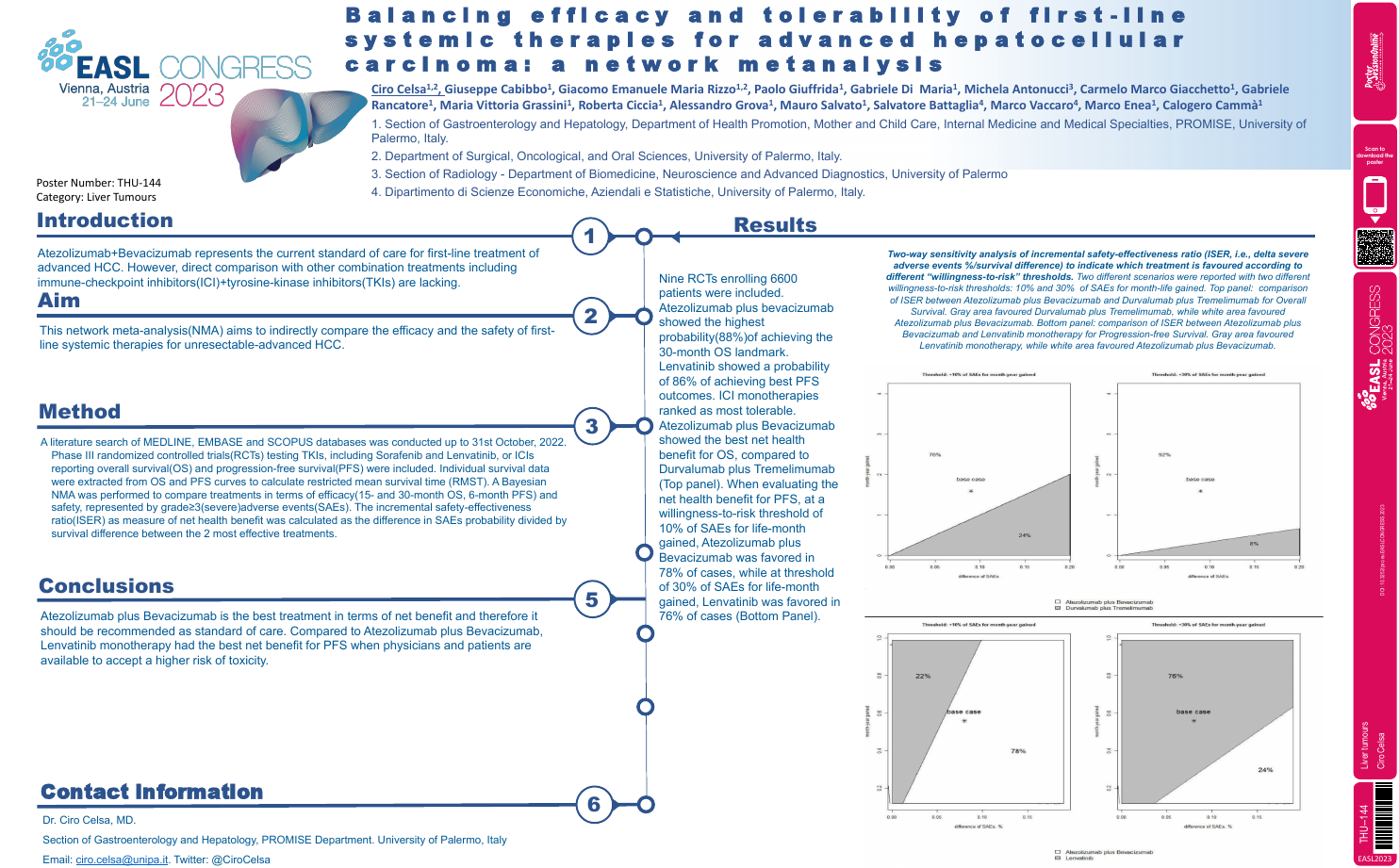
| Balancing efficacy and tolerability of f.. | Ciro Celsa .. | .. | Liver tumours.. | - - | |
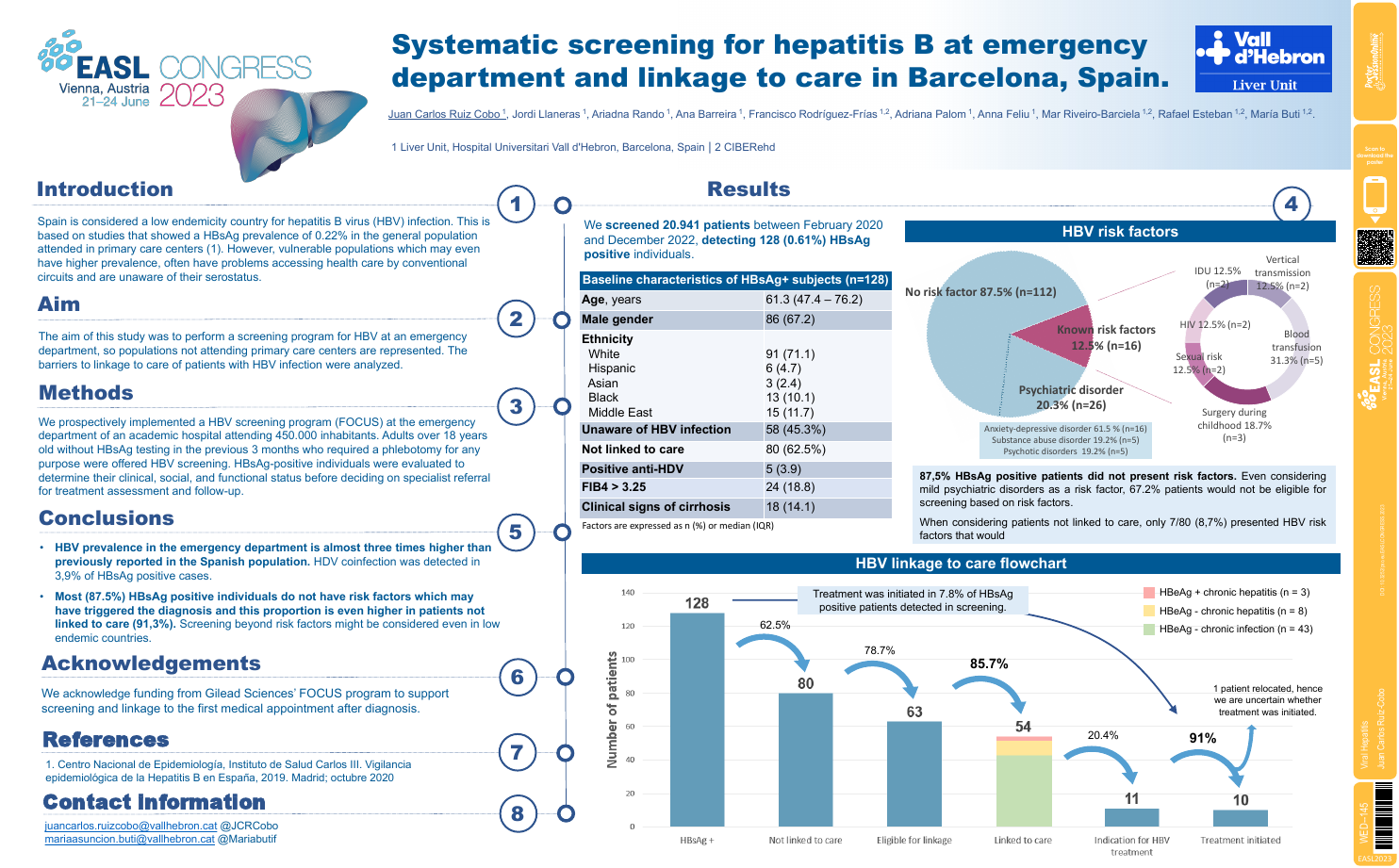
| Systematic screening for hepatitis B at .. | Juan Carlos Ruíz-Cobo .. | .. | Viral Hepatitis.. | - - | |
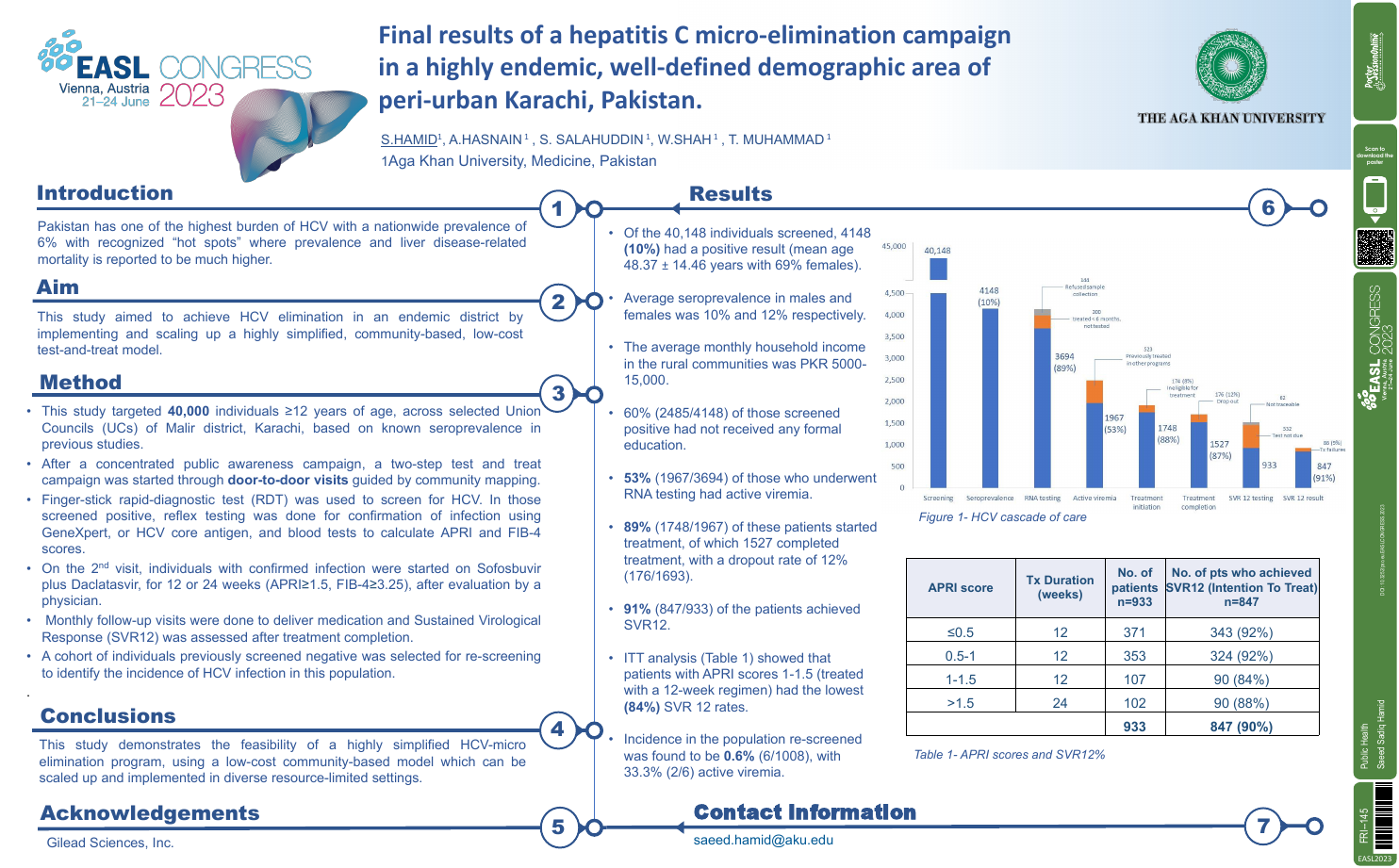
| Final results of a hepatitis C micro-eli.. | Saeed Sadiq Hamid .. | .. | Public Health.. | - - | |
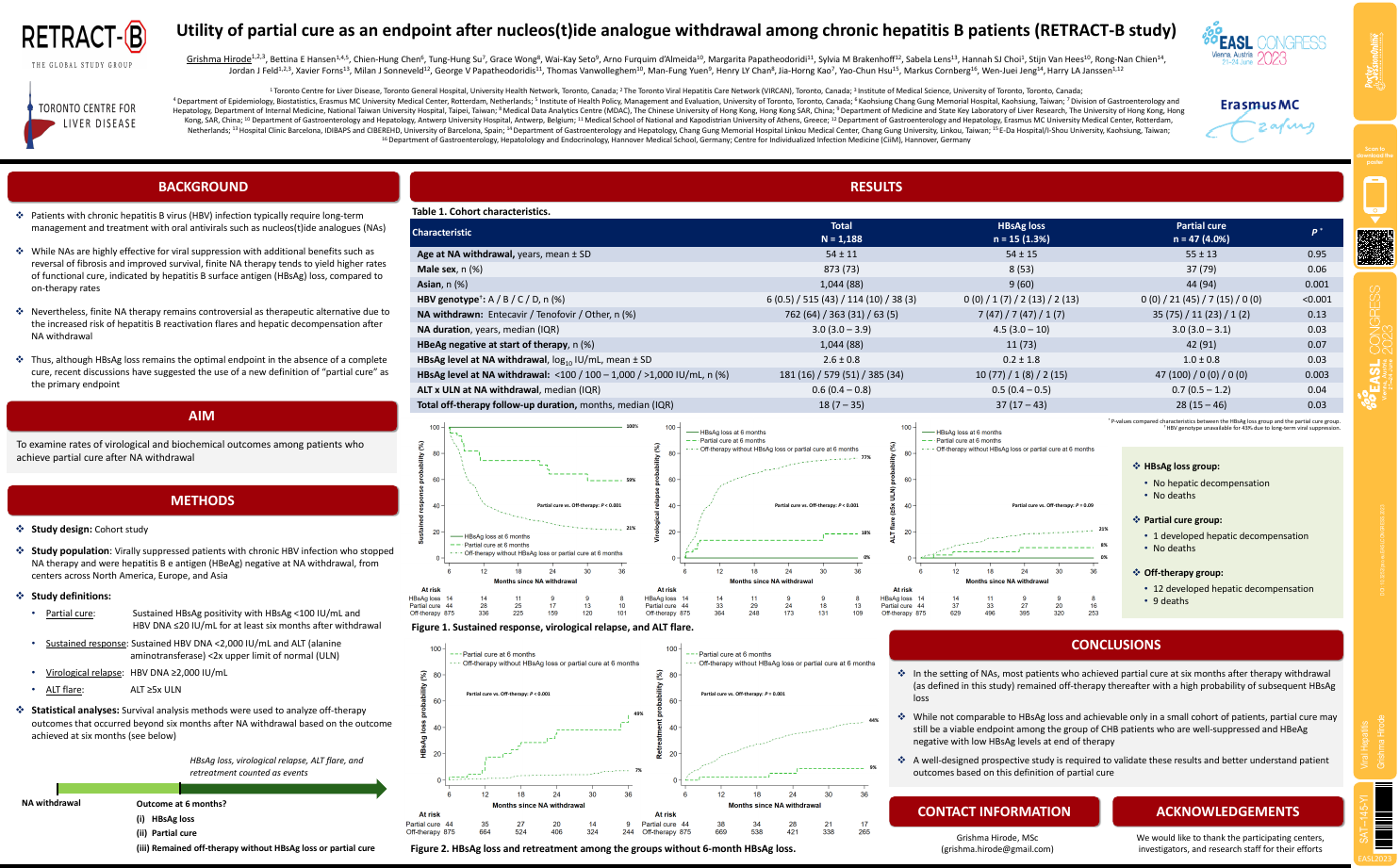
| Utility of partial cure as an endpoint a.. | Grishma Hirode .. | .. | Viral Hepatitis.. | - - | |
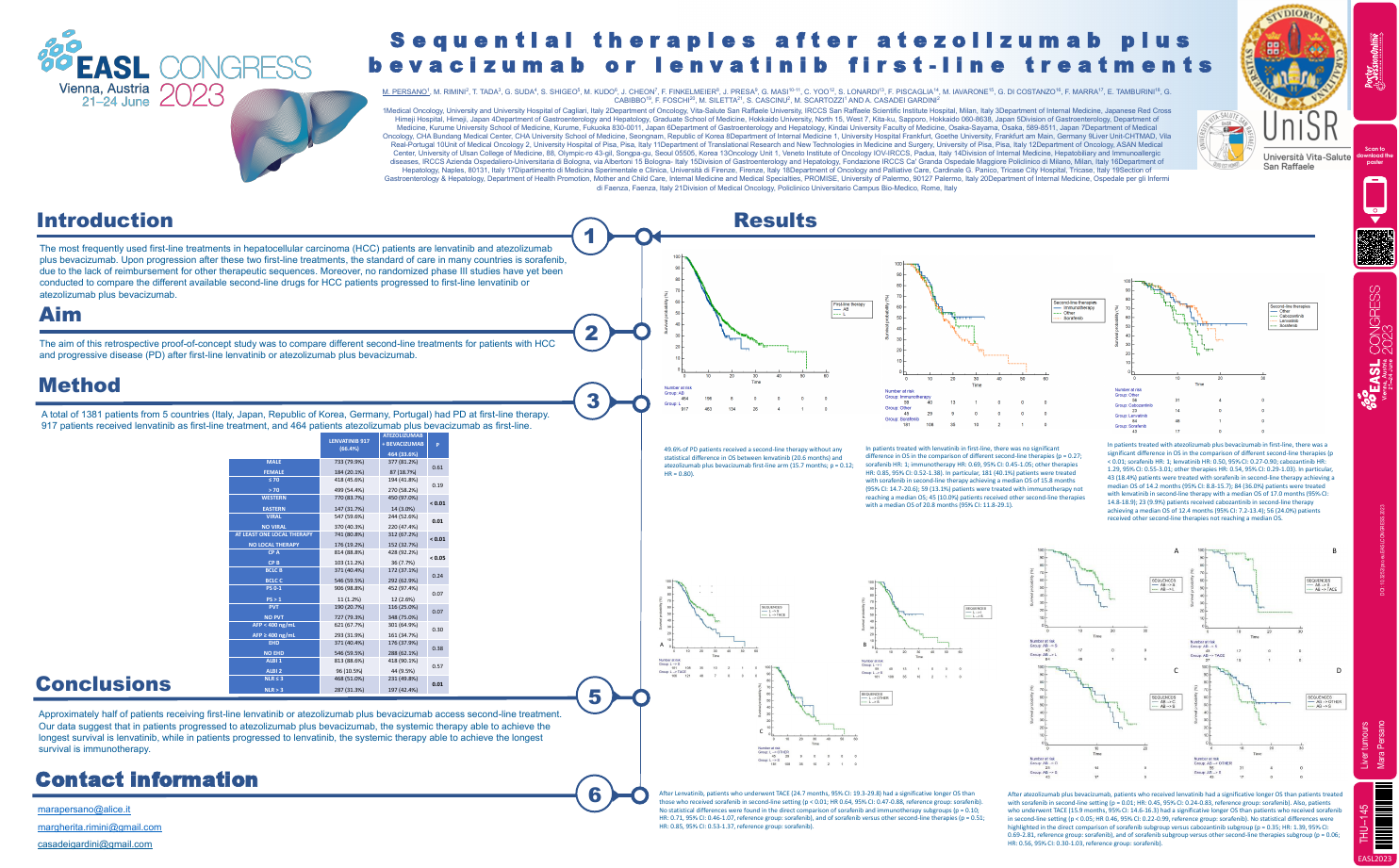
| Sequential therapies after atezolizumab .. | Mara Persano .. | .. | Liver tumours.. | - - | |
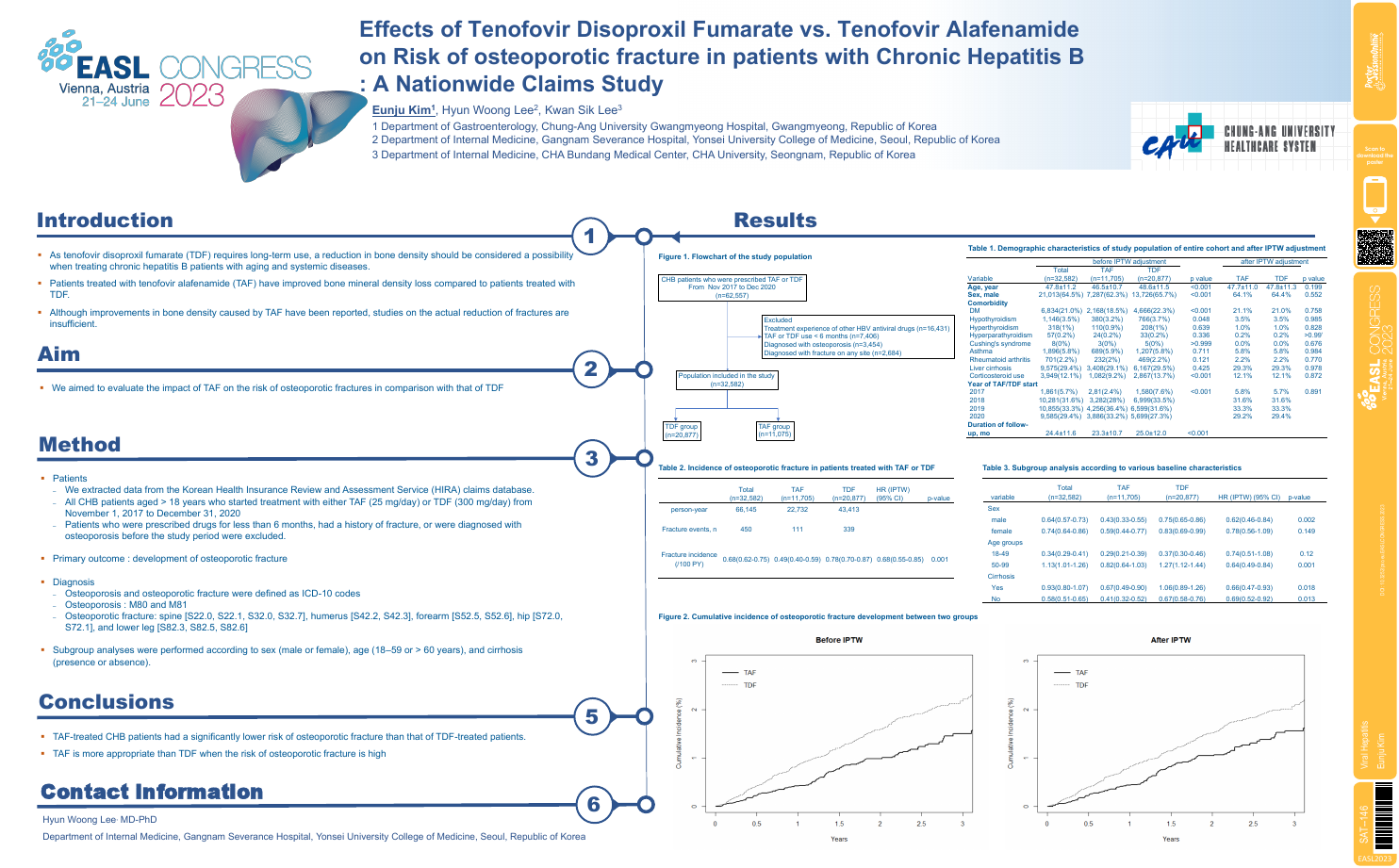
| Effects of tenofovir disoproxil fumarate.. | Eunju Kim .. | .. | Viral Hepatitis.. | - - | |
| Evaluation of hepatitis B core-related a.. | Jeanne Perpétue Vincent .. | .. | Public Health.. | - - | |
| Epidemiological and clinical profile of .. | Loreta Kondili .. | M.E. TOSTI, M.G. QUARANTA, A... | Viral Hepatitis.. | - - | |
| Effect of Tenofovir and Entecavir on occ.. | Yi-Hsiang Huang .. | .. | Viral Hepatitis.. | - - | |
| Implementing hepatitis C self-testing (H.. | Ketevan Stvilia .. | .. | Public Health.. | - - | |
| Effects of interferon-based therapies in.. | Qiran Zhang .. | .. | Viral Hepatitis.. | - - | |
| Sequential systemic treatment in patient.. | Jana Pauly .. | C. WEHLING, C. SPRINGFELD, A. .. | Liver tumours.. | - - | |
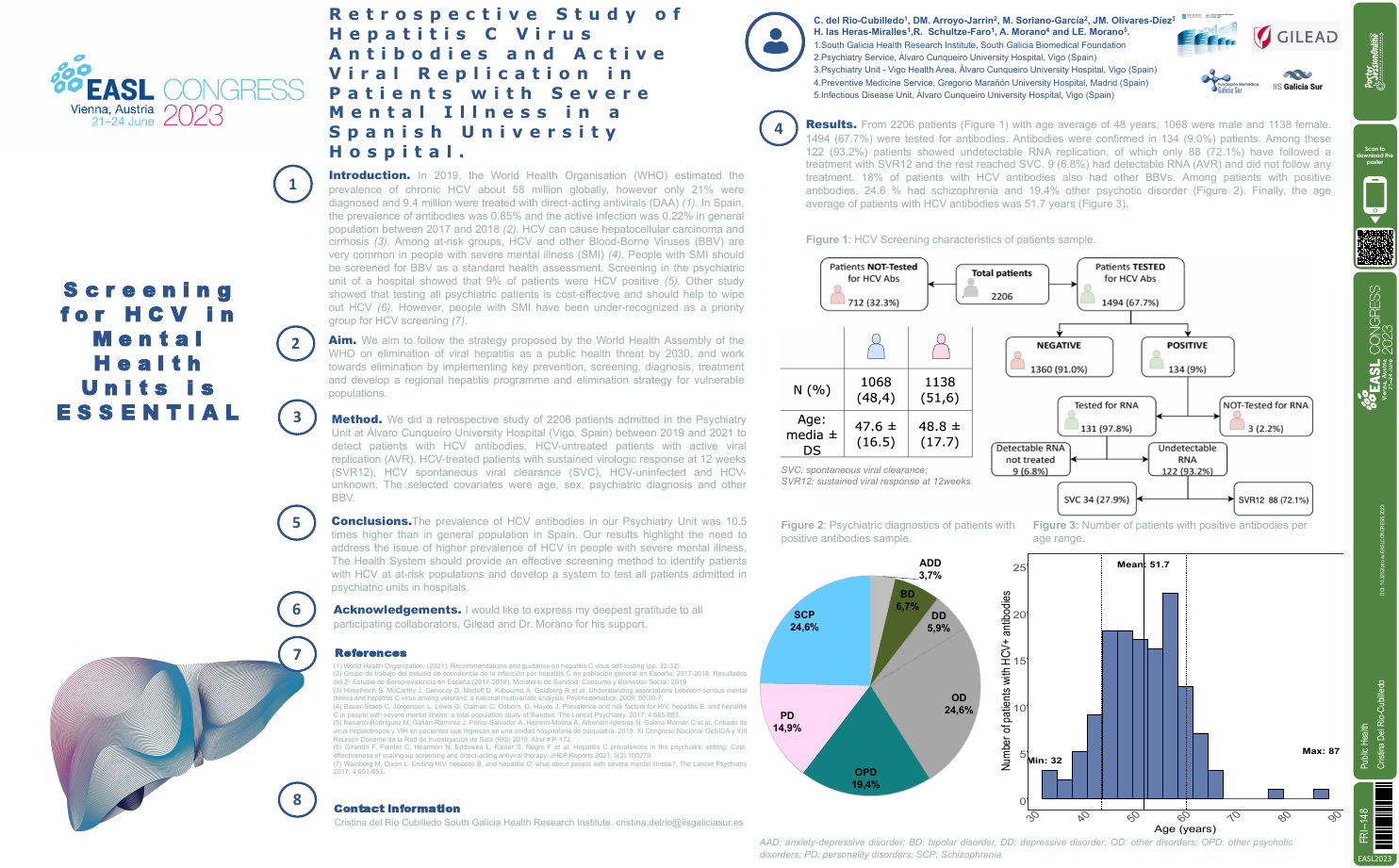
| Retrospective study of hepatitis C virus.. | Cristina Del Rio-Cubilledo .. | Denise Montserrat Arroyo Jarri.. | Public Health.. | - - | |
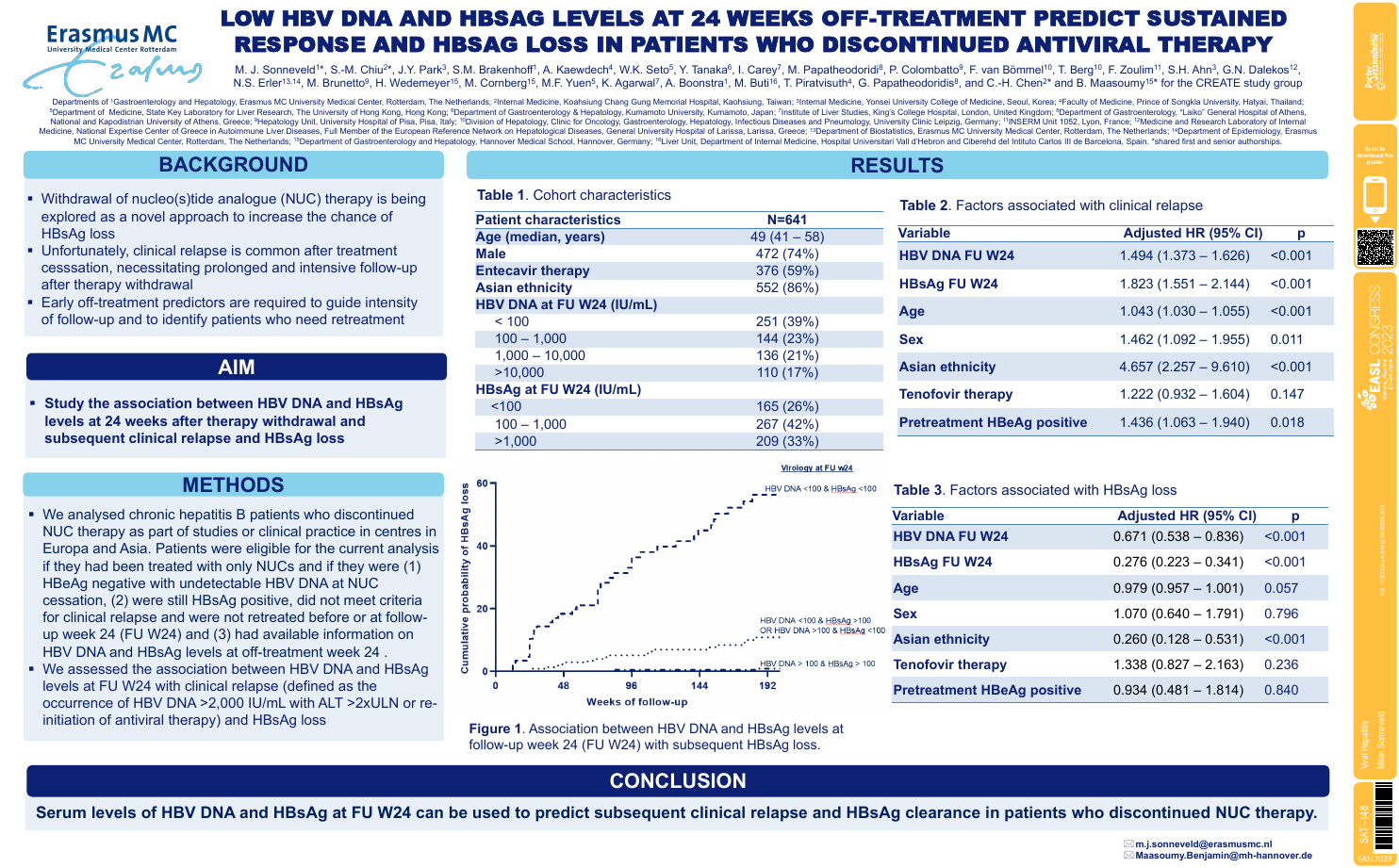
| Low HBV DNA and HBsAg levels at 24 weeks.. | Milan Sonneveld .. | .. | Viral Hepatitis.. | - - | |
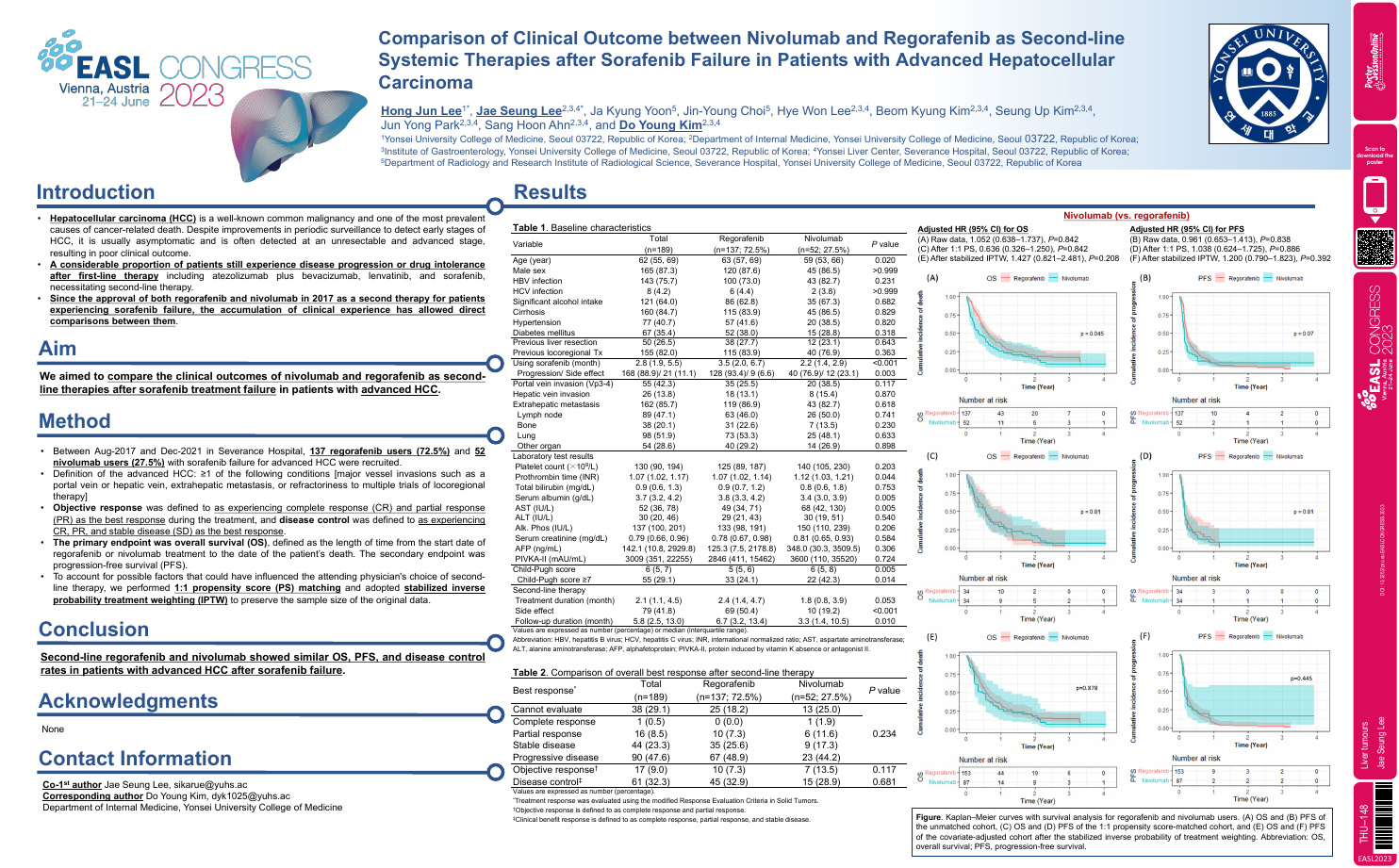
| Comparison of Clinical Outcome between N.. | Jae Seung Lee .. | .. | Liver tumours.. | - - | |
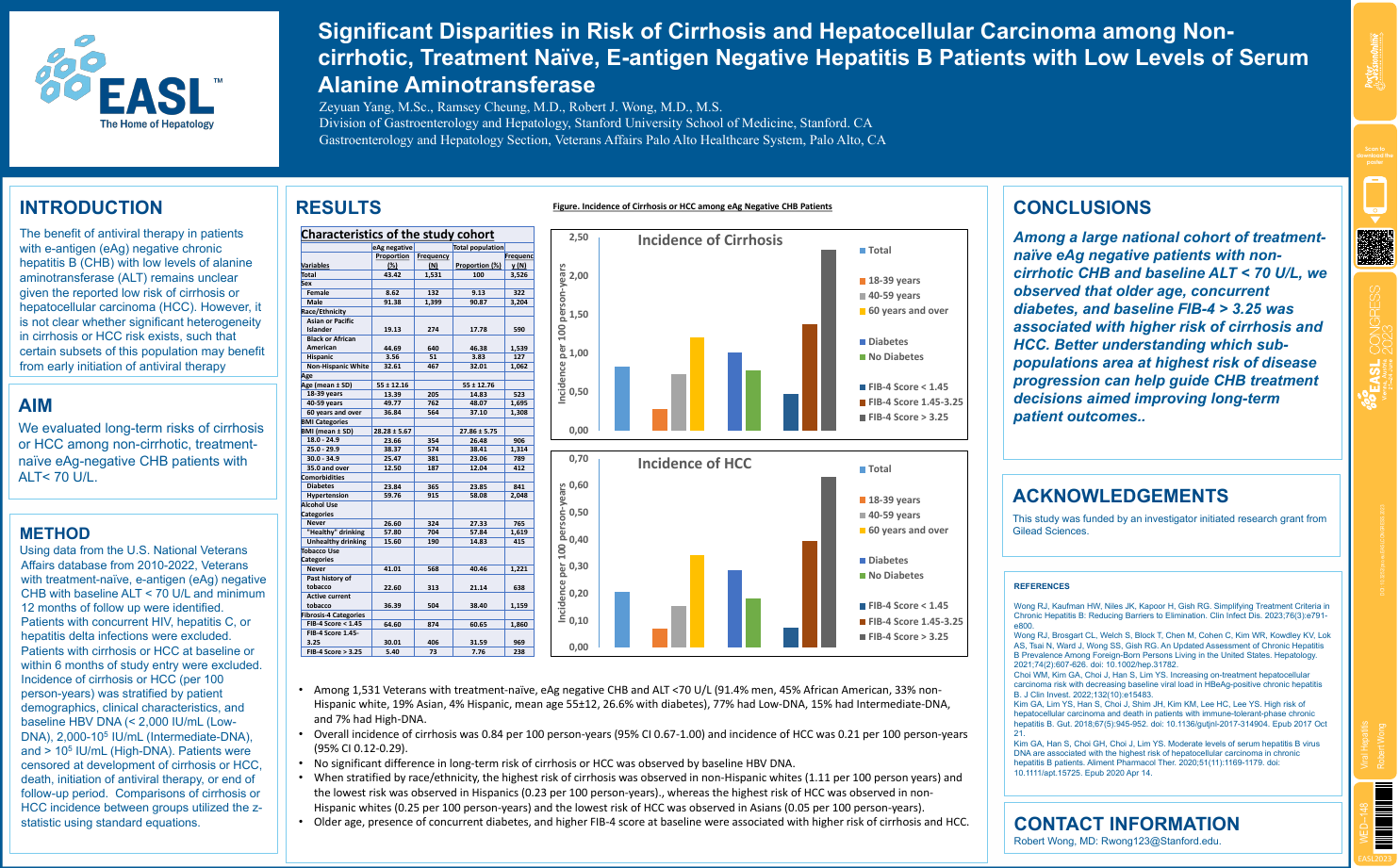
| Significant disparities in risk of cirrh.. | Robert Wong .. | .. | Viral Hepatitis.. | - - | |
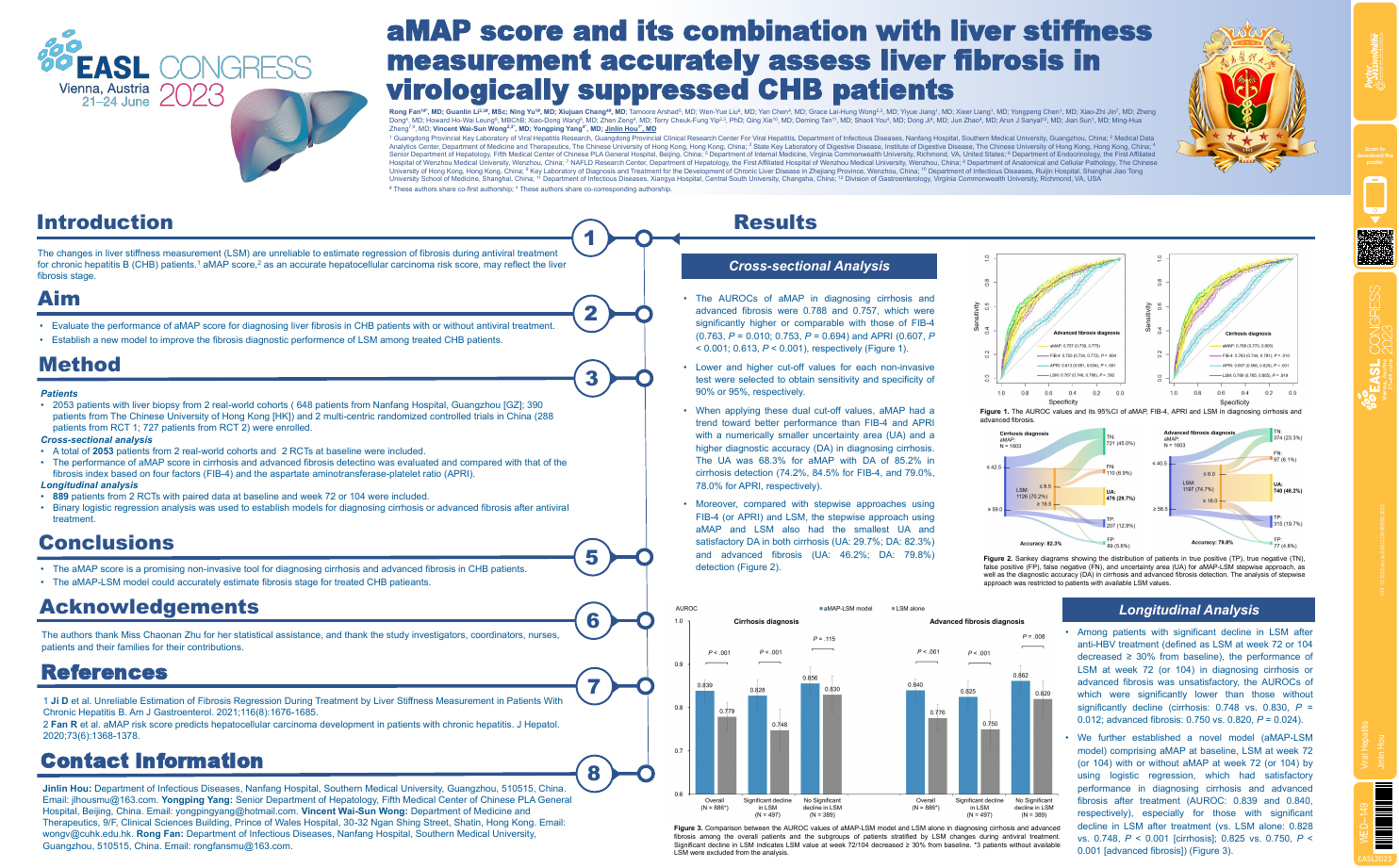
| aMAP score and its combination with live.. | Jinlin Hou .. | .. | Viral Hepatitis.. | - - | |
| Tailored message intervention by nudge t.. | Masaaki Korenaga .. | .. | Public Health.. | - - | |
Abstract
Thunderstorm-related asthma in patients sensitised to olea europaea pollen: twenty emergency department visits for asthmatic symptoms in one single day Losappio, Laura1; Heffler, Enrico2; Falco, Antonio1; Contento, Francesco1; Cannito, Cosimo1; Rolla, Giovanni2 1"Dimiccoli" Hospital, Emergency Department, Barletta, Italy; 2University of Torino - AO Mauriziano "Umberto I", Allergy and Clinical Immunology, Torino, Italy
Background: Associations between thunderstorm and asthma morbidity have been reported in several countries. Common to all epidemics of thunderstorm-related asthma is a significant increase in atmospheric allergen load during and immediately after a thunderstorm. Sensitization to Alternaria species or to grass and parietaria pollens has been suggested to play a key role in thunderstorm-related asthma. The only reported event of thunderstorm-related asthma in Mediterranean area was attributed to sensitization to parietaria pollen.
Method: here we describe a series of 20 patients who presented to Emergency Department in Barletta (94,000 inhabitants), Puglia (Italy) for sudden and severe asthmatic symptoms between May 27th and 28th 2010 (from15:36 to 5:02), immediately after a violent thunderstorm which occurred following a very hot morning (mean temperature: 29°C). All the patients have been subsequently visited by an allergist and underwent allergological work-up which included skin prick tests and a careful clinical history. Local pollen counts were available.
Result: Between May 10th and June 10th 2010, 86 Emergency Department asthma visits were recorded, 20 of them during the study day. Patients' mean age was 44.25 +/- 18.5 years (range: 9-81), 8/20 females, 2 smokers, 16 with a previous history of known respiratory allergy. Only two patients regularly took anti-asthma drugs. All 20 patients were sensitized to Olea europaea pollen, 7 of whom were monosensitized. Ten patients were sensitized to grass, 7 to parietaria, 5 to compositae, 5 to cypress, 5 to house dust mites, 3 to dog and 1 to cat danders. No patient was sensitized to Alternaria. Mean pollen count was 17 granules/m3 for Olea europaea, 6 granules/m3 for grass pollen.
Conclusion: This is, in our knowledge, the second epidemic of thunderstorm related asthma described in Mediterranean area and the first one in which sensitization to Olea europaea played a key-role. In conclusion, our report indicates that thunderstorm asthma may involve different allergens (not only fungal spores and grass or parietaria pollen) in different geographic areas, depending on the seasonality of thunderstorms and allergenic pollen.