
UKHSA Conference 2025
25-26 March 2025 Manchester
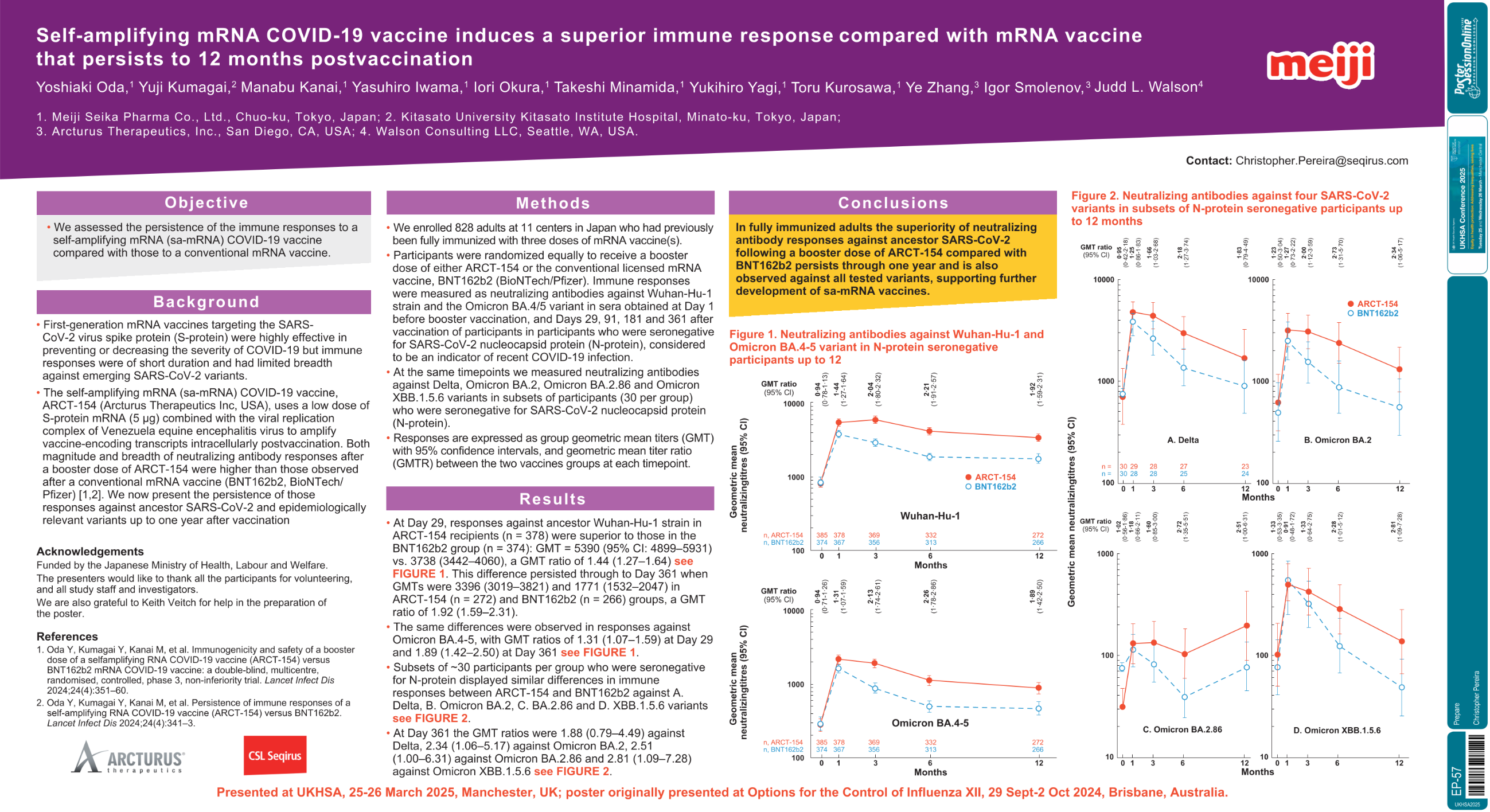




| Self-amplifying mRNA COVID-19 vaccine in.. | Christopher Pereira .. | .. | Prepare.. | - - | |
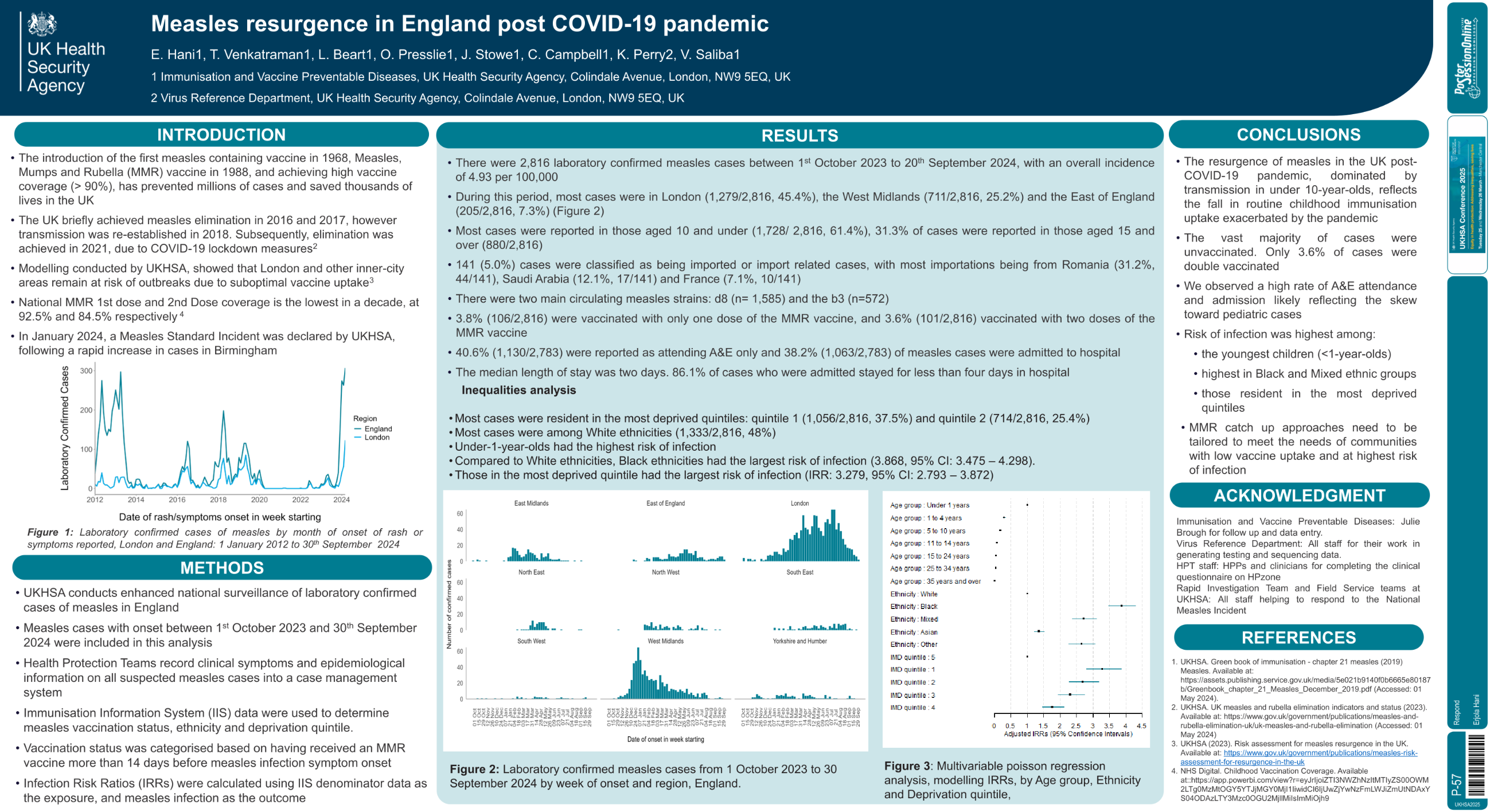
| Measles resurgence in the UK post COVID-.. | Erjola Hani .. | .. | Respond.. | - - | |
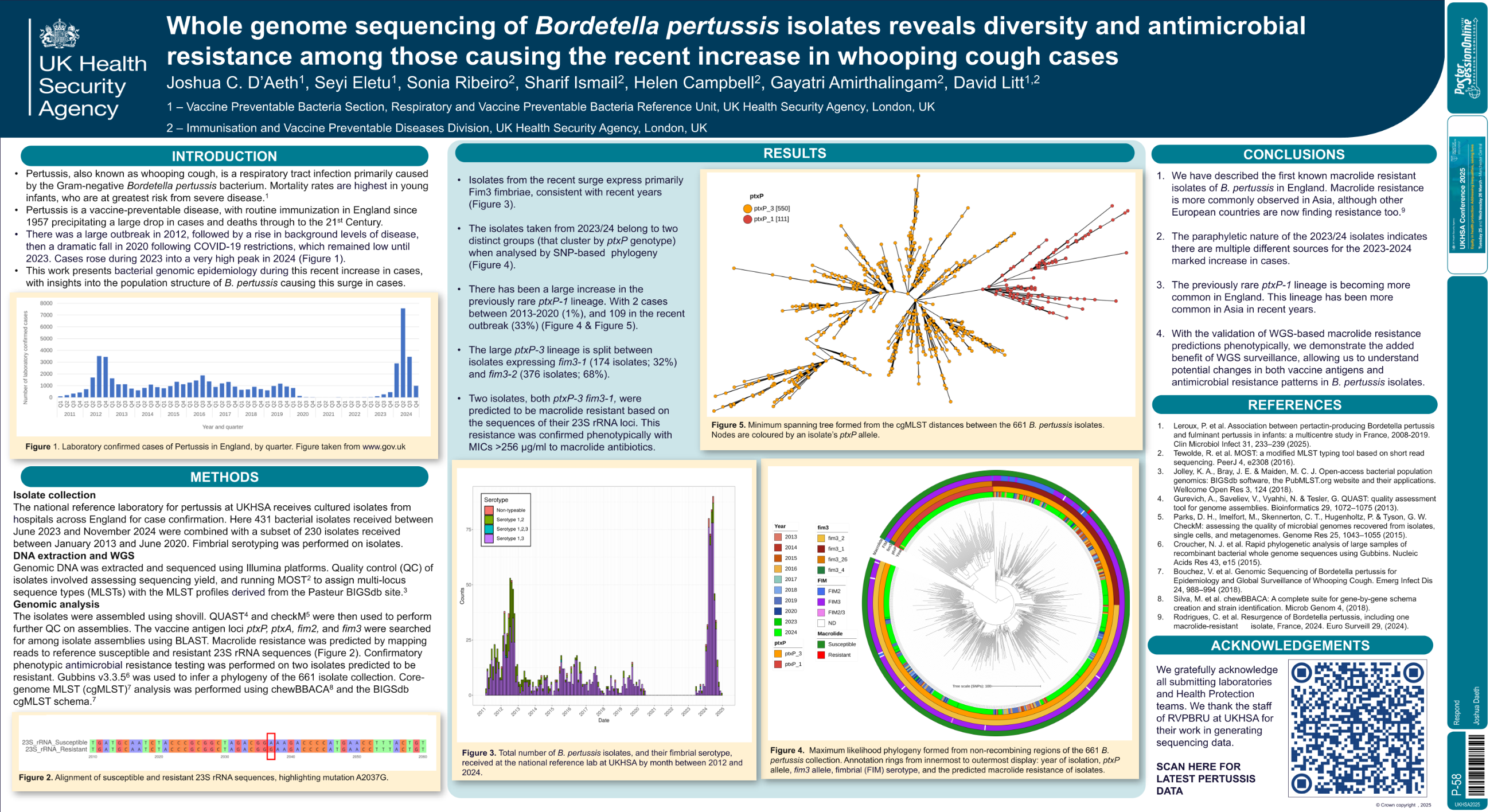
| WHOLE GENOME SEQUENCING OF BORDETELLA PE.. | Joshua DAeth .. | Seyi Eletu; Sonia Ribeiro; Sha.. | Respond.. | - - | |
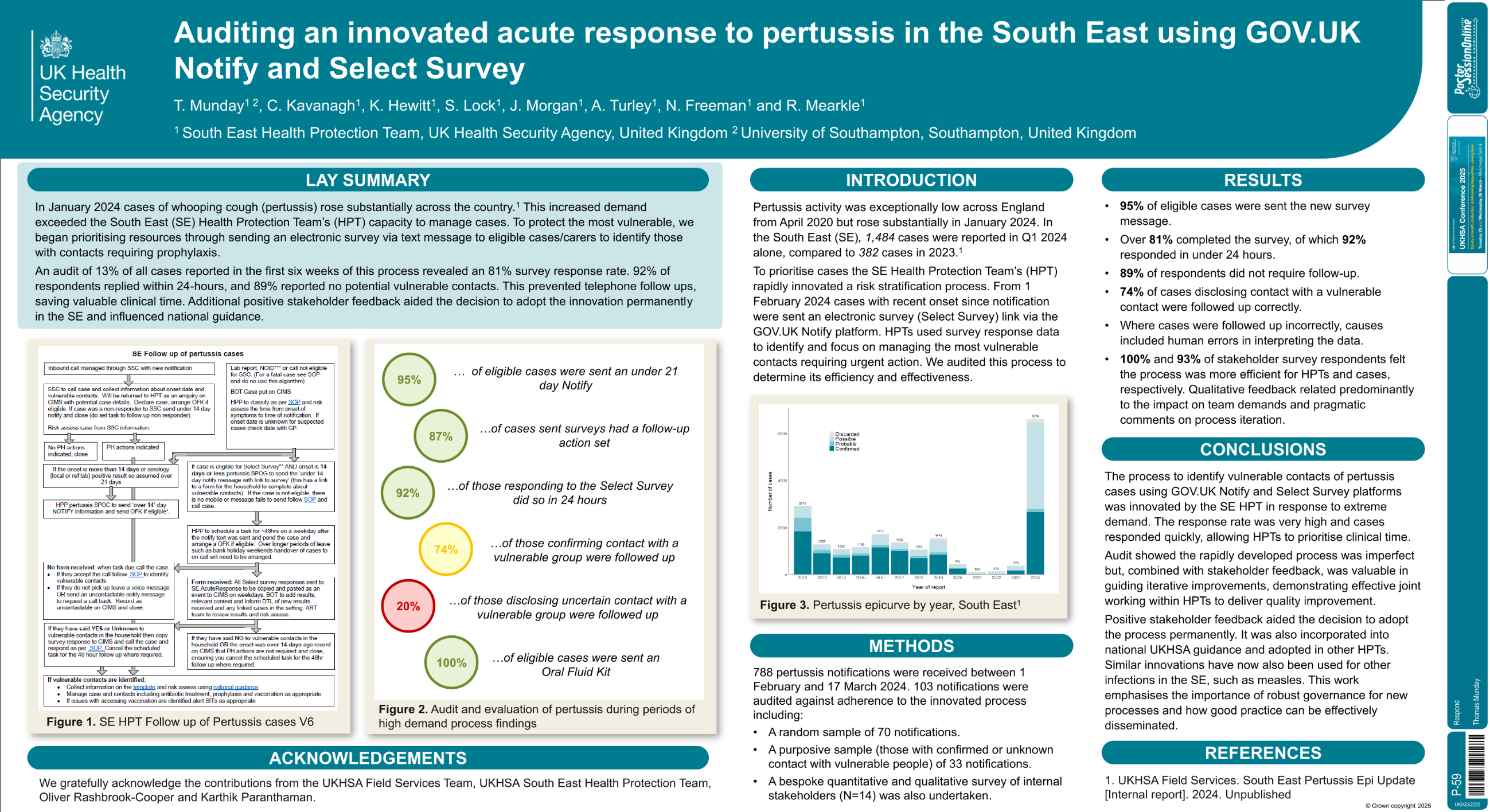
| Auditing an innovated acute response to .. | Thomas Munday .. | .. | Respond.. | - - | |
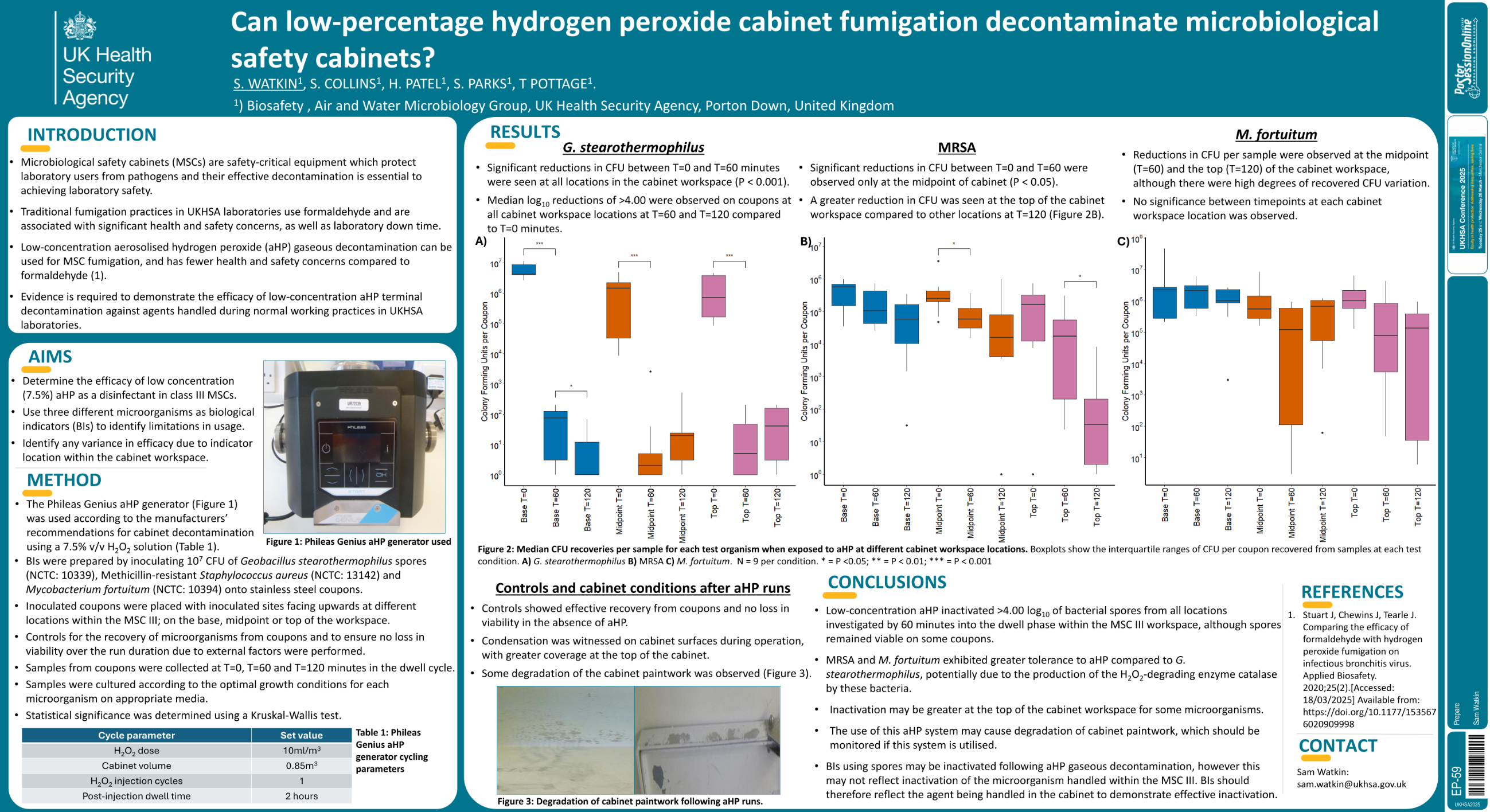
| Can low-percentage hydrogen peroxide cab.. | Sam Watkin .. | Sean Collins, Hineshaben Patel.. | Prepare.. | - - | |
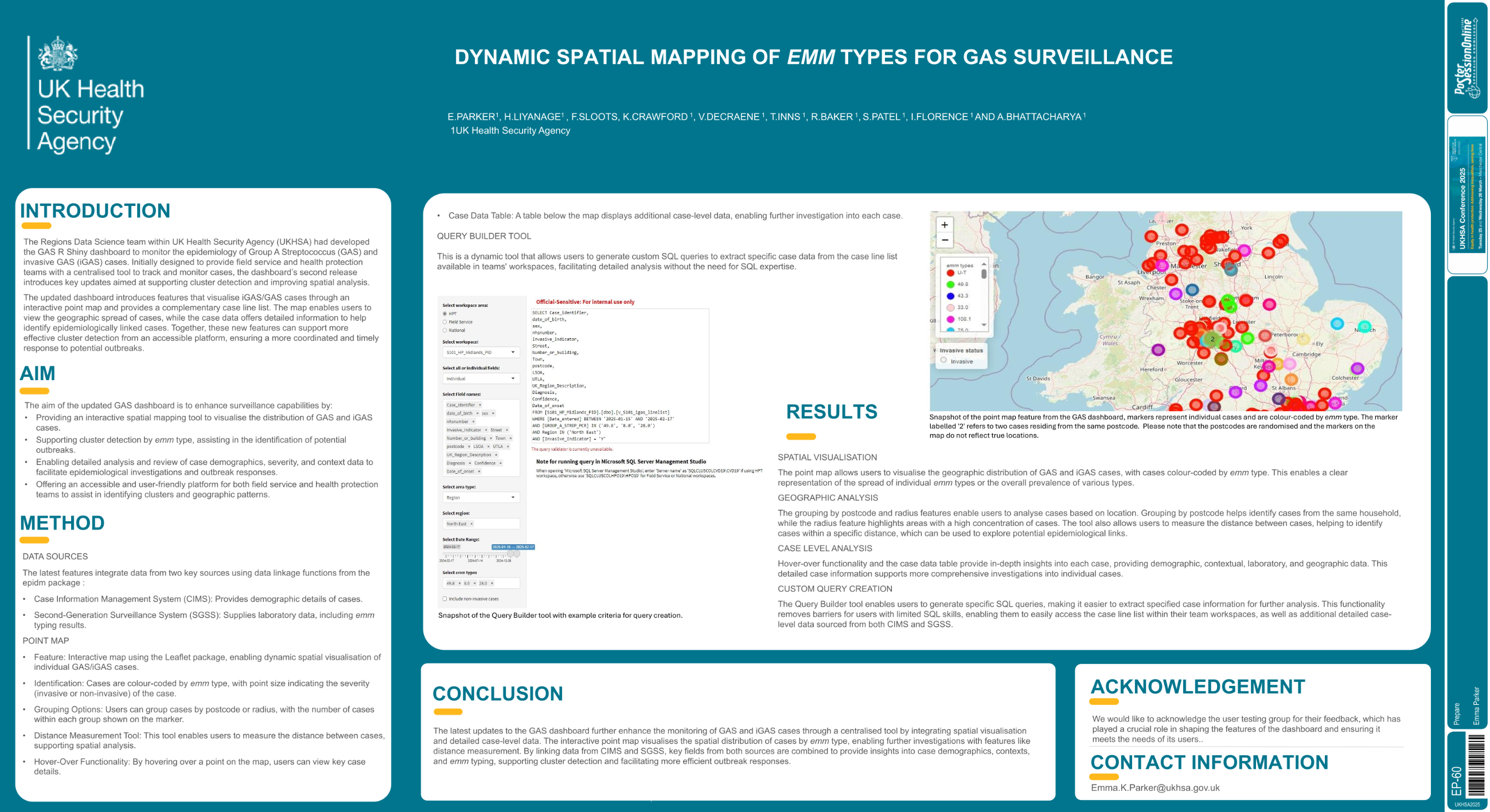
| Enhancing GAS surveillance and emm type .. | Emma Parker .. | .. | Prepare.. | - - | |
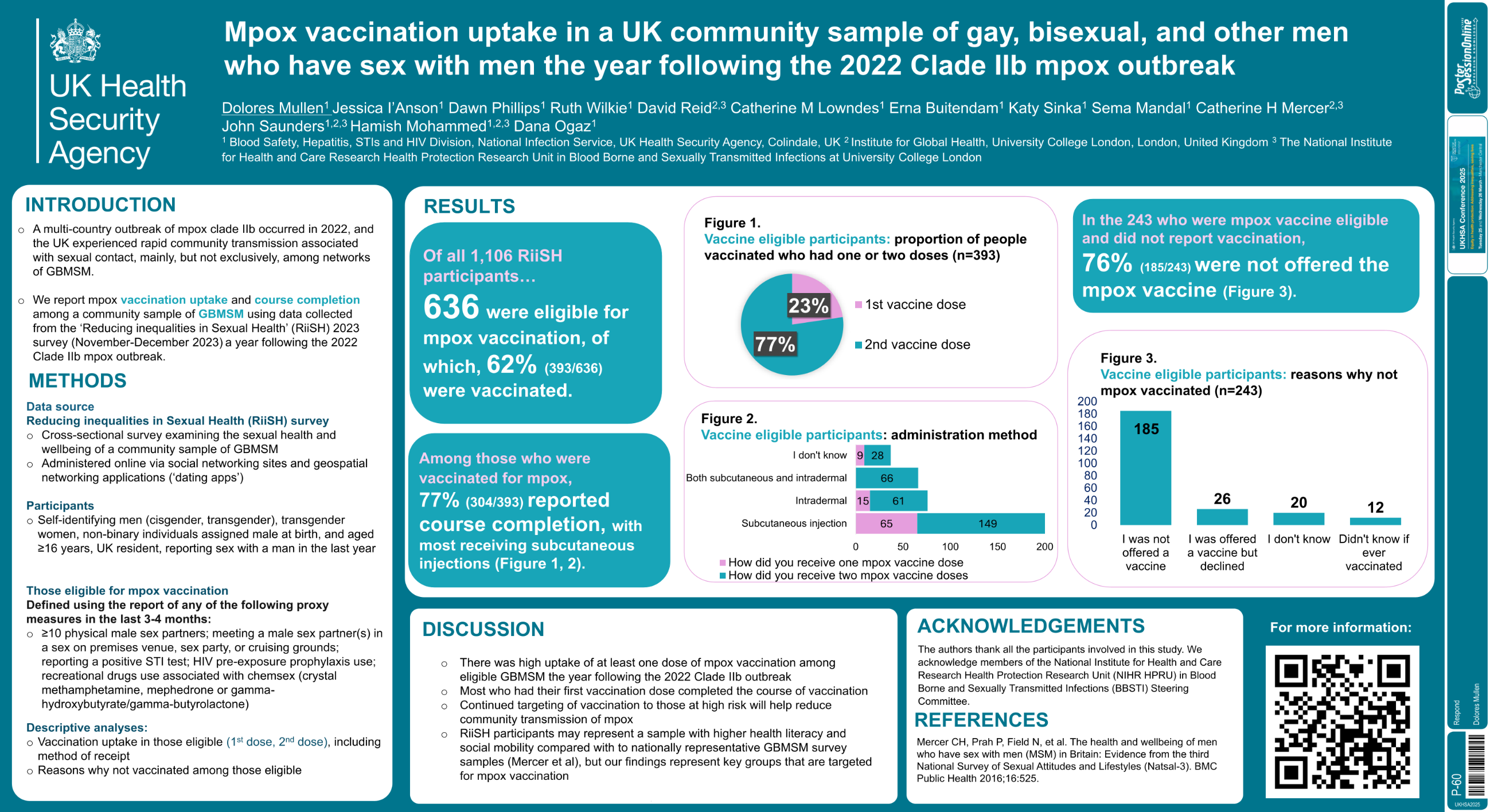
| Mpox vaccination uptake in a community s.. | Dolores Mullen .. | Jessica IAnson, Dawn Phillips,.. | Respond.. | - - | |
| UKHSA data dashboard our approach to pu.. | Jason Deakin .. | .. | Build.. | - - | |
| Preparing for chemical event response: A.. | Mari Langreiter .. | .. | Prepare.. | - - | |
| Investigating the Impact of a-Synuclein .. | William Timbury .. | .. | Prepare.. | - - | |
| From testing to development - Building a.. | Kerry Cella .. | Harry Woolnough, Lauren Dunn, .. | Build.. | - - | |
| In-situ Characterizations of Tyre Wear P.. | Rongyan Fang .. | .. | Build.. | - - | |
| Preparing for Mpox: Diagnostic Assay Eva.. | Rachael Wallis .. | Marilyn Aram, Clara Milroy, Gi.. | Prepare.. | - - | |
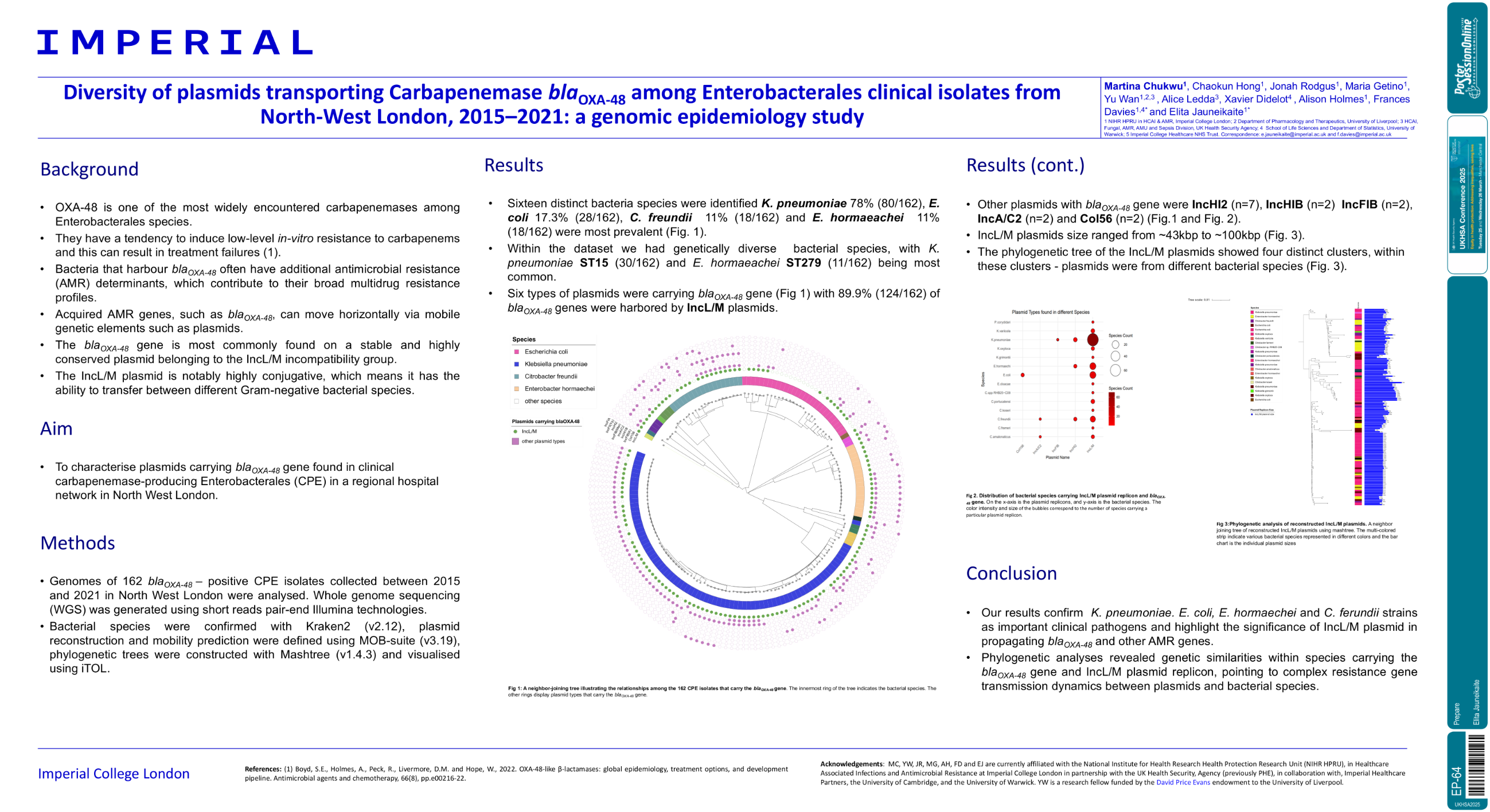
| Diversity of plasmids encoding carbapene.. | Elita Jauneikaite .. | Martina Chukwu, Chaokun Hong, .. | Prepare.. | - - | |
| Building community capacity for vaccine .. | Dawn Holford .. | Emma C. AndersonVirginia C. Go.. | Build.. | - - | |
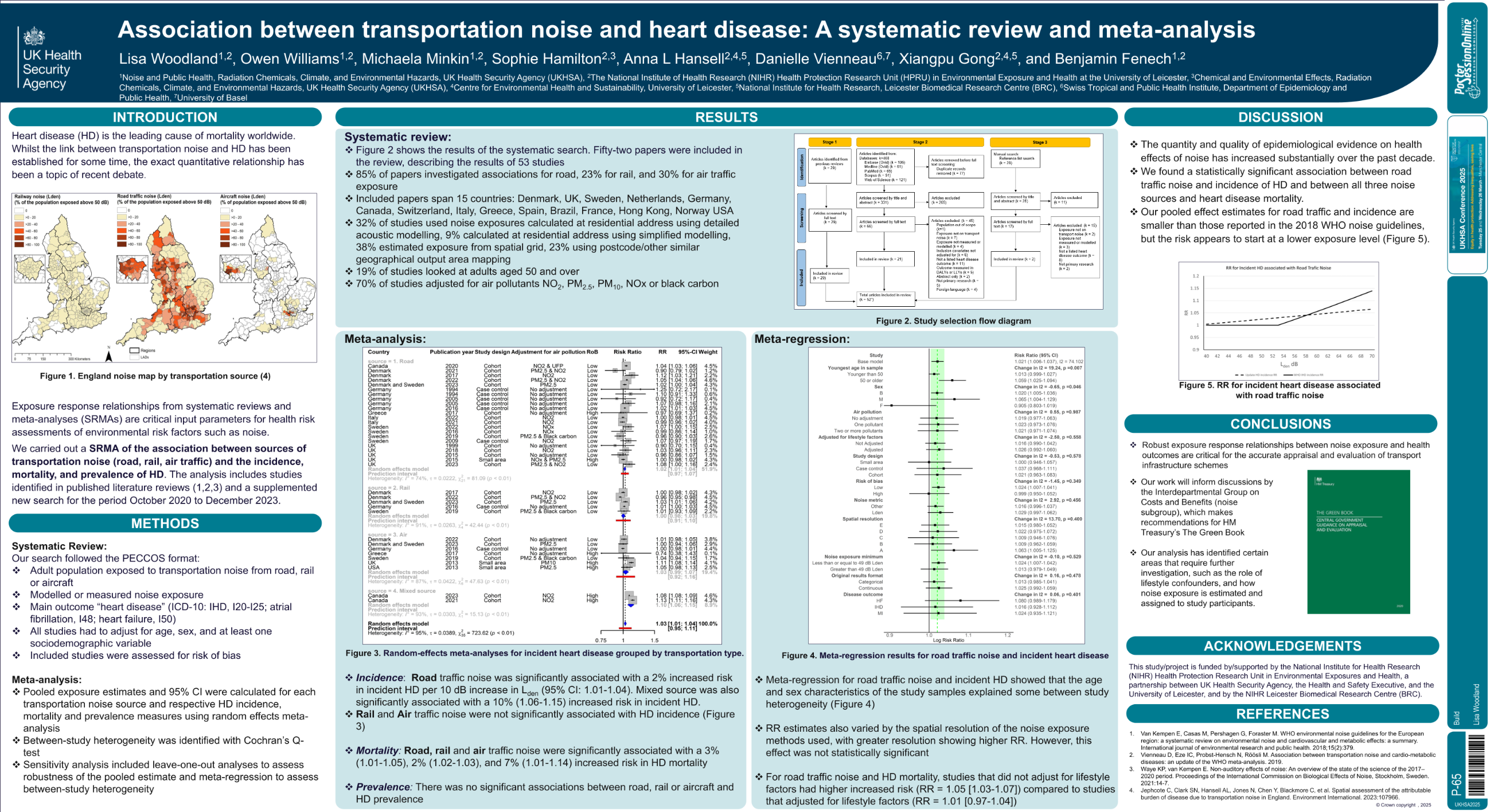
| Association between transportation noise.. | Lisa Woodland .. | Owen Williams, Michaela Minkin.. | Build.. | - - | |
| Challenges in rapid incident research: .. | Clare Foster .. | B. WEIL, W. NUTLAND, A. ATTI, .. | Respond.. | - - | |
| The Role of Community Champions in Suppo.. | Emily Strong .. | Rebecca ClarkeBen BrannanDavid.. | Respond.. | - - | |
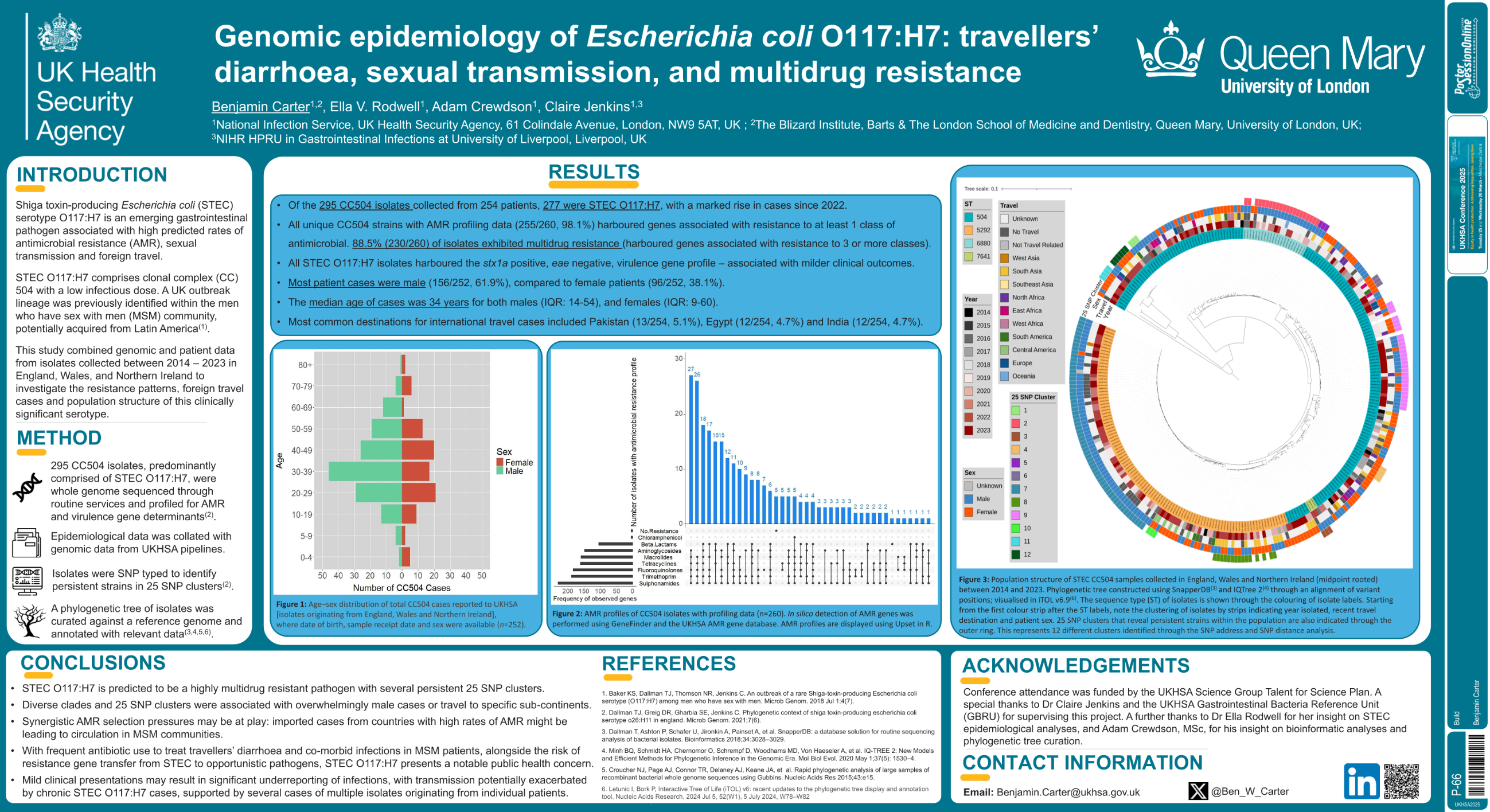
| Genomic epidemiology of Escherichia coli.. | Benjamin Carter .. | Ella V. Rodwell, Adam Crewdson.. | Build.. | - - | |
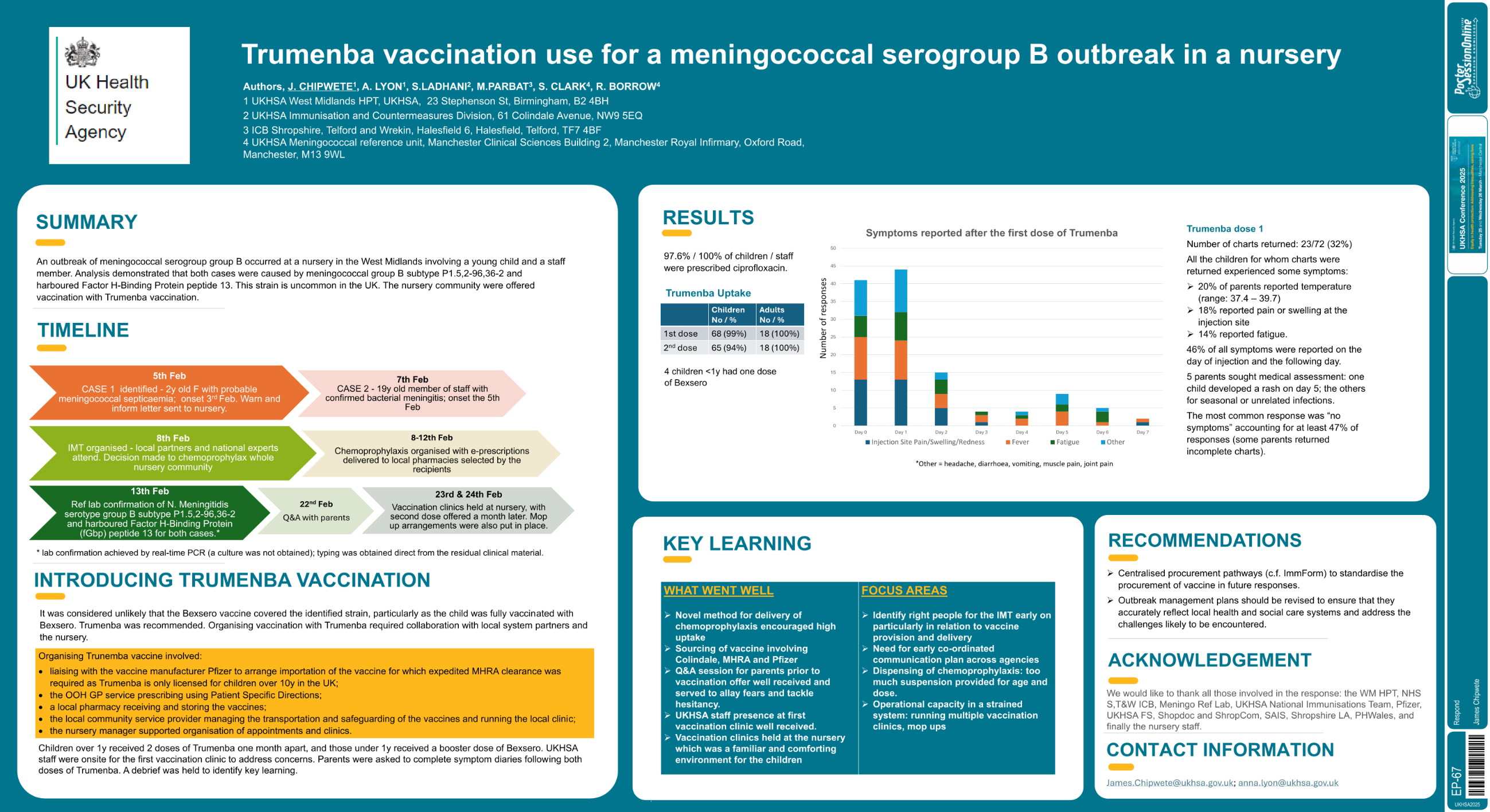
| Trumenba vaccination use for a meningoco.. | James Chipwete .. | Anna Lyon, Shamez Ladhani, Min.. | Respond.. | - - | |
Abstract
Thunderstorm-related asthma in patients sensitised to olea europaea pollen: twenty emergency department visits for asthmatic symptoms in one single day Losappio, Laura1; Heffler, Enrico2; Falco, Antonio1; Contento, Francesco1; Cannito, Cosimo1; Rolla, Giovanni2 1"Dimiccoli" Hospital, Emergency Department, Barletta, Italy; 2University of Torino - AO Mauriziano "Umberto I", Allergy and Clinical Immunology, Torino, Italy
Background: Associations between thunderstorm and asthma morbidity have been reported in several countries. Common to all epidemics of thunderstorm-related asthma is a significant increase in atmospheric allergen load during and immediately after a thunderstorm. Sensitization to Alternaria species or to grass and parietaria pollens has been suggested to play a key role in thunderstorm-related asthma. The only reported event of thunderstorm-related asthma in Mediterranean area was attributed to sensitization to parietaria pollen.
Method: here we describe a series of 20 patients who presented to Emergency Department in Barletta (94,000 inhabitants), Puglia (Italy) for sudden and severe asthmatic symptoms between May 27th and 28th 2010 (from15:36 to 5:02), immediately after a violent thunderstorm which occurred following a very hot morning (mean temperature: 29°C). All the patients have been subsequently visited by an allergist and underwent allergological work-up which included skin prick tests and a careful clinical history. Local pollen counts were available.
Result: Between May 10th and June 10th 2010, 86 Emergency Department asthma visits were recorded, 20 of them during the study day. Patients' mean age was 44.25 +/- 18.5 years (range: 9-81), 8/20 females, 2 smokers, 16 with a previous history of known respiratory allergy. Only two patients regularly took anti-asthma drugs. All 20 patients were sensitized to Olea europaea pollen, 7 of whom were monosensitized. Ten patients were sensitized to grass, 7 to parietaria, 5 to compositae, 5 to cypress, 5 to house dust mites, 3 to dog and 1 to cat danders. No patient was sensitized to Alternaria. Mean pollen count was 17 granules/m3 for Olea europaea, 6 granules/m3 for grass pollen.
Conclusion: This is, in our knowledge, the second epidemic of thunderstorm related asthma described in Mediterranean area and the first one in which sensitization to Olea europaea played a key-role. In conclusion, our report indicates that thunderstorm asthma may involve different allergens (not only fungal spores and grass or parietaria pollen) in different geographic areas, depending on the seasonality of thunderstorms and allergenic pollen.