





| A Multicenter, Open-Label, Phase 3, Randomized Controlled Trial of Duvelisib Versus Investigator´s C.. | Kate Cwynarski | 625. T Cell, NK Cell, or NK/T Cell Lymphomas: Clinical and Epidemiolog.. | |
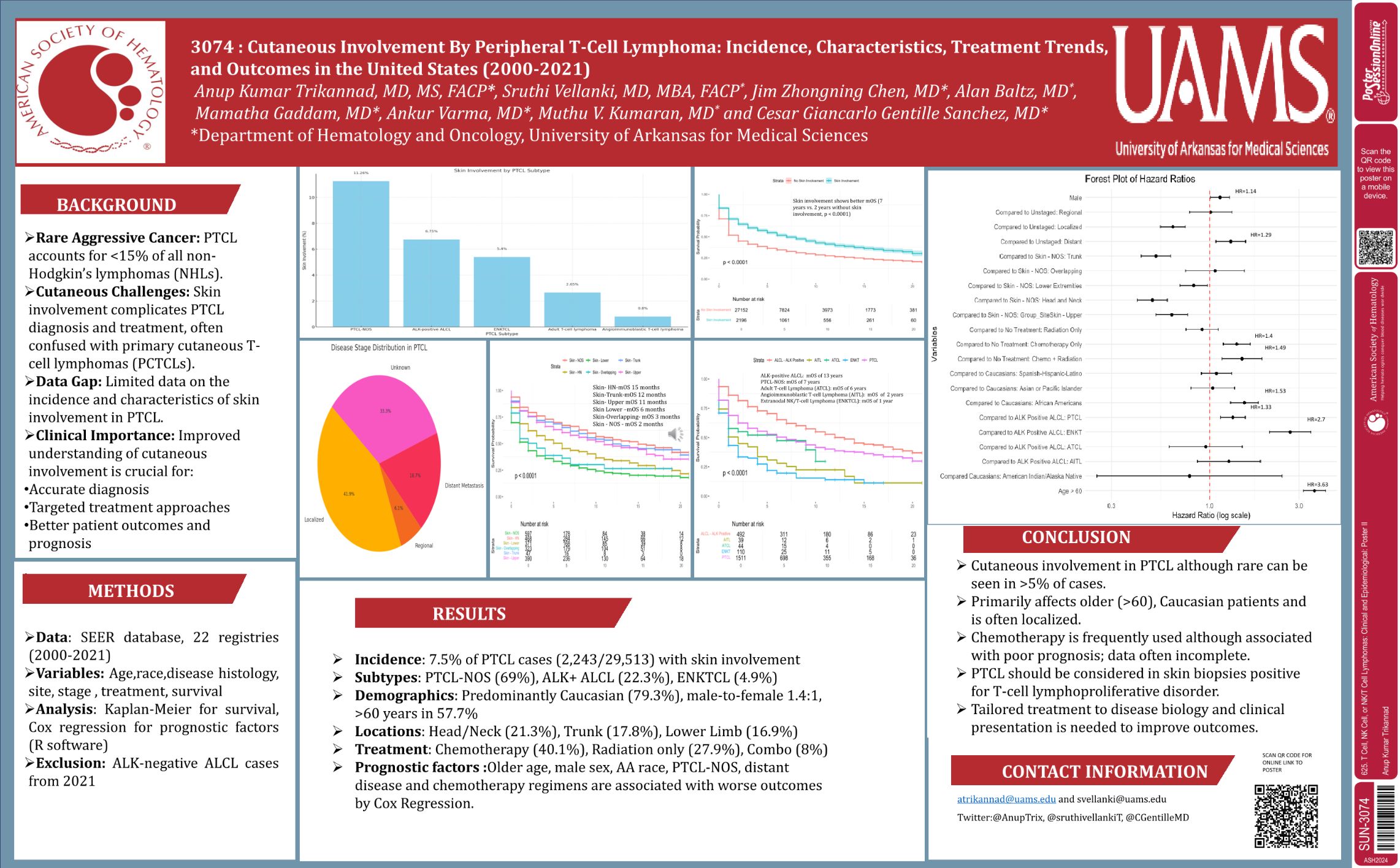
| Cutaneous Involvement By Peripheral T-Cell Lymphoma: Incidence, Characteristics, Treatment Trends, a.. | Anup Kumar Trikannad | 625. T Cell, NK Cell, or NK/T Cell Lymphomas: Clinical and Epidemiolog.. | |
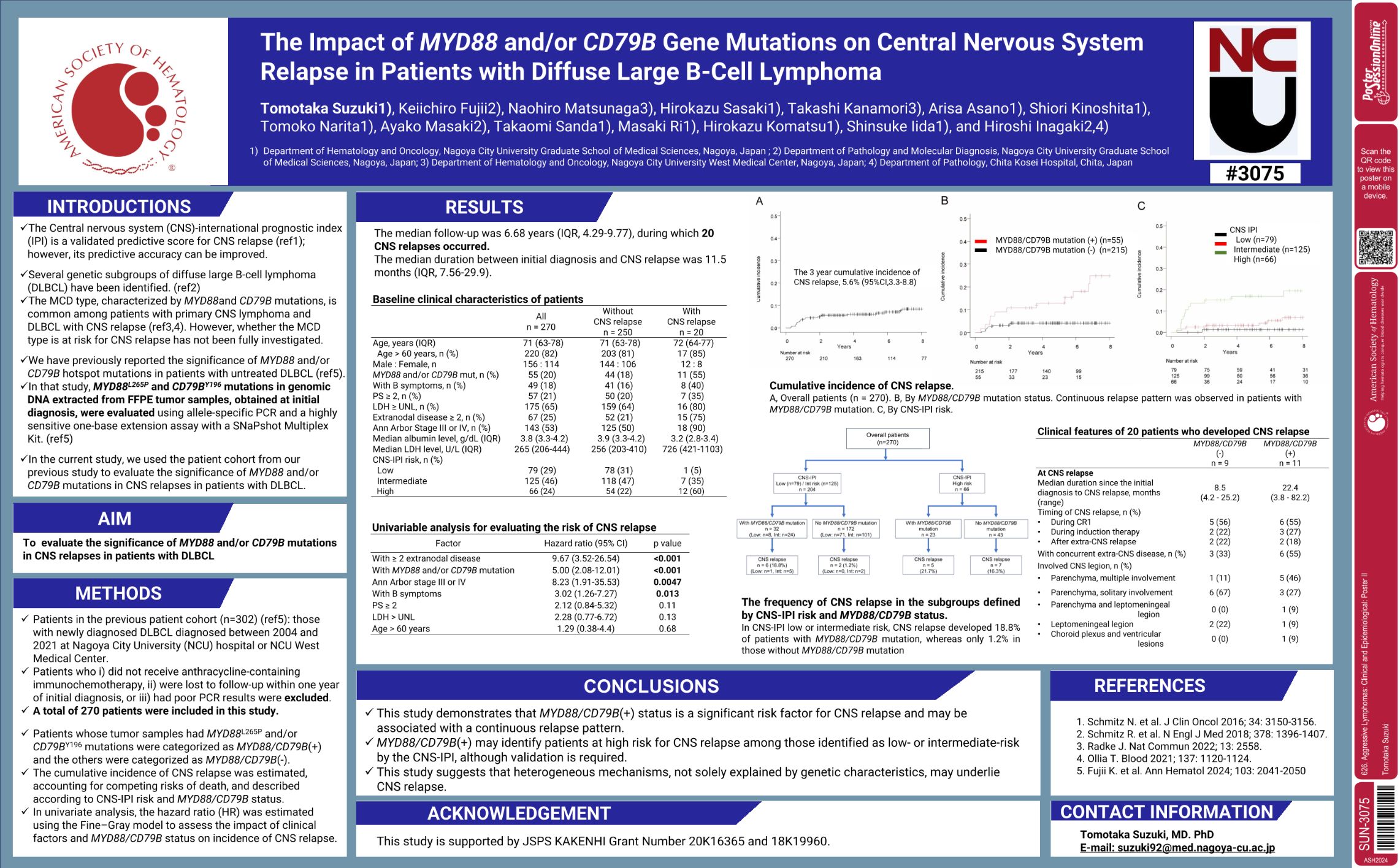
| The Impact of MYD88 and/or CD79B Gene Mutations on Central Nervous System Relapse in Patients with D.. | Tomotaka Suzuki | 626. Aggressive Lymphomas: Clinical and Epidemiological: Poster II | |
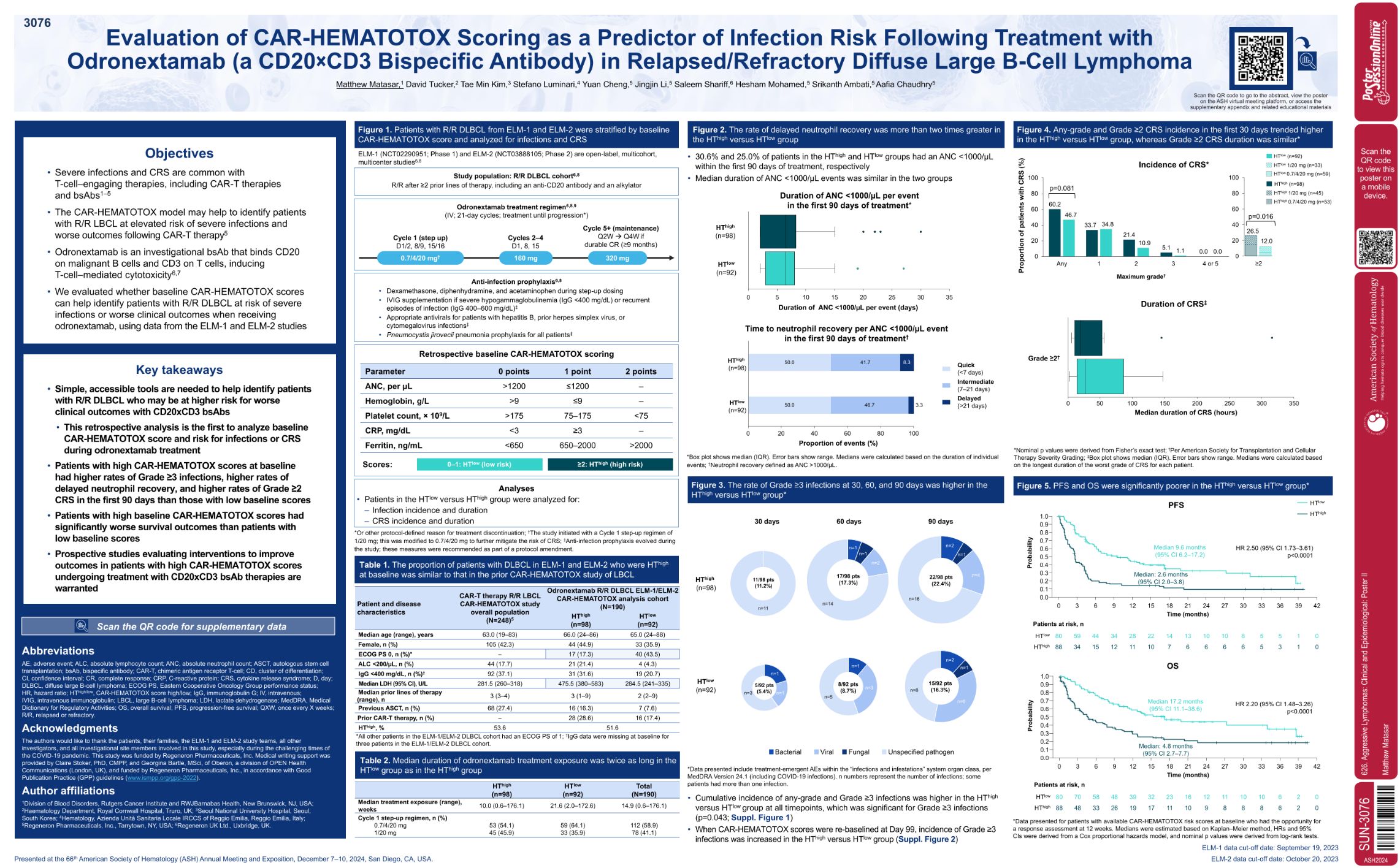
| Evaluation of CAR-Hematotox Scoring As a Predictor of Infection Risk Following Treatment with Odrone.. | Matthew Matasar | 626. Aggressive Lymphomas: Clinical and Epidemiological: Poster II | |
| Diagnostic Utility of the 18f-FDG PET/CT Scan in Solid Organ Transplant Patients with EBV Reactivati.. | Hua-Jay J Cherng | 626. Aggressive Lymphomas: Clinical and Epidemiological: Poster II | |
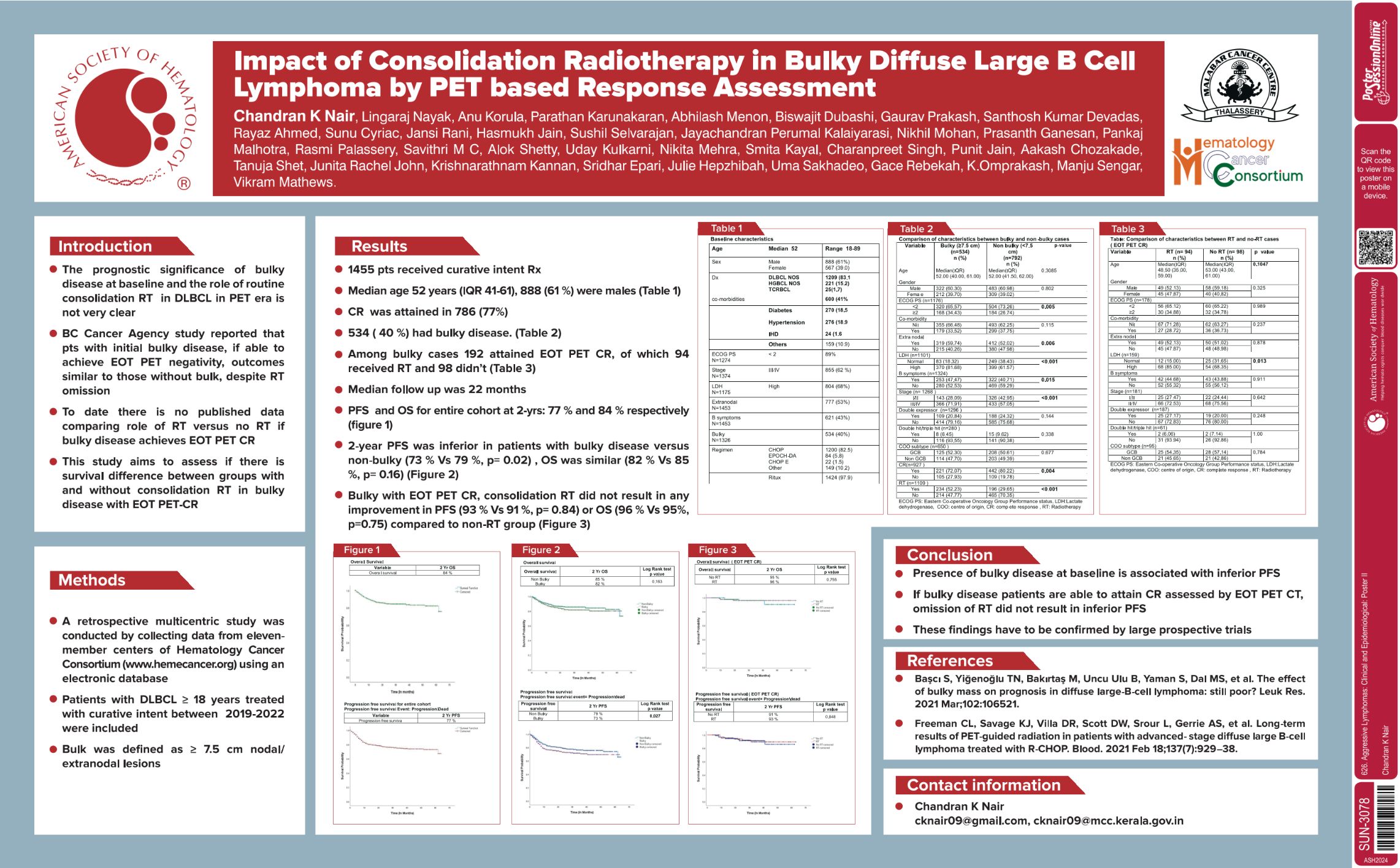
| Impact of Consolidation Radiotherapy in Bulky Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma By PET Based Response As.. | Chandran K Nair | 626. Aggressive Lymphomas: Clinical and Epidemiological: Poster II | |
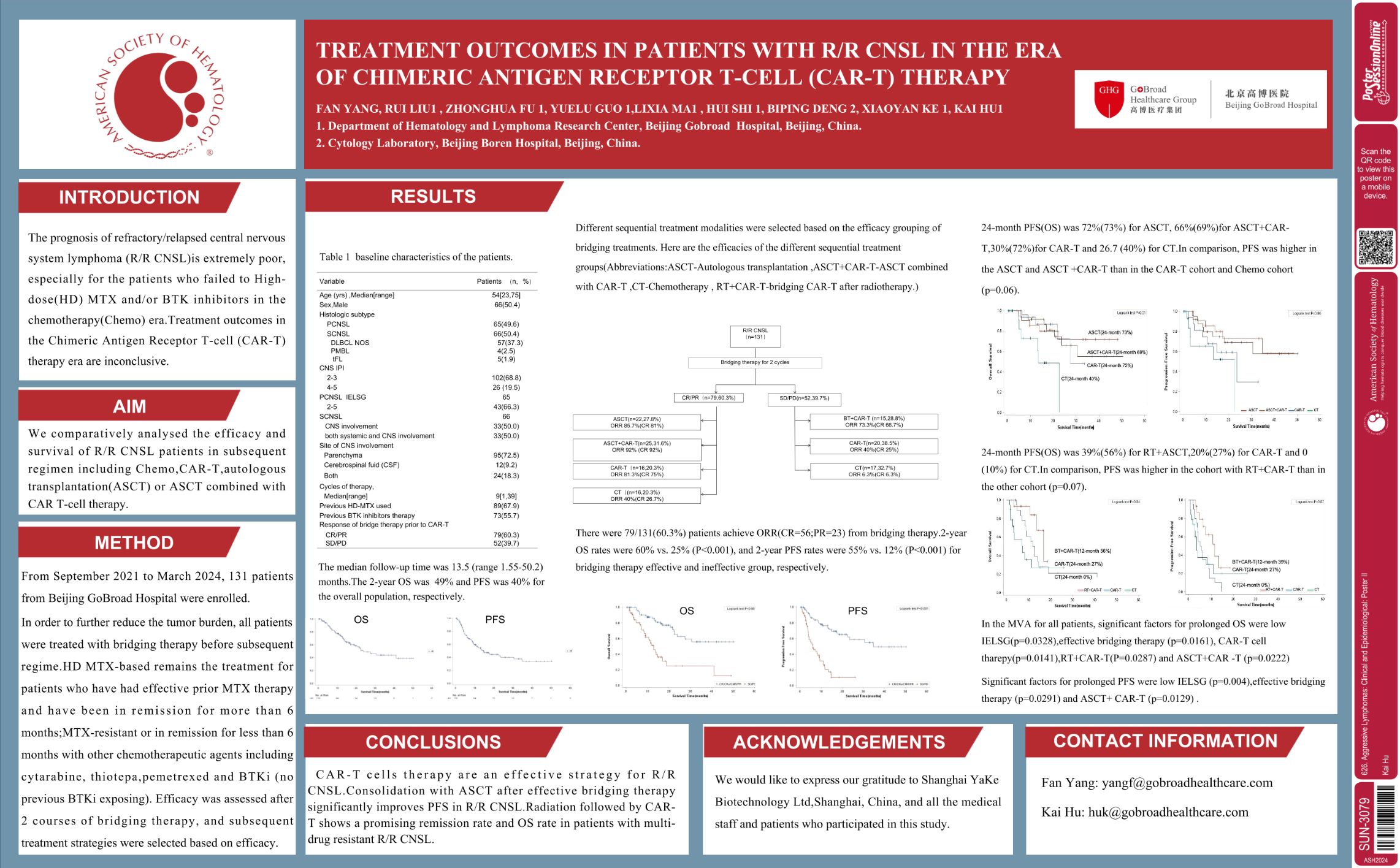
| Treatment Outcomes in Patients with R/R CNSL in the Era of Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-Cell (CAR-T) .. | Kai Hu | 626. Aggressive Lymphomas: Clinical and Epidemiological: Poster II | |
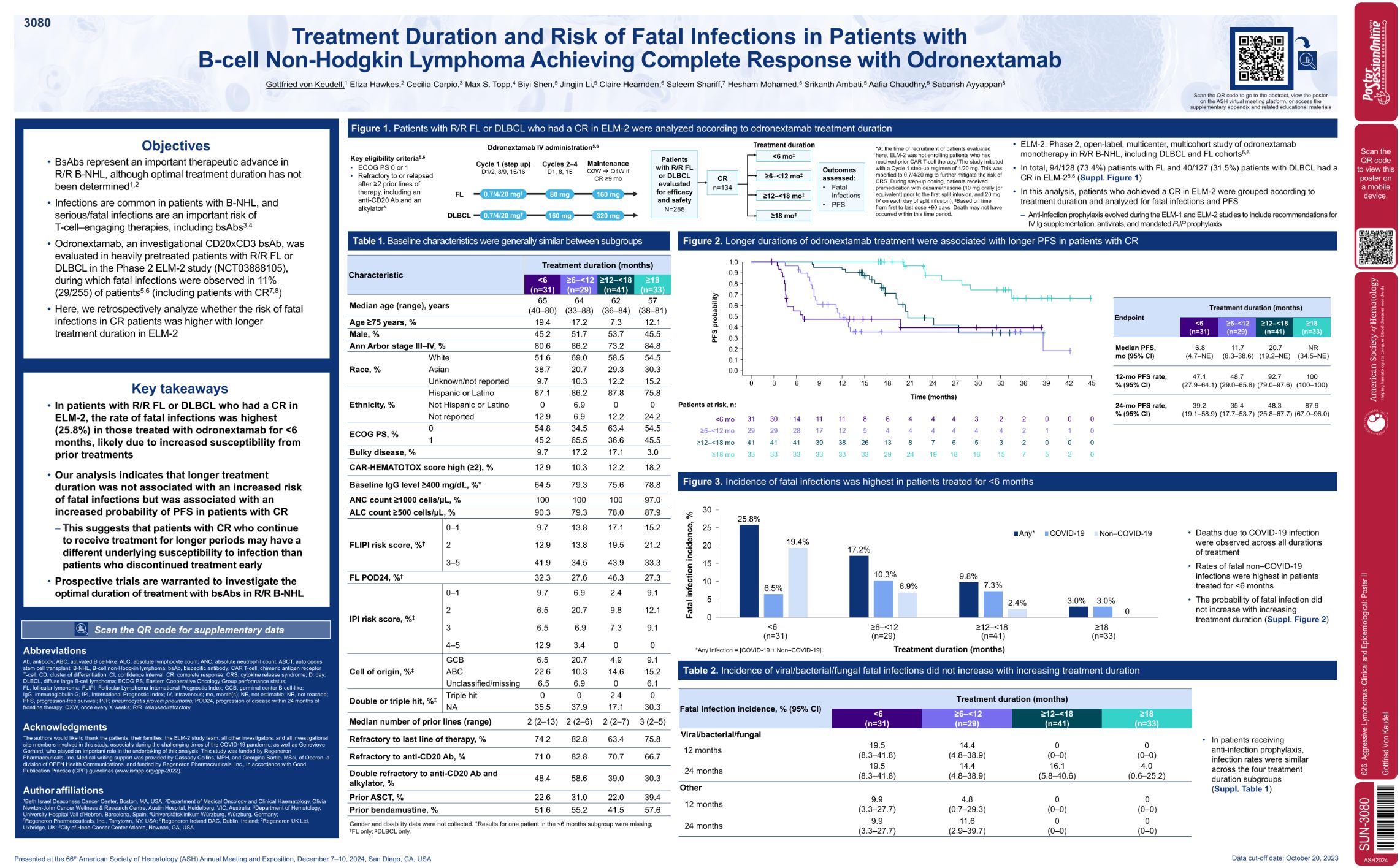
| Treatment Duration and Risk of Fatal Infections in Patients with B-Cell Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma Achievi.. | Gottfried von Keudell | 626. Aggressive Lymphomas: Clinical and Epidemiological: Poster II | |
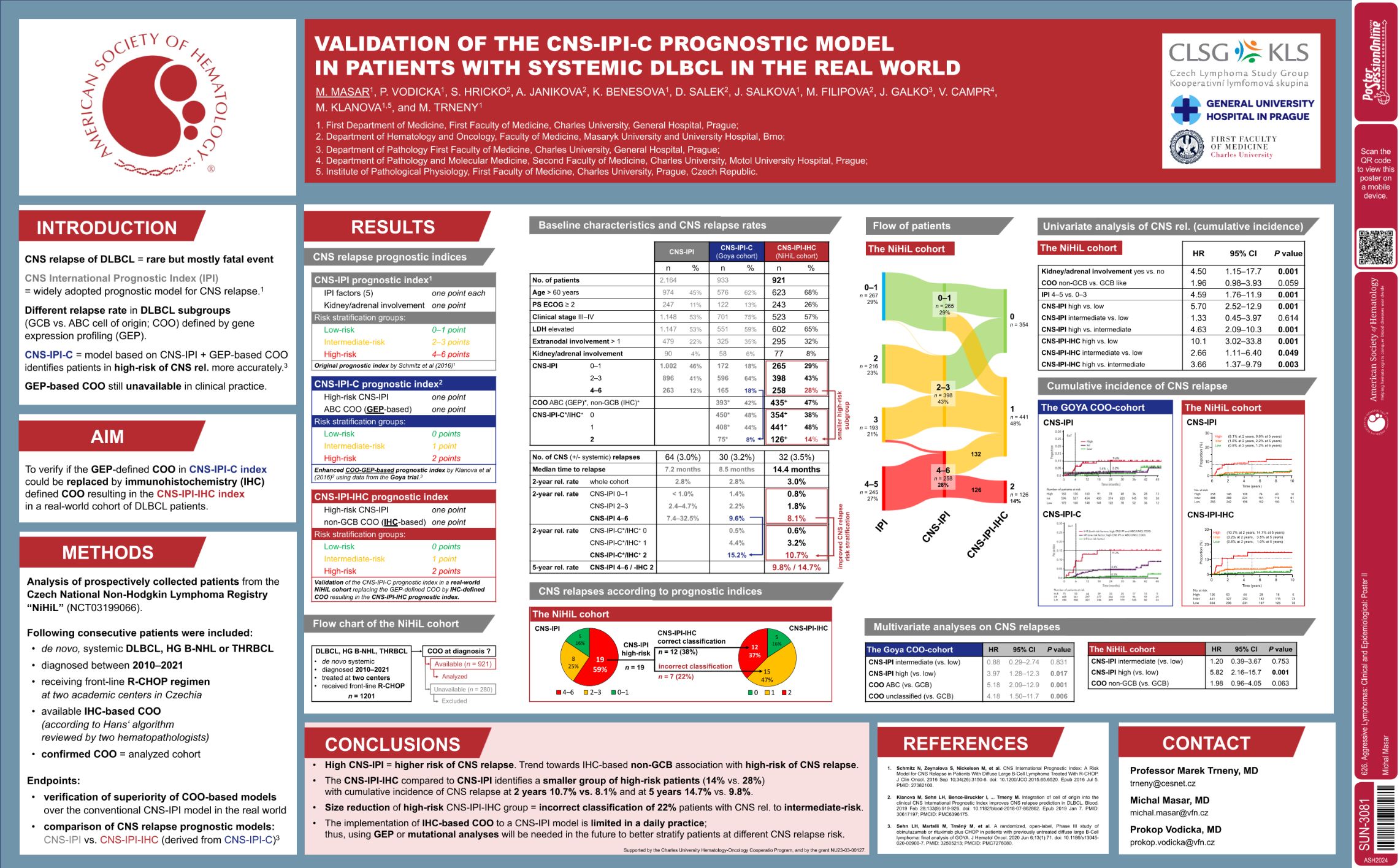
| Validation of the CNS-IPI-C Prognostic Model in Patients with Systemic DLBCL in the Real World | Michal Masar | 626. Aggressive Lymphomas: Clinical and Epidemiological: Poster II | |
| Outcomes of Patients with Refractory and Relapsed Primary Mediastinal B Cell Lymphoma: A Canadian Si.. | Rintu Sharma | 626. Aggressive Lymphomas: Clinical and Epidemiological: Poster II | |
| Title: Development of a Pathologic Prognostic Index (PPI) for Newly Diagnosed Large B Cell Lymphoma .. | Vincent Ni | 626. Aggressive Lymphomas: Clinical and Epidemiological: Poster II | |
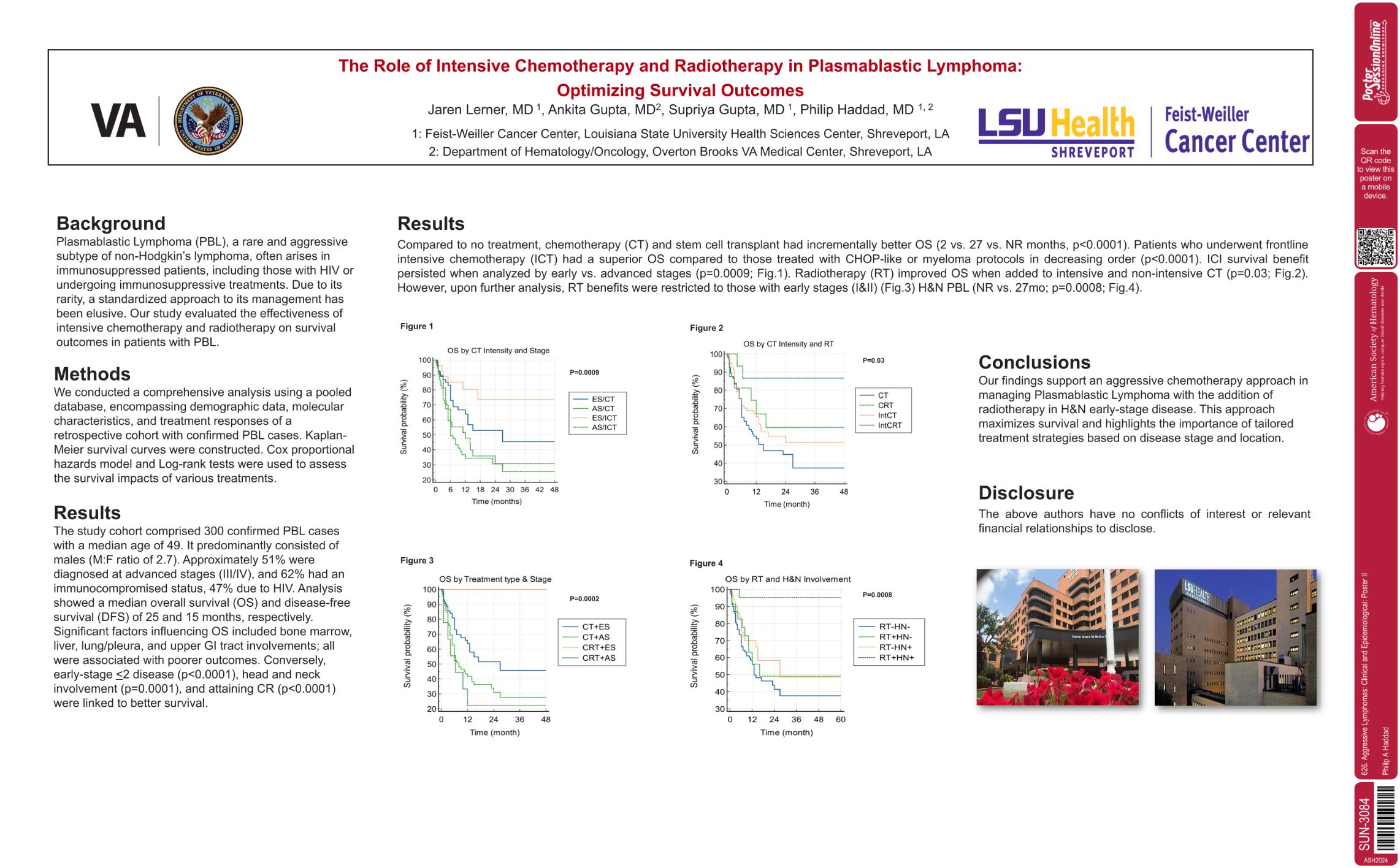
| The Role of Intensive Chemotherapy and Radiotherapy in Plasmablastic Lymphoma: Optimizing Survival O.. | Philip A Haddad | 626. Aggressive Lymphomas: Clinical and Epidemiological: Poster II | |
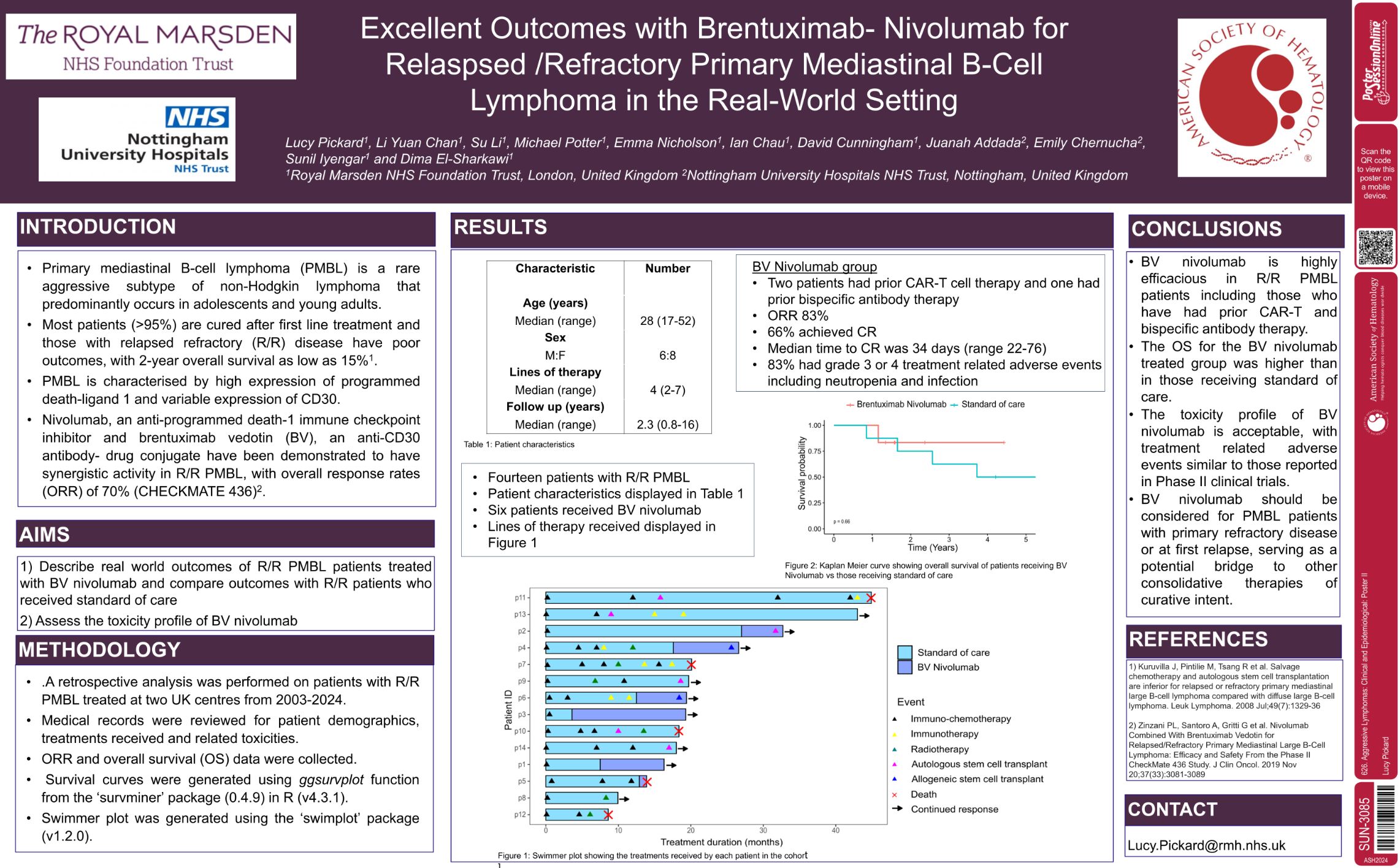
| Excellent Outcomes with Brentuximab-Nivolumab for Relapsed/ Refractory Primary Mediastinal B-Cell Ly.. | Lucy Pickard | 626. Aggressive Lymphomas: Clinical and Epidemiological: Poster II | |
| CD20-Negative Relapsed/Refractory Mature B-Cell Non-Hodgkin Lymphomas and Mature B-Cell Leukemia in .. | Luciana Vinti | 626. Aggressive Lymphomas: Clinical and Epidemiological: Poster II | |
| A Survival Prognostic Model for Gastro-Intestinal Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma | Shaojie Wu | 626. Aggressive Lymphomas: Clinical and Epidemiological: Poster II | |
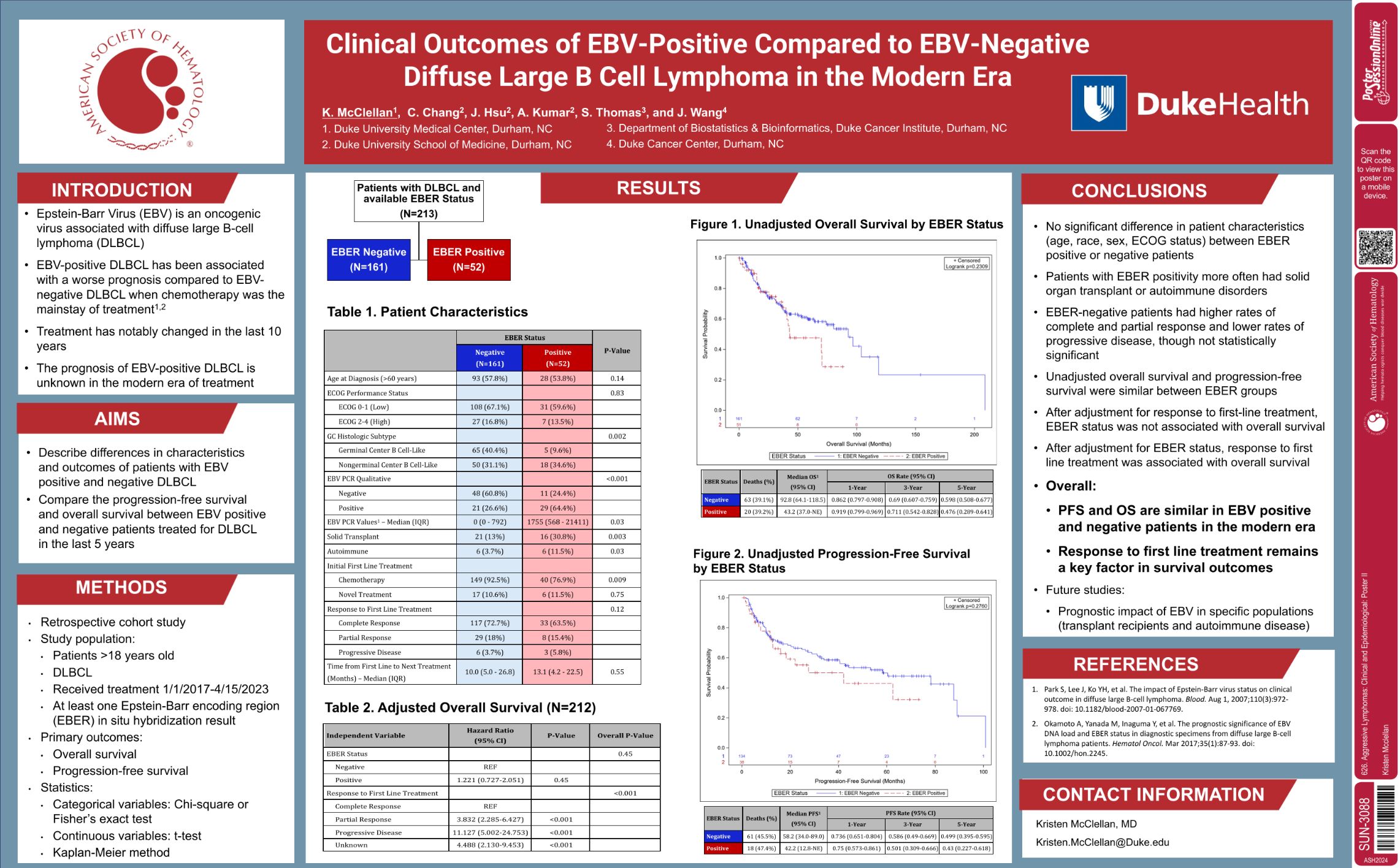
| Clinical Outcomes of EBV-Positive Compared to EBV-Negative Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma in the Mode.. | Kristen McClellan | 626. Aggressive Lymphomas: Clinical and Epidemiological: Poster II | |
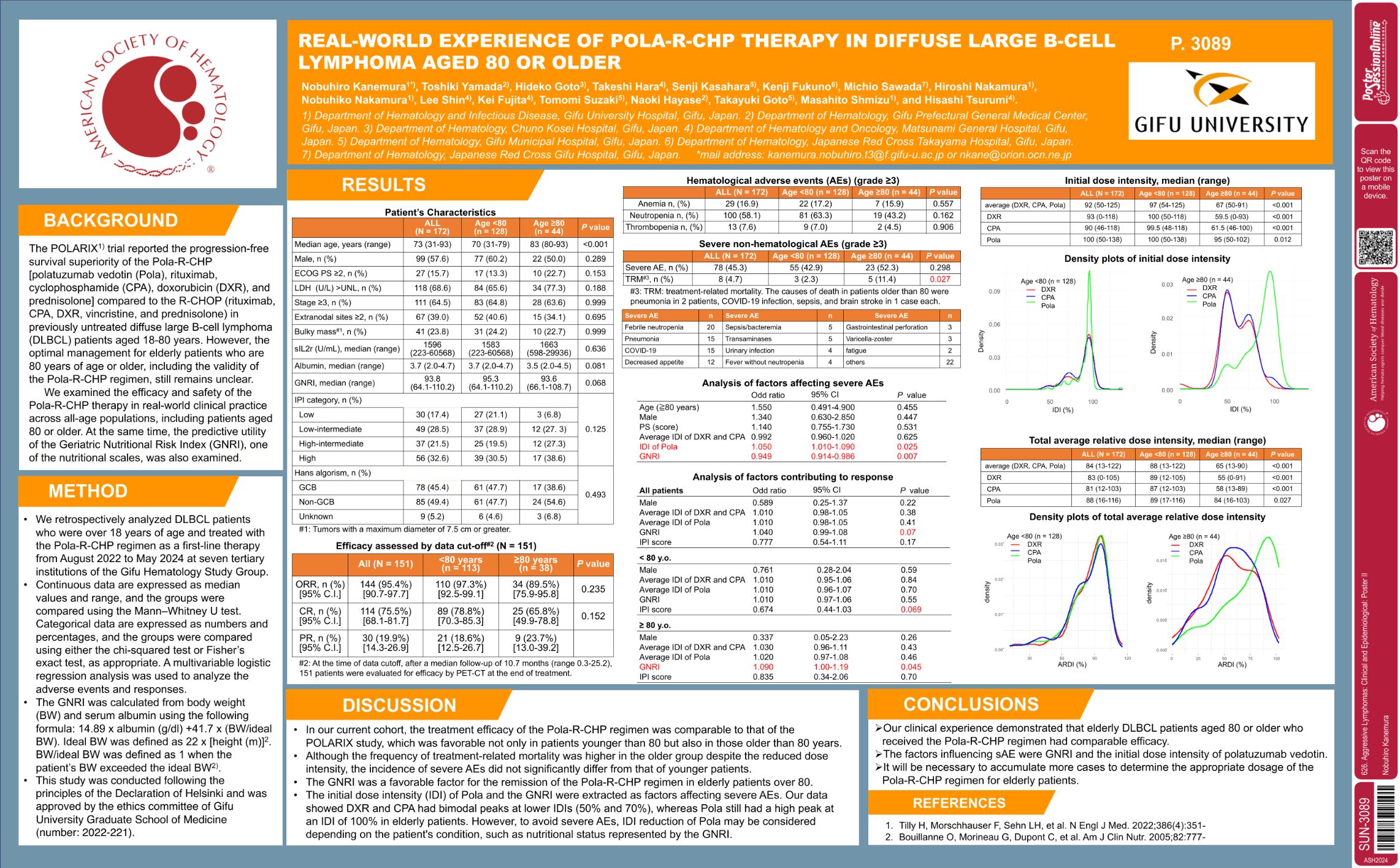
| Real-World Experience of Pola-R-CHP Therapy in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma Aged 80 or Older | Nobuhiro Kanemura | 626. Aggressive Lymphomas: Clinical and Epidemiological: Poster II | |
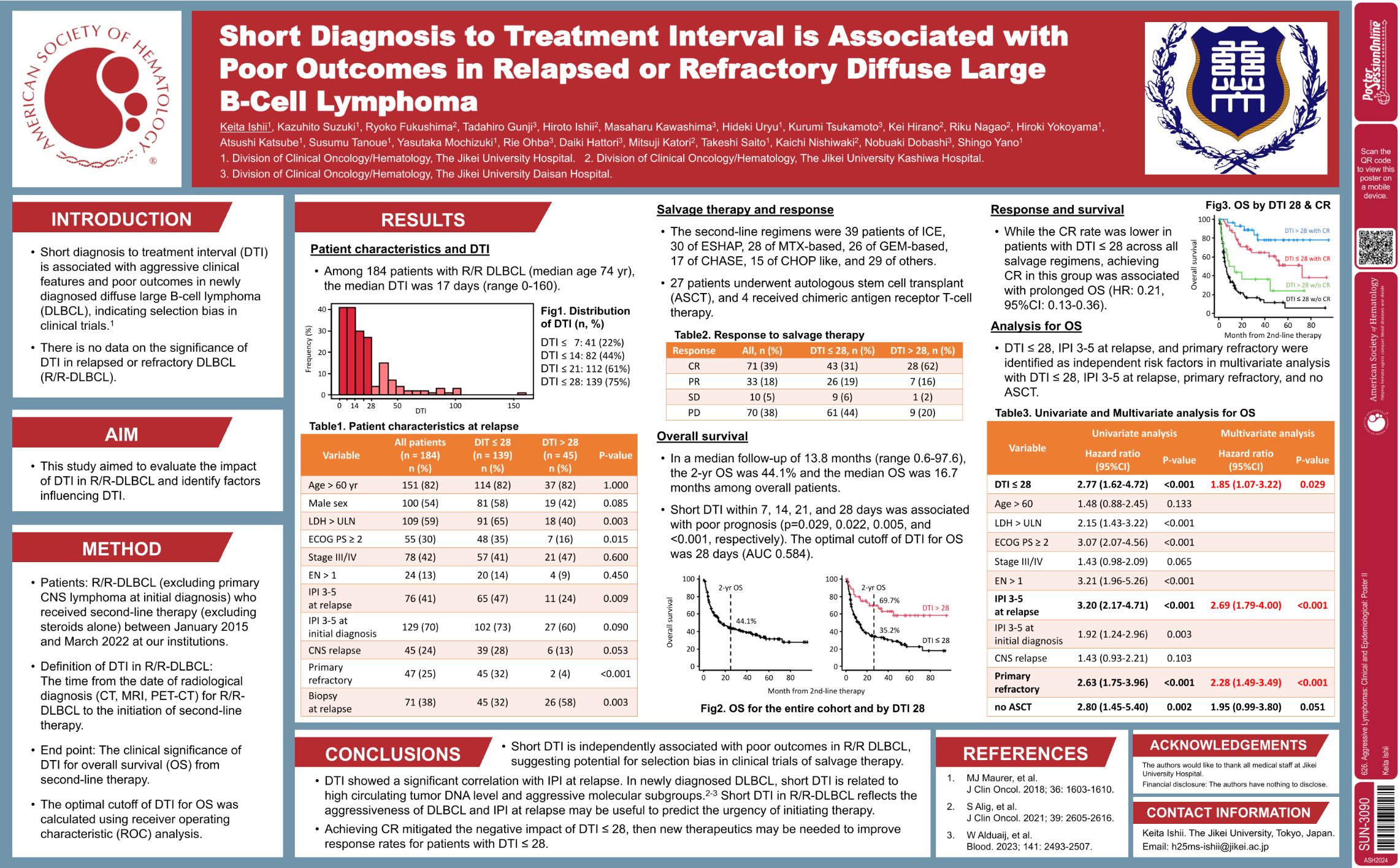
| Short Diagnosis to Treatment Interval Is Associated with Poor Outcomes in Relapse or Refractory Diff.. | Keita Ishii | 626. Aggressive Lymphomas: Clinical and Epidemiological: Poster II | |
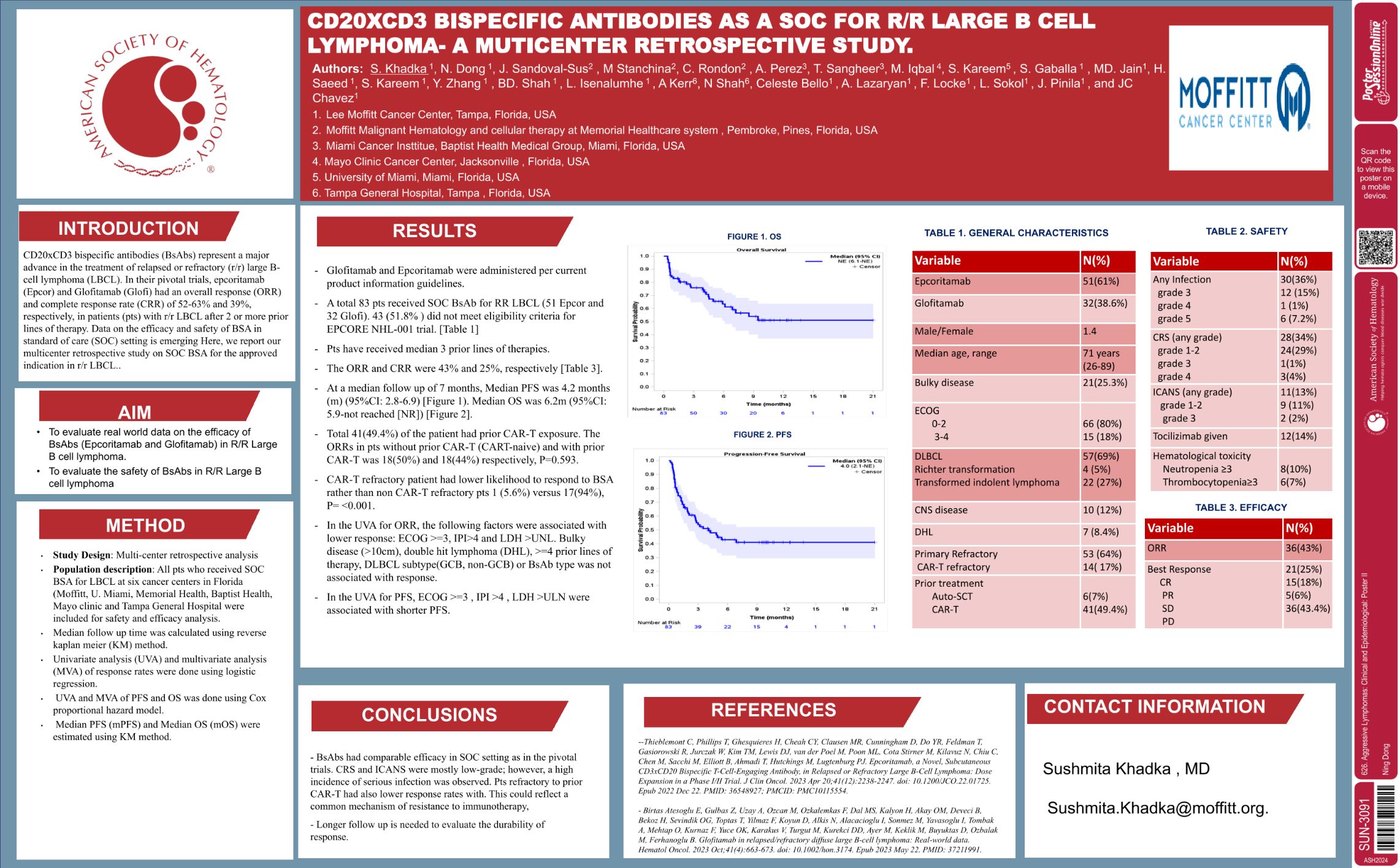
| CD20xCD3 Bispecific Antibodies As Standard of Care (SOC) for Relapse/Refractory (R/R) Large B-Cell L.. | Ning Dong | 626. Aggressive Lymphomas: Clinical and Epidemiological: Poster II | |
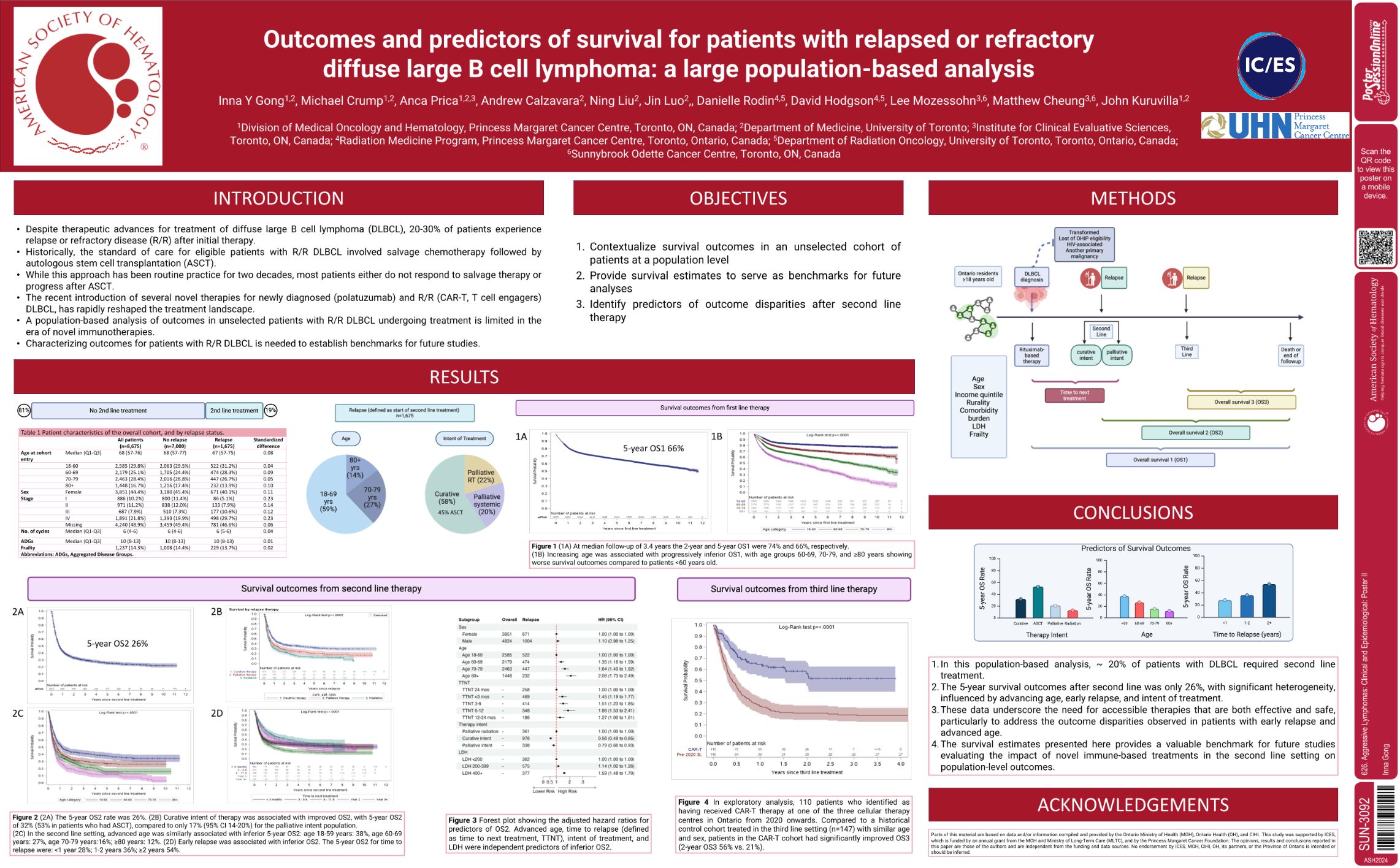
| Outcomes and Predictors of Survival for Patients with Relapsed or Refractory Diffuse Large B Cell Ly.. | Inna Gong | 626. Aggressive Lymphomas: Clinical and Epidemiological: Poster II | |
Abstract
Thunderstorm-related asthma in patients sensitised to olea europaea pollen: twenty emergency department visits for asthmatic symptoms in one single day Losappio, Laura1; Heffler, Enrico2; Falco, Antonio1; Contento, Francesco1; Cannito, Cosimo1; Rolla, Giovanni2 1"Dimiccoli" Hospital, Emergency Department, Barletta, Italy; 2University of Torino - AO Mauriziano "Umberto I", Allergy and Clinical Immunology, Torino, Italy
Background: Associations between thunderstorm and asthma morbidity have been reported in several countries. Common to all epidemics of thunderstorm-related asthma is a significant increase in atmospheric allergen load during and immediately after a thunderstorm. Sensitization to Alternaria species or to grass and parietaria pollens has been suggested to play a key role in thunderstorm-related asthma. The only reported event of thunderstorm-related asthma in Mediterranean area was attributed to sensitization to parietaria pollen.
Method: here we describe a series of 20 patients who presented to Emergency Department in Barletta (94,000 inhabitants), Puglia (Italy) for sudden and severe asthmatic symptoms between May 27th and 28th 2010 (from15:36 to 5:02), immediately after a violent thunderstorm which occurred following a very hot morning (mean temperature: 29°C). All the patients have been subsequently visited by an allergist and underwent allergological work-up which included skin prick tests and a careful clinical history. Local pollen counts were available.
Result: Between May 10th and June 10th 2010, 86 Emergency Department asthma visits were recorded, 20 of them during the study day. Patients' mean age was 44.25 +/- 18.5 years (range: 9-81), 8/20 females, 2 smokers, 16 with a previous history of known respiratory allergy. Only two patients regularly took anti-asthma drugs. All 20 patients were sensitized to Olea europaea pollen, 7 of whom were monosensitized. Ten patients were sensitized to grass, 7 to parietaria, 5 to compositae, 5 to cypress, 5 to house dust mites, 3 to dog and 1 to cat danders. No patient was sensitized to Alternaria. Mean pollen count was 17 granules/m3 for Olea europaea, 6 granules/m3 for grass pollen.
Conclusion: This is, in our knowledge, the second epidemic of thunderstorm related asthma described in Mediterranean area and the first one in which sensitization to Olea europaea played a key-role. In conclusion, our report indicates that thunderstorm asthma may involve different allergens (not only fungal spores and grass or parietaria pollen) in different geographic areas, depending on the seasonality of thunderstorms and allergenic pollen.