
ERC Congress - Resuscitation 2024
31 October - 2 November, Athens, Greece
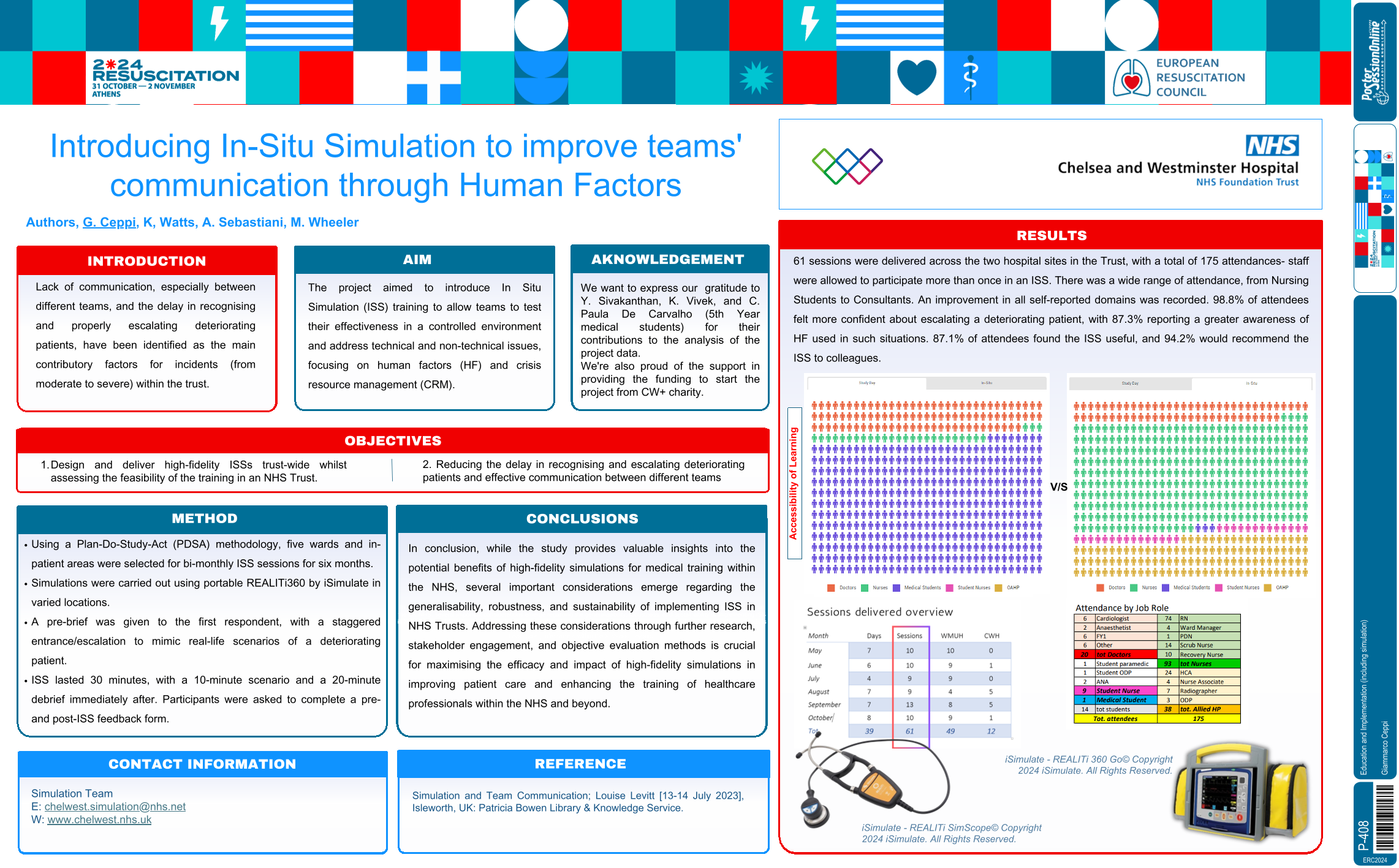









| Introducing In Situ Simulation to improv.. | Giammarco Ceppi .. | Aurora Sebastiani, Mark Wheele.. | Education and Implementation (including .. | - - | |
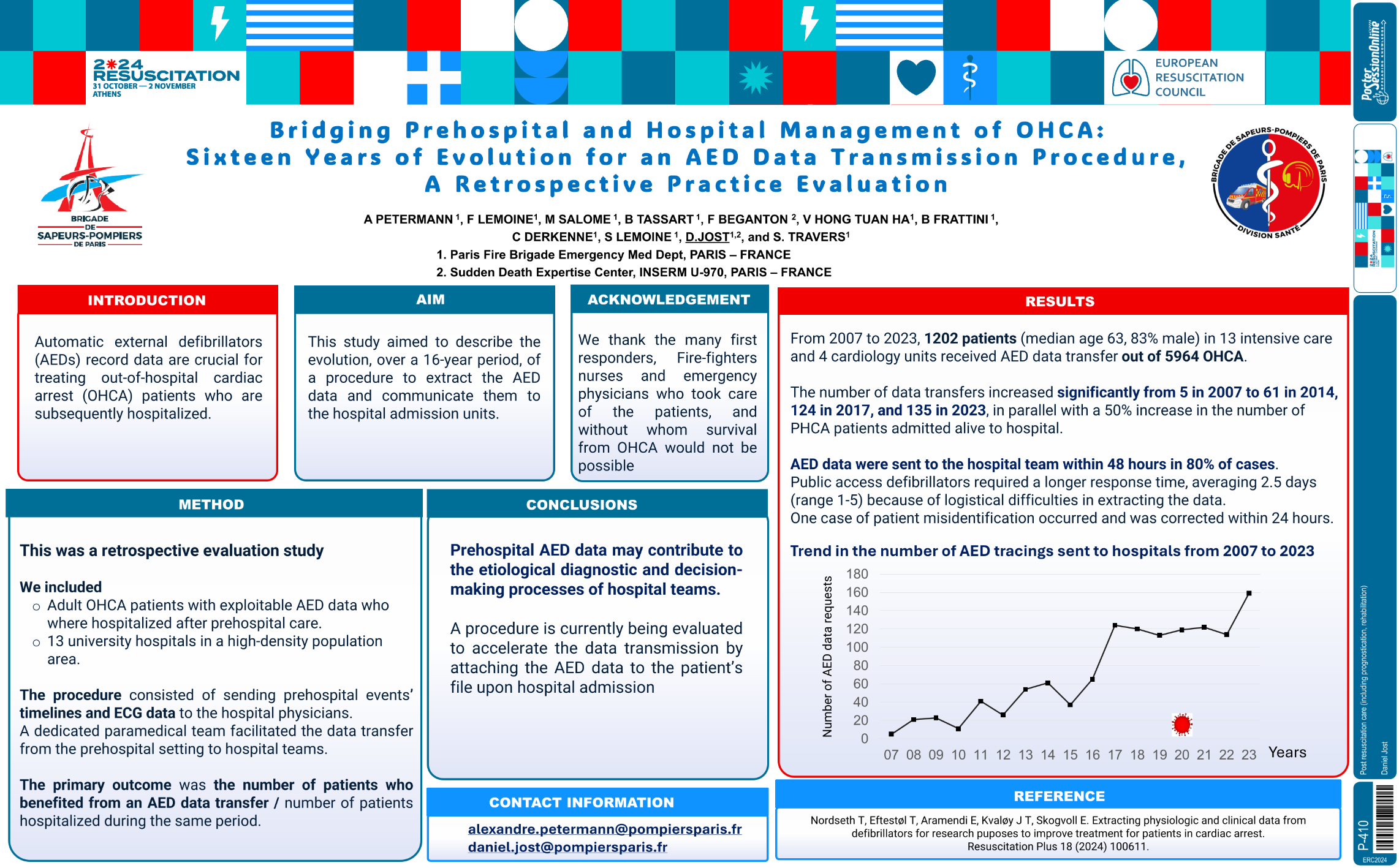
| Bridging Prehospital and Hospital Manage.. | Daniel Jost .. | Alexandre Petermann, Frédéric .. | Post resuscitation care (including progn.. | - - | |
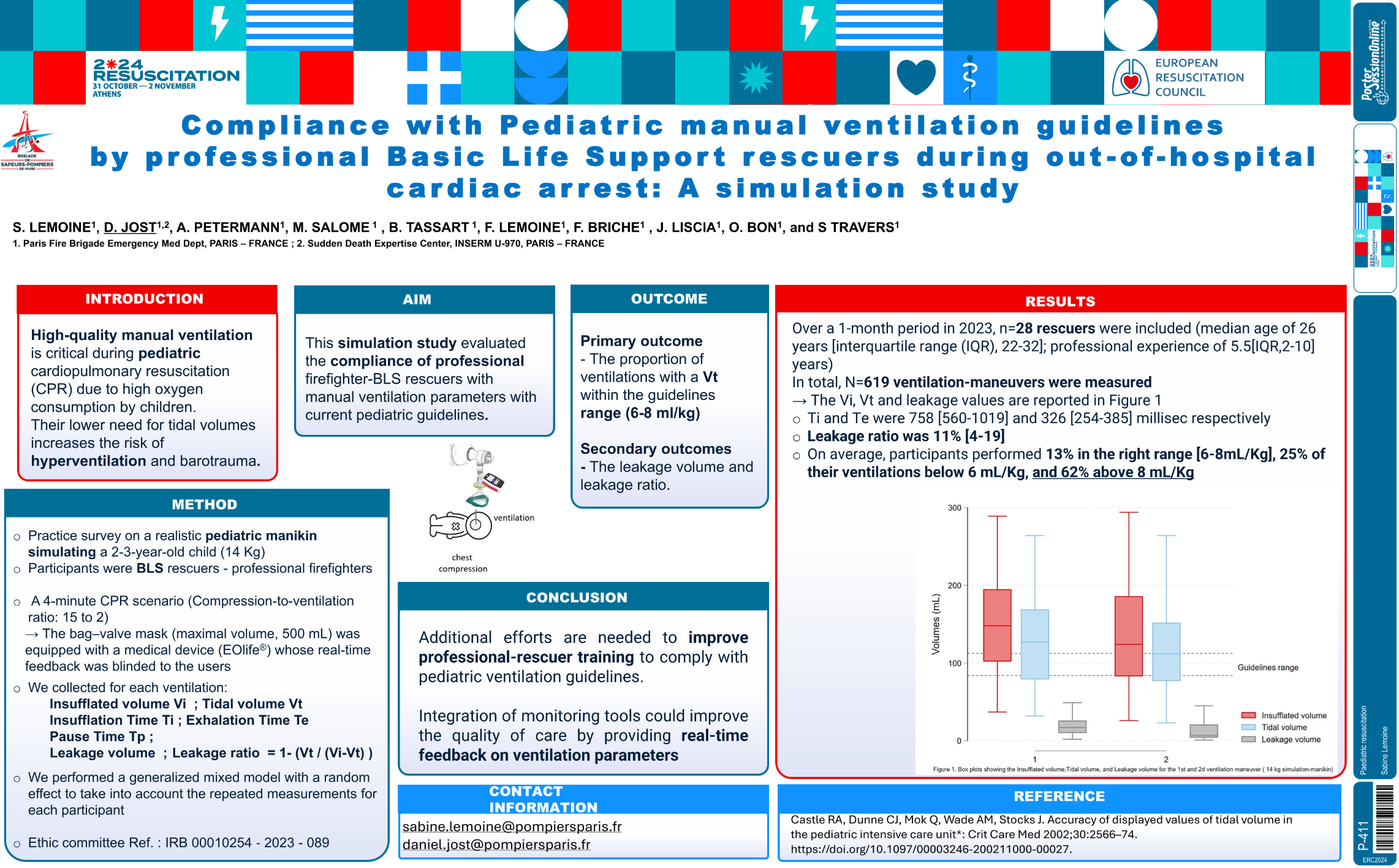
| compliance with pediatric manual ventila.. | Sabine Lemoine .. | .. | Paediatric resuscitation.. | - - | |
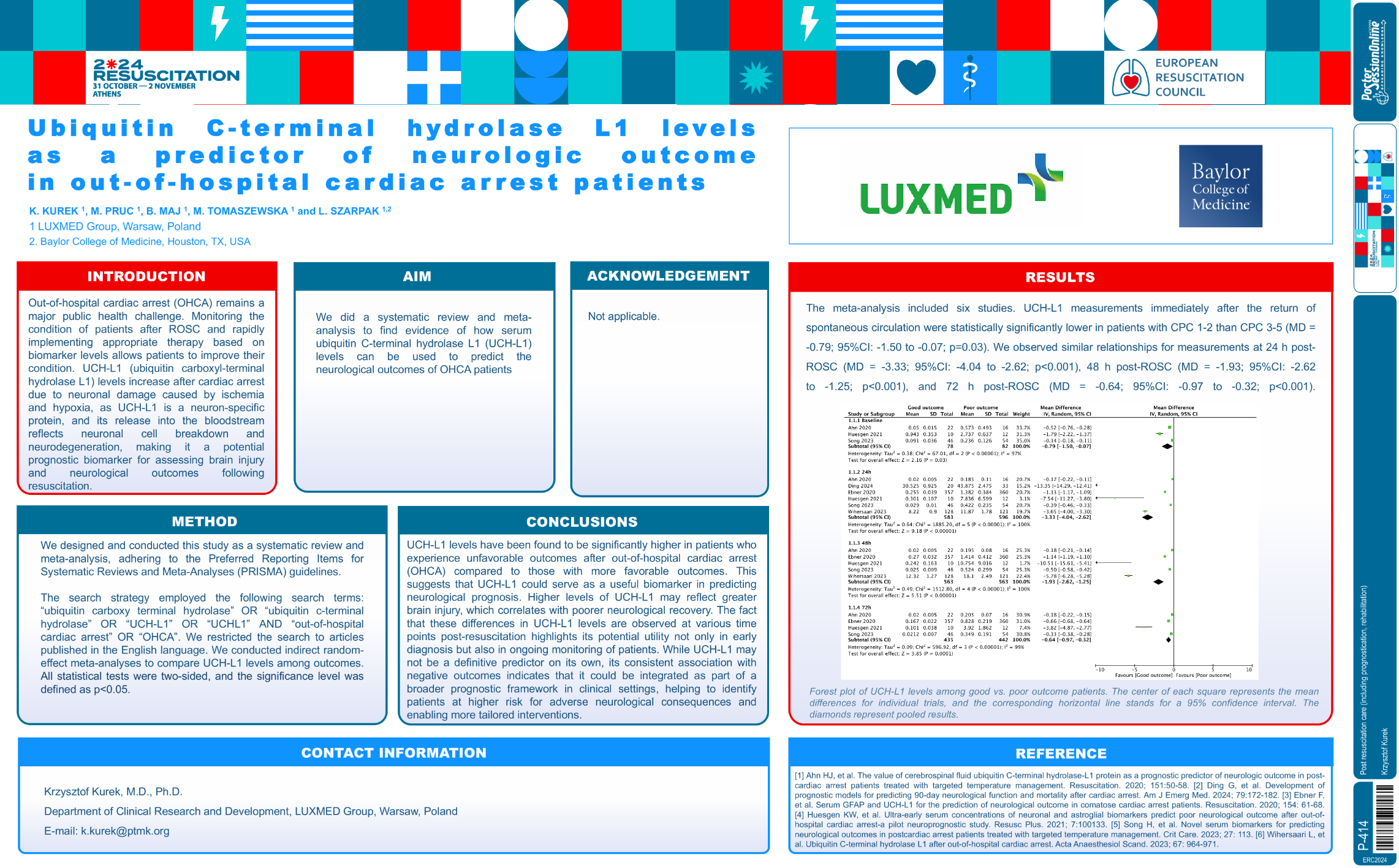
| Ubiquitin C-terminal hydrolase L1 levels.. | Krzysztof Kurek .. | Michal PRUC, Bartosz MAJ, Moni.. | Post resuscitation care (including progn.. | - - | |
| The use of mild therapeutic hypothermia .. | Maximilian Ehrenbrandtner .. | Stephan Innerkofler, Sebastian.. | Post resuscitation care (including progn.. | - - | |
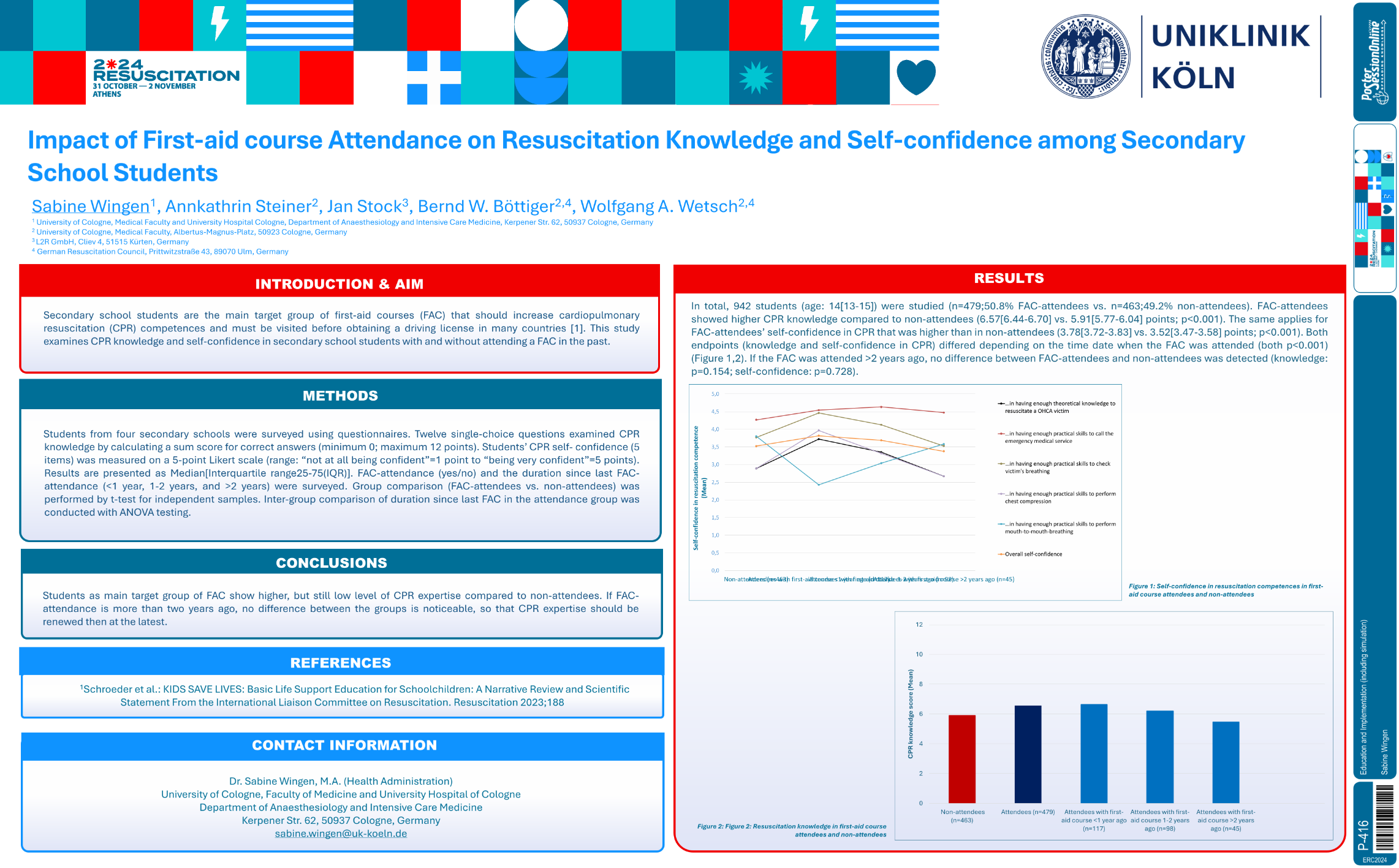
| Impact of First-aid course Attendance on.. | Sabine Wingen .. | .. | Education and Implementation (including .. | - - | |
| Analysis of variables associated with Te.. | SERGIO CAZORLA-CALDERON .. | .. | Resuscitation Systems (including dispatc.. | - - | |
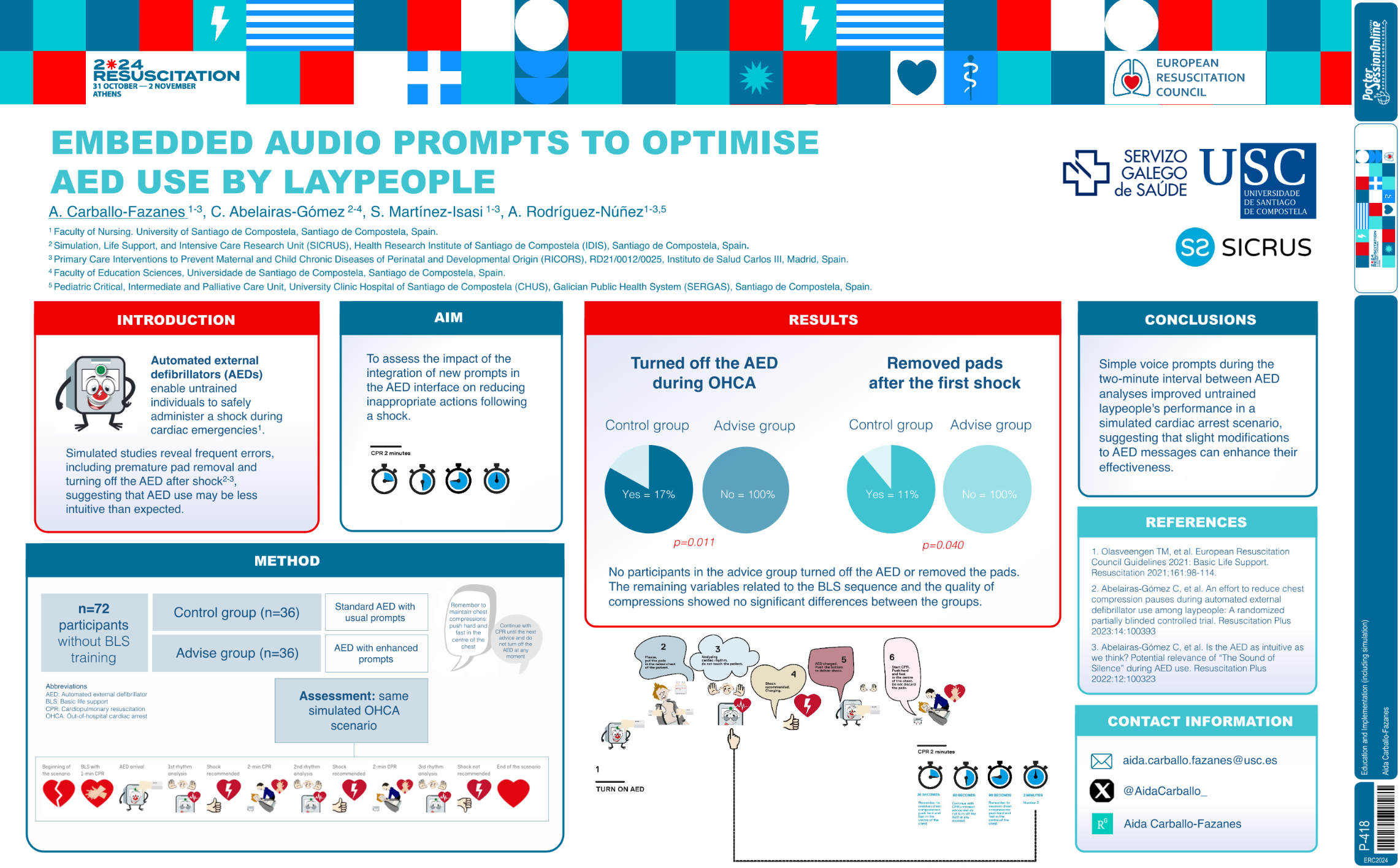
| Embedded audio prompts to optimise AED u.. | Aida Carballo-Fazanes .. | Cristian Abelairas-GómezSantia.. | Education and Implementation (including .. | - - | |
| Use of echocardiography in the identific.. | Montserrat Tió .. | Gemma López, Silvia Moreno, Ja.. | Advanced Life Support (including manual .. | - - | |
| Feasibility of real-time compression fre.. | Wolfgang A. Wetsch .. | .. | New technology.. | - - | |
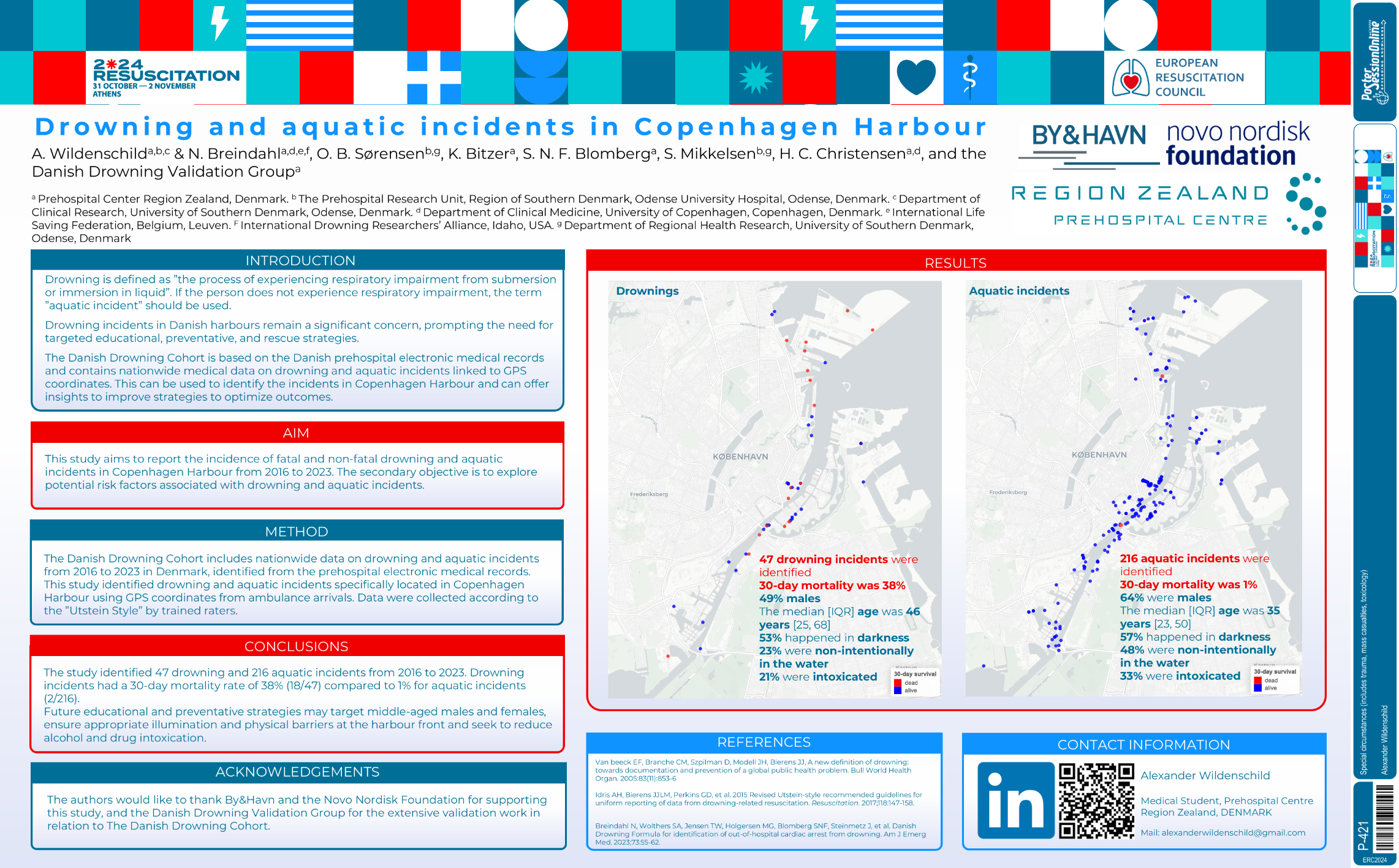
| Drowning and aquatic incidents in Copenh.. | Alexander Wildenschild .. | N. Breindahl, O. B. Srensen, K.. | Special circumstances (includes trauma, .. | - - | |
| Senior Nursing Students Experiences of S.. | selin keskin kiziltepe .. | Atiye Erbas, Filiz Erturk .. | Education and Implementation (including .. | - - | |
| Fatigue three months after out-of-hospit.. | Vicky L Joshi .. | .. | Post resuscitation care (including progn.. | - - | |
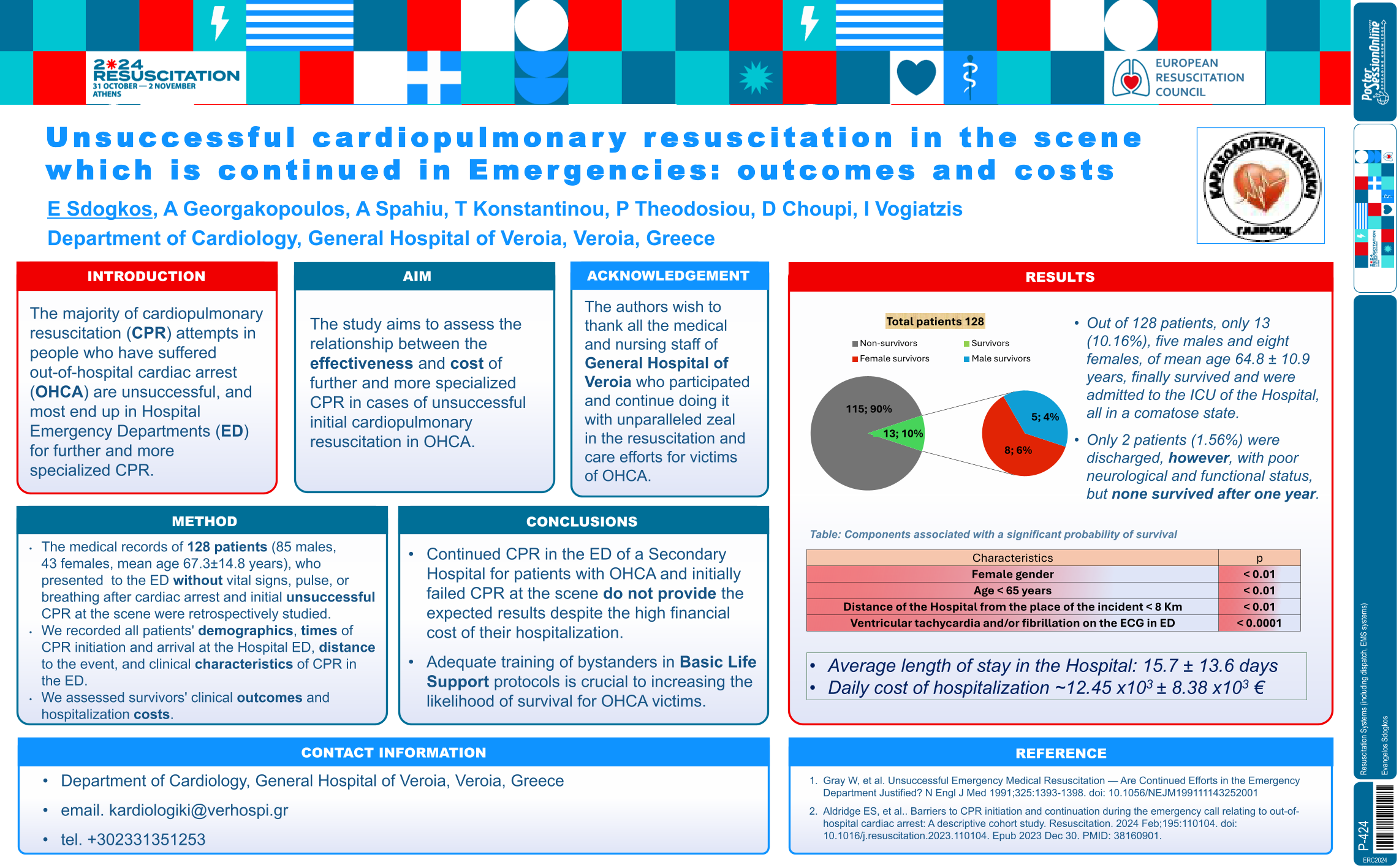
| Unsuccessful cardiopulmonary resuscitati.. | Evangelos Sdogkos .. | Evangelos Sdogkos, Angelos Geo.. | Resuscitation Systems (including dispatc.. | - - | |
| Carotid artery blood flow during CPR and.. | Barbara Fyntanidou .. | .. | Advanced Life Support (including manual .. | - - | |
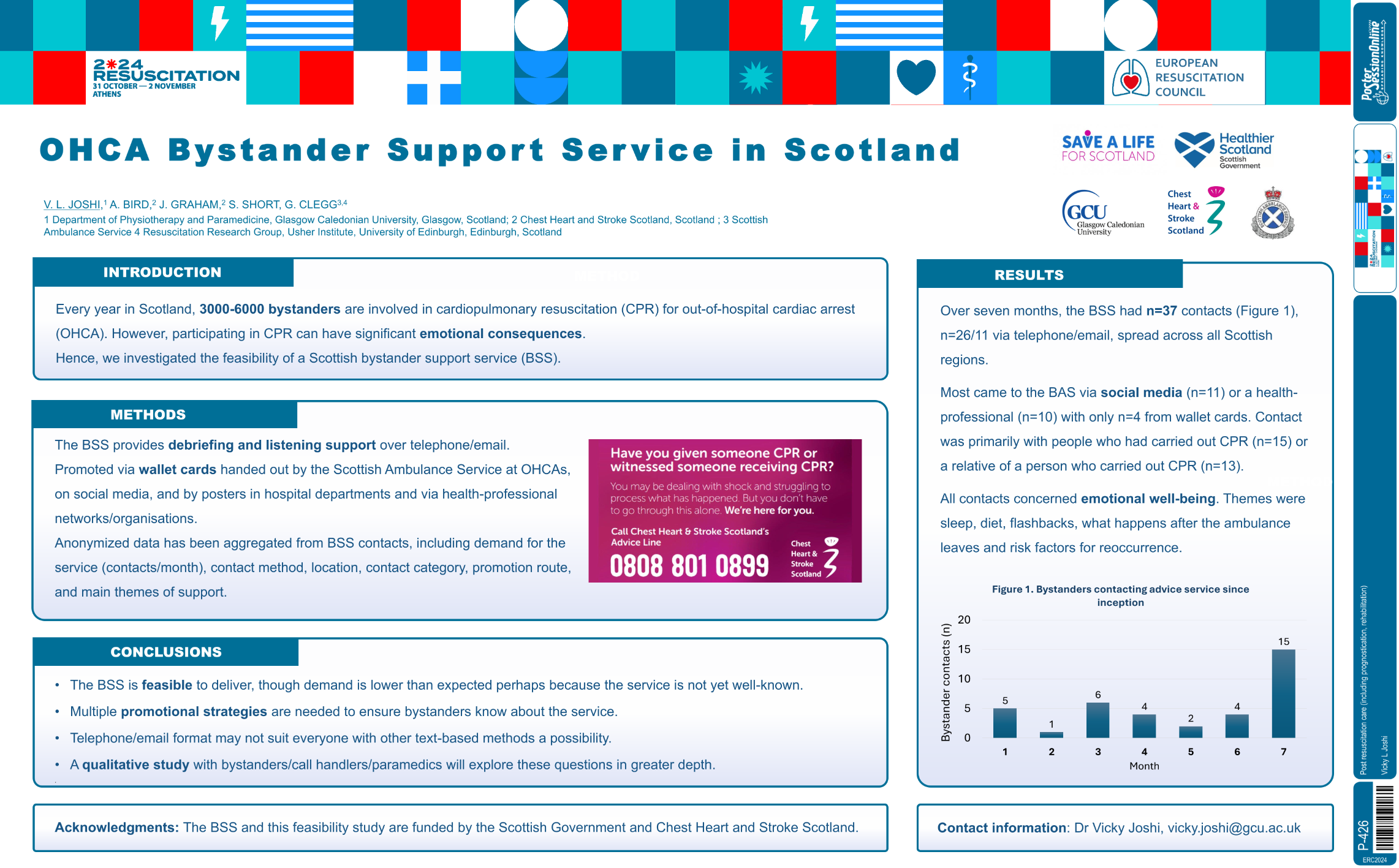
| Feasibility of a new out-of-hospital car.. | Vicky L Joshi .. | .. | Post resuscitation care (including progn.. | - - | |
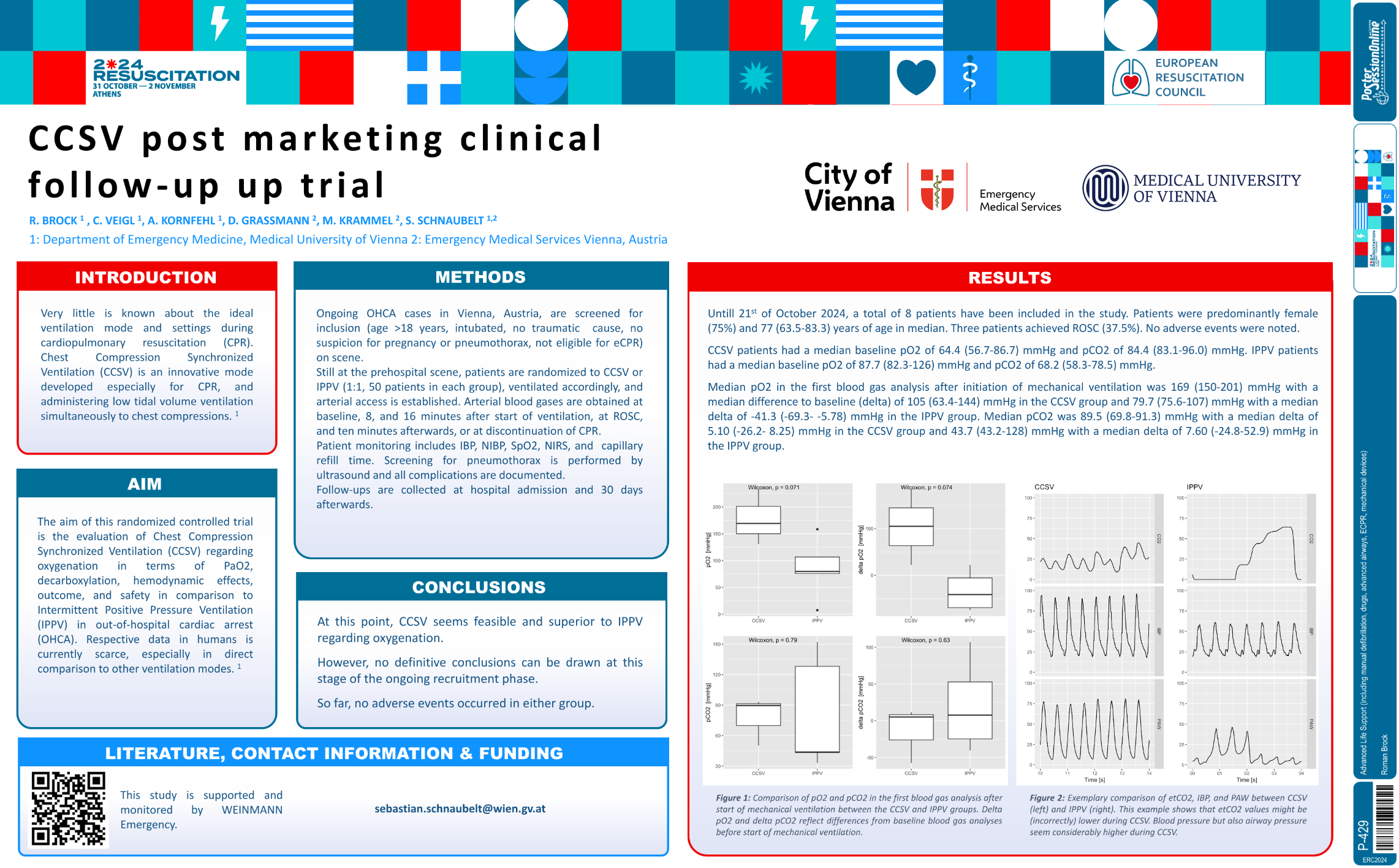
| CCSV post market clinical follow-up tria.. | Roman Brock .. | C Veigl, A Kornfehl, D Grassma.. | Advanced Life Support (including manual .. | - - | |
| POOR QUALITY OF LIFE PREDICTS CARDIAC EV.. | Naomi Kondo Nakagawa .. | G.N. ANDRADE, J.A. NASCIMENTO,.. | Epidemiology and outcomes.. | - - | |
| ? low cost experimental model of cardiac.. | Barbara Fyntanidou .. | .. | New technology.. | - - | |
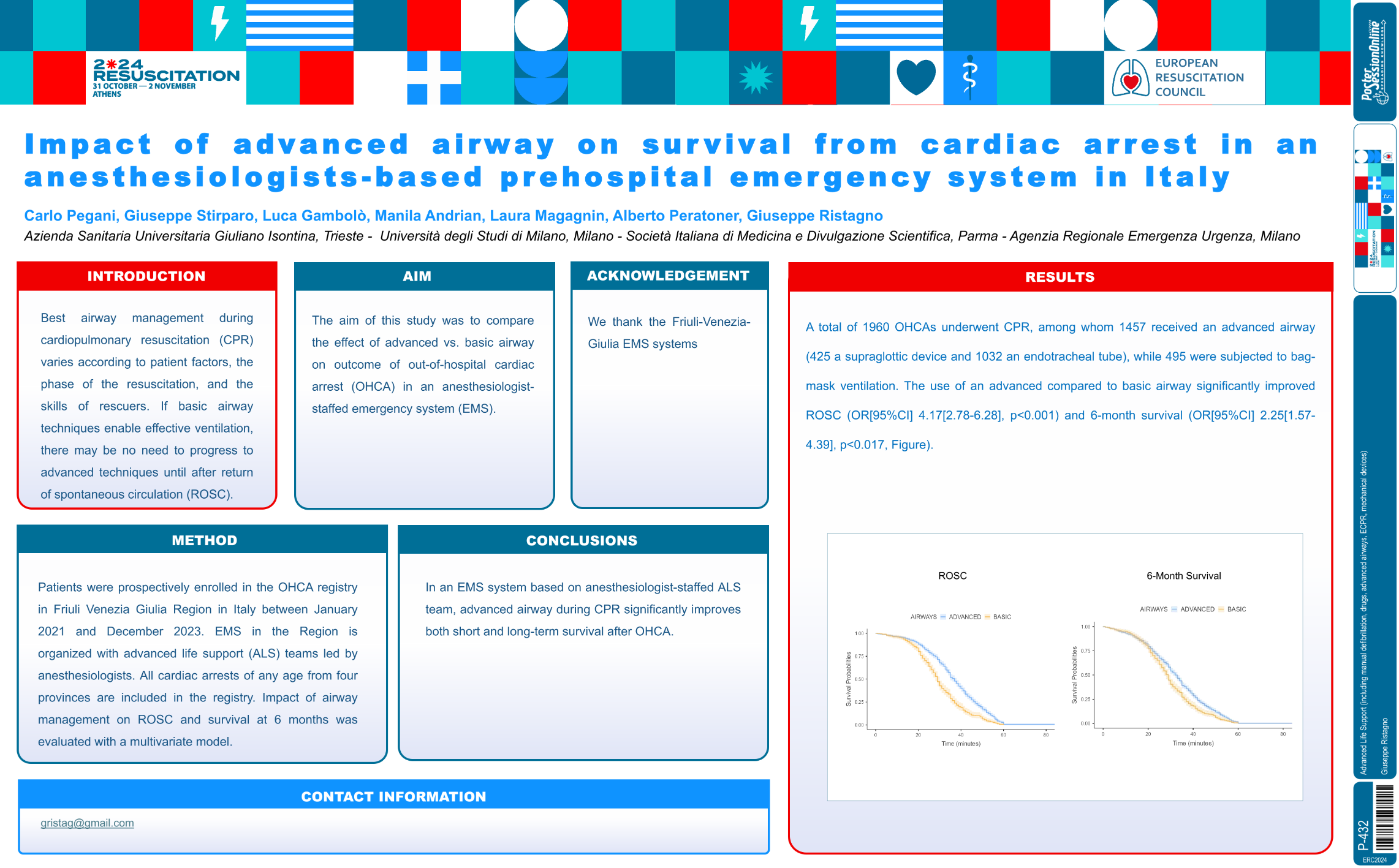
| Impact of advanced airway on survival fr.. | Giuseppe Ristagno .. | .. | Advanced Life Support (including manual .. | - - | |
Abstract
Thunderstorm-related asthma in patients sensitised to olea europaea pollen: twenty emergency department visits for asthmatic symptoms in one single day Losappio, Laura1; Heffler, Enrico2; Falco, Antonio1; Contento, Francesco1; Cannito, Cosimo1; Rolla, Giovanni2 1"Dimiccoli" Hospital, Emergency Department, Barletta, Italy; 2University of Torino - AO Mauriziano "Umberto I", Allergy and Clinical Immunology, Torino, Italy
Background: Associations between thunderstorm and asthma morbidity have been reported in several countries. Common to all epidemics of thunderstorm-related asthma is a significant increase in atmospheric allergen load during and immediately after a thunderstorm. Sensitization to Alternaria species or to grass and parietaria pollens has been suggested to play a key role in thunderstorm-related asthma. The only reported event of thunderstorm-related asthma in Mediterranean area was attributed to sensitization to parietaria pollen.
Method: here we describe a series of 20 patients who presented to Emergency Department in Barletta (94,000 inhabitants), Puglia (Italy) for sudden and severe asthmatic symptoms between May 27th and 28th 2010 (from15:36 to 5:02), immediately after a violent thunderstorm which occurred following a very hot morning (mean temperature: 29°C). All the patients have been subsequently visited by an allergist and underwent allergological work-up which included skin prick tests and a careful clinical history. Local pollen counts were available.
Result: Between May 10th and June 10th 2010, 86 Emergency Department asthma visits were recorded, 20 of them during the study day. Patients' mean age was 44.25 +/- 18.5 years (range: 9-81), 8/20 females, 2 smokers, 16 with a previous history of known respiratory allergy. Only two patients regularly took anti-asthma drugs. All 20 patients were sensitized to Olea europaea pollen, 7 of whom were monosensitized. Ten patients were sensitized to grass, 7 to parietaria, 5 to compositae, 5 to cypress, 5 to house dust mites, 3 to dog and 1 to cat danders. No patient was sensitized to Alternaria. Mean pollen count was 17 granules/m3 for Olea europaea, 6 granules/m3 for grass pollen.
Conclusion: This is, in our knowledge, the second epidemic of thunderstorm related asthma described in Mediterranean area and the first one in which sensitization to Olea europaea played a key-role. In conclusion, our report indicates that thunderstorm asthma may involve different allergens (not only fungal spores and grass or parietaria pollen) in different geographic areas, depending on the seasonality of thunderstorms and allergenic pollen.